Compressional fracture of the spine in children: symptoms, treatment and rehabilitation
Compression fractures of the spine in children are less common than in adults. Among all the injuries of the back, about 2% of cases are assigned to the lesion. But each of these cases needs careful diagnosis, proper treatment, and rather lengthy rehabilitation. Therefore, parents should know what the symptoms of injury are, how to provide emergency first aid, and what basic principles should be followed in the rehabilitation process. We will tell more in this material.
About injury
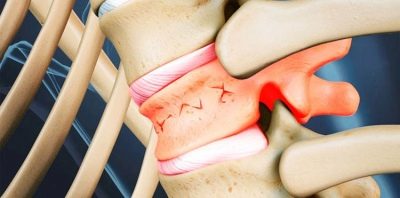
Compression is the process of compression. Fracture is considered a violation of the integrity of bone tissue. Thus, a compression fracture means a violation in which a fracture is combined with compression. When a spinal cord is injured with compression, a violation of the structure of one or several vertebrae is observed with an obligatory compressive effect, as a result of which the height of the vertebral bodies is disturbed.
A child can get such an injury anywhere - in a physical education class, on the playground, when falling from a bicycle. Usually, compression occurs as a result of the forced load on the longitudinal axis of the spine, a sharp bending motion. Quite often, compression occurs as a result of flexing and hitting at the same time.
It should be noted that the compression injury of the spine does not always imply damage to only one vertebra. Several vertebrae may be broken at once.
A child may be injured without injury as such. This becomes possible if he has osteoporosis or a tumor in the vertebral region, for example, a hemangioma inside the vertebral body. In this situation, it is not necessary to fall from the swing or jump from the roof of the garage. It would be enough to have a sharp flexion movement so that the vertebra would be damaged, and its adjacent vertebrae would compress it.
Compression fracture can occur with anyone who is completely injured by any part of the ridge. But most often, according to the observations of children's traumatologists, children break the lower vertebrae of the thoracic and the upper lumbar.
The structural feature of children's vertebrae is that their height is more perfect, depreciation is better than height in adults, and therefore compression cases of ridge fractures in childhood occur less frequently. But the injury is dangerous, and therefore requires special treatment from both the doctors and the parents of the child.
The danger of this injury is the risk of disability. Inside the spinal column is located the spinal cord, numerous nerve endings that are responsible for the functioning of the internal organs.
If nerves and the spinal cord are clamped during the compress, the child may be paralyzed. But there is also good news: the bone tissue of children is more elastic, it recovers faster, and therefore the chances of successful rehabilitation, if the injury happened in childhood, is much higher than with similar damage, but in an adult.
How is it going?
Knowing what a trauma with compression looks like, as well as the essence of the processes at this moment in the spine, one can easily imagine what events might have preceded the injury. Most often, children get a compression fracture when landing on straight legs.Some practice such jumping from the sofa to the floor, and some from the roof of the garage in the yard. Altitude, of course, is important, but in fact both those and others are at risk of serious injury and unpleasant consequences. Jumping on straight legs is often done by schoolchildren in physical education classes, because when performing a long jump most of the guys who are far from sports violate the technique of doing the exercise, and physical education teachers do not always follow this.
Vertebral fracture with compression is often the result of falling on the ass. It is important to understand that landing on the buttocks from a height of your own height is not as dangerous as falling from a greater height, for example, from a moving swing.
If a child makes a fall, one or two vertebra usually suffers, the injury is isolated. If the injury was caused by a shock after a jump from a great height, in case of an accident, then it is most often combined, accompanied by injuries to the abdominal cavity, brain, limbs.
Types of vertebral compression
To determine the type of injury, the exact location of the fracture is of prime importance, On this basis, there are several types of compression fractures:
- cervical;
- chest:
- lumbar;
- sacral;
- coccyx.
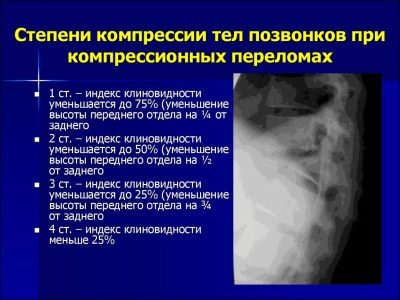
Most rarely among karapuz and teenagers, fractures with compression occur in the neck and tailbone. But injuries of the thoracic and lumbar spine are common. Depending on the degree of compression and reduction of the vertebral height, the following types of injury are distinguished:
- 1 degree compression injury - the height of the injured vertebra is reduced by less than one third;
- grade 2 compression fracture - the height of the injured vertebra is reduced by less than half;
- Grade 3 compression injury - The height of the damaged vertebra is reduced by more than half.
