Hernia in newborns and infants
Hernia in newborns and infants is a pathology that requires close attention from parents and doctors. We will tell you more about this hernia in such small children, and how to treat them.
How hernia is formed
Any hernia is an anomaly in which internal organs “look out”, leaving the place set by physiology. Organs or their parts pass through the hole, the gap, which is normal or defective, and the integrity of the skin or other membranes is not disturbed. Protrusion is possible in the space between the muscles, if it was formed under the influence of certain factors, under the skin (with an external hernia) or into the internal cavities (with an internal hernia disease).
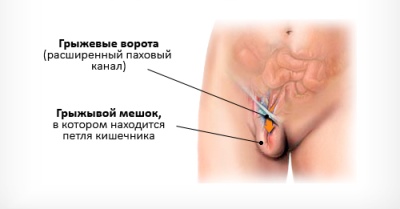
This formation occurs when nature violates the provided balance between internal pressure and shell resistance. The structure of any hernia is about the same, it includes the hernial sac (stretched sheath), the hernial ring - the hole through which the exit occurred and the hernial contents (what is inside the bag).
Danger hernia it does not even consist in the fact that it has appeared and is taking place, but in the fact that at any moment, under the influence of certain factors or without obvious reasons, it may be hurt. This condition occurs when the hernial ring is narrow and the contents of the bag tend to change in volume (for example, the intestinal loop as the contents umbilical or inguinal hernia may fill with feces).
The consequences of such a state are always negative - it is necrosis of a clamped organ or a certain part of it, a threatening condition for the patient’s life. In an infant, who still cannot complain about certain symptoms, it is sometimes quite difficult to identify a hernia. It all depends on the care of parents and their awareness of where the hernias appear and how they look.
Types of hernias in infants
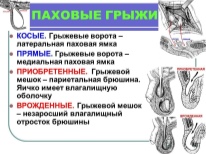
All hernias are divided into congenital and acquired. By the nature of the pathology of the disease, diseases associated with such formations are divided into complicated and non-complicated. In addition, the international classification provides for the division into primary and recurrent hernia. There are also postoperative hernias.
According to the ability to mobility, these formations can be reducible and not reducible. About a quarter of all diagnoses are internal formations, more than 75% are allocated to external ones. Among children of the first year of life the following types of hernias are most common:
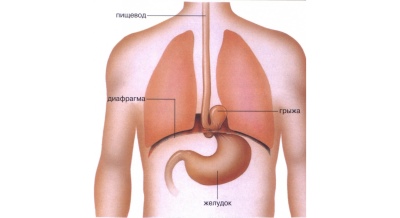
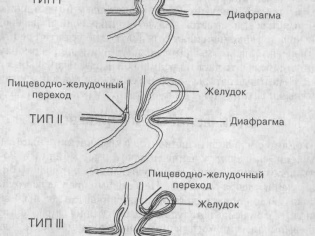
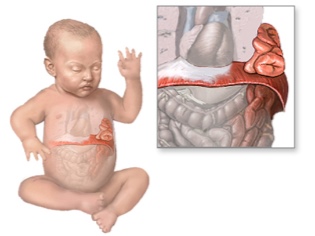
Diaphragmatic hernia
With such a pathology, part of the internal organs, which should be located in the abdominal cavity, rise up into the chest.
- The reasons. Diaphragmatic hernia in children of the first year of life are always congenital. The reasons why such a hernia is formed at some point in the prenatal development of a child are not fully investigated by scientists, but doctors are inclined to believe that the matter is insufficient elasticity of the connective tissue, impaired metabolism of the expectant mother, and also a genetic “malfunction” .
- Symptoms Symptoms are manifested by severe difficulty in breathing in a child, a special form of the abdomen in the shape of a rook.They immediately notice the doctors in the hospital. In rare cases, the disease is opened only after a day or two. The current level of diagnosis allows you to see such a hernia on an ultrasound during pregnancy.
- Treatment. The treatment is always only surgical, and now there is even the possibility of a correction even before the birth of the child. But such intervention is associated with relatively high risks for the fetus and its mother, and therefore the operation is sometimes postponed for the postpartum period. The baby is sent for an urgent operation immediately from the delivery room. It takes place in two stages - first, the crumbs are made into a patch on the hole in the diaphragm from their own piece of skin. And after a while this patch is removed. If the hernia is not bilateral, the predictions are quite optimistic: in 80% of cases, doctors manage to save the life and health of the child. In the case of bilateral herniated diaphragm most likely to be fatal.
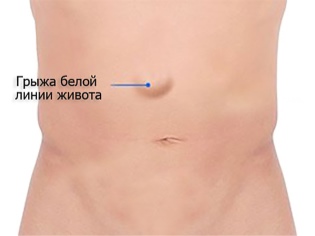
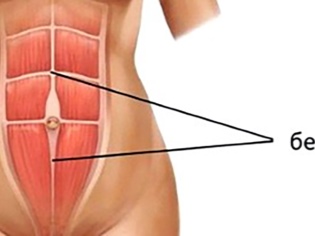
Hernia white line of the abdomen in a child
These formations, passing in the center of the abdomen perpendicular to the bosom, can be small and rather large - up to 10 centimeters in diameter. The exit of the internal organs occurs between the weak muscle lines of the median line.