Grade 3 fracture is considered the most severe, since it actually causes crushing of the vertebral body.
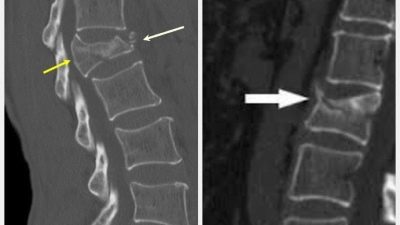
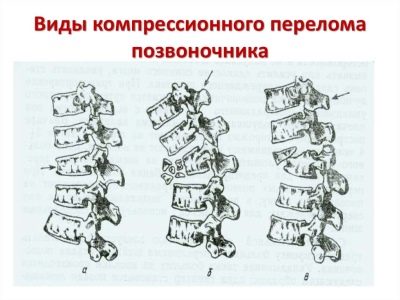
Additionally, traumatologists determine the type of lesion of the vertebra. On this basis, they emit explosive, impacted fractures and fractures with a split vertebra.
Fractures resulting from trauma are called traumatic, and fractures that are a consequence of a tumor or other pathology in the spine are pathological.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a compression fracture is sharp, severe pain. If the vertebra is broken in the thoracic spine, the child may additionally experience difficulty in breathing at the time of injury. Some time later, the child may begin to complain of pain in the area of damage, which subsides somewhat in the prone position, but invariably increases in the standing, sitting, and also during movements.
In a severe fracture, a child may experience vomiting, severe headache, and numbness of the extremities. If you examine the damaged spine, a small swelling may appear in the area of the fracture. Touching an injured vertebra causes the child to experience an attack of pain, and the muscles next to the injured vertebra are tense.
Often determine the fracture of the spine helps the method of pressing the palm on the head (on the crown). In this case, the pain in the vertebra should increase. But when determining the damage in children, this method is contraindicated - additional compression can lead to increased compression and burdening the baby.
Pathological fractures (due to a tumor or osteochondrosis) are rarely accompanied by severe symptoms. They often appear completely unnoticed. The child begins to complain of pain even when the height of the vertebra becomes greatly reduced, when there is a feeling of numbness in the fingers or feet.
In case of compression of the roots, the first symptoms may not be pain in the vertebrae at all, but other disorders: loss of hearing or vision (in case of trauma in the cervical region), headaches, numbness of the extremities (in case of injury in the lumbar region), difficulty in deep breaths (with lesions in the thoracic region). department).
First aid
The correctness of first aid to a child with a suspected spinal compression fracture is important, and each parent must at least in general terms imagine how to help the child.First of all, it should be noted that in case of any fall (using the methods described above), when complaining of back pain, adults should first suspect compression. This is the case in which it is better to be safe.
It is better not to touch the child, not to try to transport it to the hospital or emergency room on your own. Moving can lead to a change in the position of the injured vertebra and aggravate the condition of the baby. Try not to change your body position.
If it is not possible to leave the child in place before the arrival of the ambulance doctors, one should carefully, with outside help (by the arms and legs, supported by the third person’s back), transfer the child to a firm surface and lay on his back.
In no case should the victim be planted; with the vertical position, the pressure on the vertebrae increases many times. If there is a suspicion of a fracture in the coccygeal zone, the child should be laid on the stomach.
If there are drugs nonsteroidal group of painkillers, then you can make the child an injection. For this fit "Diclofenac», «Ketanov"In the age dose. But it is not necessary to give the painkiller pills to the child, because the swallowing reflex may be impaired, the child chokes. Coughing, which then occurs reflexively, can lead to an additional displacement of the injured vertebrae.
Transporting a child to a medical facility is only possible on a hard stretcher. The child is necessarily immobilized and fixed as rigidly as possible. If parents volunteer to help doctors plunge the stretcher into the ambulance carriage, it should be remembered that all movements should be very careful and smooth.
Treatment
The trauma is initially treated in a hospital setting. The child will be on a hard “shield” - bed for 6 weeks. He will be given painkillers, and will also be shown a special set of exercises in physical therapy in order to strengthen his muscles.
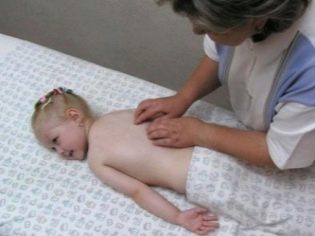
After a month and a half, the doctor allows a special massage and a visit to the physiotherapy room. Particularly useful at this stage of rehabilitation are electrophoresis and calcium sessions.