- The reasons. Such hernias can be acquired, but they always have fundamentally congenital pathologies of connective tissue, which can disperse, forming rather large “pockets” due to crying, coughing, constipation, when the infant is strongly straining the peritoneum. The weakness of the connective tissue is caused by some unfavorable intrauterine factors, such as malnutrition, oxygen, metabolic disorders, as well as genetic disorders.
- Symptoms Such a hernia is unstable in size, and this is its main distinguishing feature. With any movement of the abdominal muscles, it will visually decrease, then increase. After eating, the child behaves more restlessly than before eating; he is tormented by belching, constipation. In its development, the hernia of the white line goes through several stages: first, a gap appears, which will soon become a hernial ring, after a while you can see a bulging of the hernia sac. In the supine position, the hernia becomes more visible. And only when the bag is fully formed, symptoms appear.
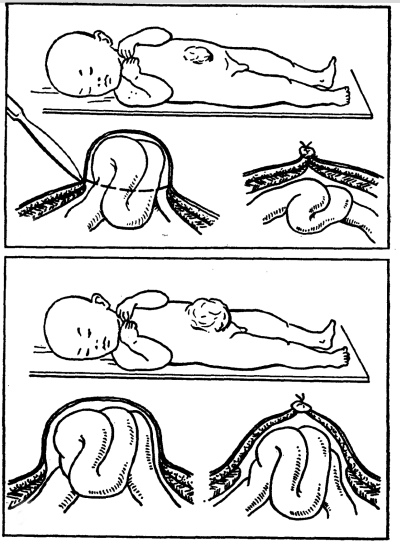
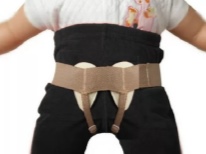
- Treatment. A small hernia does not always need treatment; medicine knows many cases when it goes through a stage of independent reverse development as a child grows. But this process can not be allowed to drift. Doctors such simple hernias are set through the skin by hand, after which the bulging point is fixed with adhesive tape. The baby is given a massage. If conservative treatment does not work, the hernia grows in size and there is a very real risk of pinching it, usually a decision is made about the operation, because today it is the only alternative. Surgeons set it down and hem the pathological hole or fix it with a mesh implant.
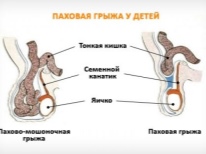
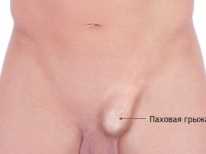
Inguinal hernia
This type of pediatric hernia disease always has a congenital factor. During the period of intrauterine development, the testicles in boys form in the stomach, and therefore descend through the inguinal canal down. If by the time of birth the “tail” of the peritoneum that is lowered together with the testicles does not overgrow, and the inguinal canal continues to communicate directly with the abdominal cavity, a hernia in the groin may develop.
In girls, such pathologies occur several times less often, and they are associated with a similar “pocket” (vaginal appendage) cleft, which is formed when the formed uterus is dropped at 5 months after the mother’s pregnancy, from above into the pelvic area.
- The reasons. The probability of developing an inguinal hernia is affected by the state of the abdominal muscles of the child. In some, it appears at birth, and in some it is found only in a few months. Her bulging contribute to a strong cry, constipation, abdominal distension.
- Symptoms Usually not restrained inguinal hernia does not give the child any trouble. It does not hurt, does not itch. At rest and sleep becomes visually indistinguishable. In boys, education often appears on the testicles. A scrotal hernia can be both unilateral and bilateral. But in girls, the hernial sac usually protrudes from two sides, while it should be sought on the labia.
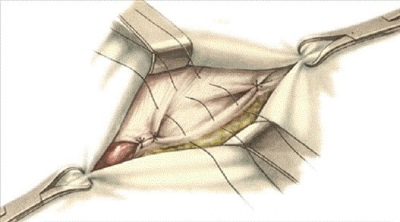
Treatment. An inguinal hernia does not disappear on its own, as the midline white line or umbilical hernia sometimes does. An operation is always needed to heal. During surgery, the doctor completely excises the hernial sac, preserving its contents as far as possible. This measure is determined by the state of the organs that are part of it. If there was no infringement, there was no necrosis, then the doctor sets the organs to their proper places and sutures the hole that became the entrance gate for the internal organs.
If necessary, plastic restoration of the damaged or dilated inguinal canal is done, it is brought to normal size to prevent secondary prolapse of the abdominal organs. Operations make both abdominal and laparoscopic methods.
About what is dangerous inguinal hernia, will tell the pediatric surgeon Alexander Sumin in the next video.