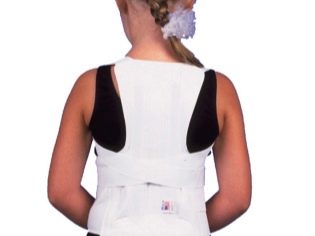
Within two months after this, the child must wear a special orthopedic fixing corset. In case of an uncomplicated compression fracture, he will be able to return to classes at school not earlier than in six months. Full recovery will take 2-3 years.
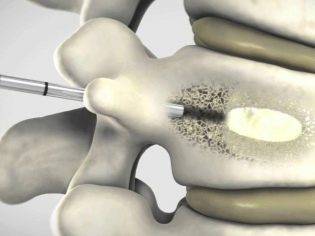
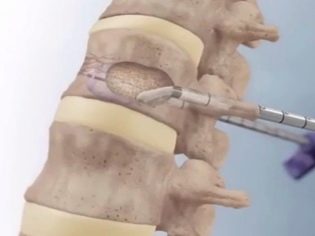
For complicated fractures, surgical treatment is indicated. Children perform two types of operations - vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Both types of interventions fall into the category of high-tech medical care.
In the first case, the doctors make a small incision and a special bone cement is inserted into the body of the vertebra, which solidifies and does not allow the vertebra to collapse. When kifolastic pre-adjust the shape of the vertebra, then enter the same bone fixing cement. Each type of surgery has its own indications and contraindications.
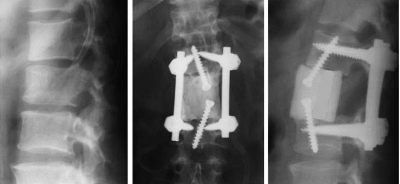
If, as a result of the injury, the roots and nerves are clamped, an open spinal surgery is usually performed, during which surgeons release the roots manually. To stabilize a moving broken vertebra, various metal structures can be used - screws, rods, etc. The exact type of device is determined by the doctor depending on the nature of the injury.
Completely destroyed vertebrae are replaced by bone grafts, prostheses. The postoperative period and rehabilitation after surgical treatment of a compression fracture is quite difficult and long. They will require patience and great work from relatives and doctors. Massage, physiotherapy, as well as systematic physical therapy exercises are strictly supervised by a specialist in the field of physical therapy and restorative gymnastics.
Komarovsky about injury
The well-known pediatrician Yevgeny Komarovsky argues that parents should not engage in "amateur activities" and apply compresses, bandages and test traditional medicine on their children during the treatment and during the recovery period after receiving a spinal compression injury. The other extreme, against which Komarovsky warns, is excessive hypodynamia during rehabilitation. Parents should understand that the movement will only benefit the child, and recovery will be faster.
Useful as a pediatrician swimming, walking in the fresh air, training on a stationary bike, if, of course, the attending doctor does not object to this kind of physical activity.
The rules of competent first aid Komarovsky considers almost the main, able to influence the whole process of treatment and recovery. He recommends memorizing a few important rules that will come in handy after getting injured before the doctors arrive:
- rest;
- lack of movement;
- cold;
- painkiller from a home first aid kit.
Komarovsky categorically does not advise parents to try to probe or right out something on their own. In addition to giving the child a lot of pain, it can significantly complicate the task of doctors - if there was no clamping of the roots, parents often organize it with their inept and unwise actions.
In the case of pathological fractures that do not differ in acute symptoms, the best that parents can do is not to avoid annual medical examinations. It will help in time to identify this type of injury, if it occurs.
Forecasts
Since children's bones recover much faster than adults, an uncomplicated first-degree fracture usually has very favorable predictions — the integrity of the vertebrae is restored without significant consequences for the child's health.
Compression fracture of the second or third degree often have long-term effects - occasional pain may persist, the likelihood of intervertebral hernia increases, which will require separate time-consuming surgical intervention.
Forecasts with a complicated fracture of the third degree, when a crushed vertebra has to be made up, are considered less favorable. Often, after this, the child is supposed to be assigned a disability, which will significantly limit his physical health and his choices in choosing a future profession.
Timely treatment and proper rehabilitation significantly increases the chances that working capacity will be restored in full. Following the recommendations of the doctor will allow parents to quickly bring the child to his feet.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you about how to have a healthy back in the next video.