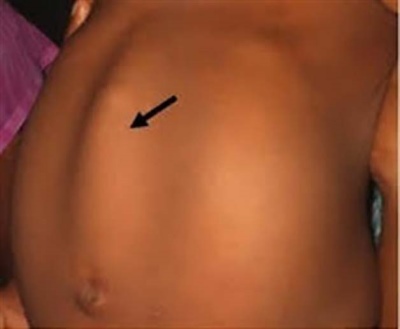
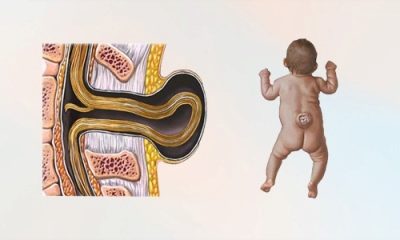
Umbilical hernia
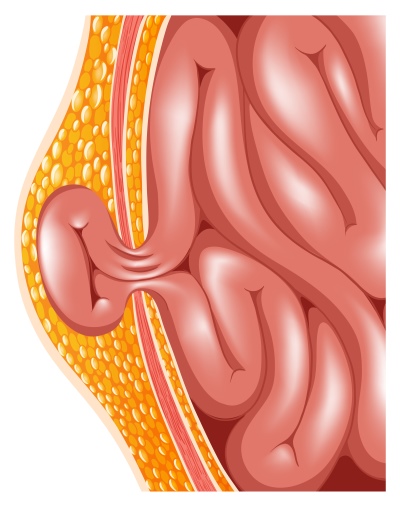
This is the most common hernia in newborns and children under one year. It is not directly related to congenital developmental pathologies, except, if you try, you can find several causes of connective tissue weakness, which, however, are characteristic of all hernial diseases. However, such a hernia is not obligatory satellites of gross defects of fetal development.
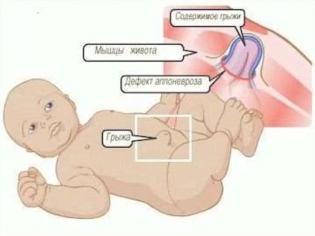
The umbilical cord, which becomes unnecessary with birth, is cut off. Remains umbilical ring. It should be overgrown in infants with the very connective tissue with which many babies have such problems. Usually this process is completed by the end of the neonatal period. If the process is slow or does not occur at all, then a hernial sac from a weak peritoneum is formed, in which intestinal loops, part of the omentum and other internal organs protrude through the umbilical ring.
- The reasons. The appearance of a hernia provokes a strong load on the abdominal muscles. If a child cries long and hard, suffers from severe recurrent constipation and abdominal distention, his chances of acquiring an umbilical hernia are very high. In premature babies, the incidence of pathology is higher than in full-term ones.
Sometimes a hernia does not appear in the first months of life, but closer to the year. In this case, doctors consider as one of the reasons for the early setting of the baby on the legs or hanging in the jumpers and moving in the walkers. While the peritoneum is not ready to perceive the vertical load, the child must crawl - this is a more natural way for him to move. The reason for the appearance of a hernia can be in the wrong or poorly tied navel in the hospital, as well as in the infection.
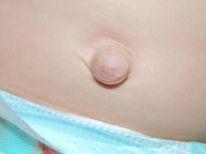
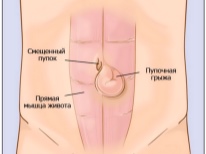
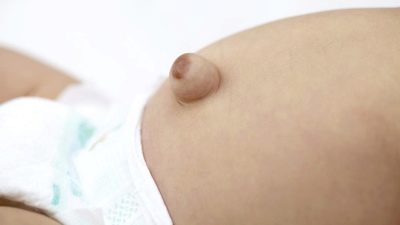
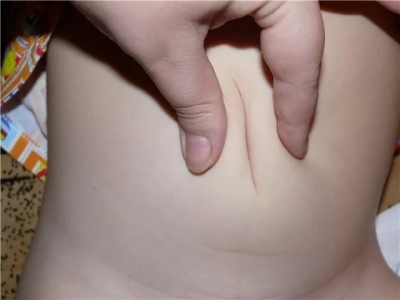
- Symptoms It is not difficult to determine an umbilical hernia in a child - swelling appears in the area of the umbilical ring, which has a bluish color, if intestinal loops are clamped, or reddish, if an epiploon or part of the liver gets into the hernial bag. Hernia looks like a small size (1-5 cm in diameter), a rounded nodule with smooth or irregular edges. She bulges from a child when he cries, strains at stool or coughs. In a quiet state, lying on his back, this nodule is imperceptible. When you lightly press your finger on the knot, it is easily set back. It is already possible to inspect the home by yourself for a month old child, it is desirable to monitor the state of the navel very carefully for at least one year.
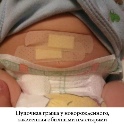
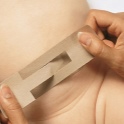
- Treatment. The vast majority of babies have an umbilical hernia that passes without a trace on its own as the abdominal muscles grow and strengthen.Often, pediatric surgeons set it down, fix it with a plaster and show parents how to change this plaster from time to time. Additionally appointed massage, which is designed to strengthen the press. Surgical treatment for up to 5 years try not to prescribe without urgent need. This need arises only when an infringement occurs, but this, fortunately, is quite rare.
When carrying out planned operations, children after 6 years of age use standard hernia procedures. Today, children do both conventional and laser surgery. After removing the hernial bag, the surgeon can make a plastic navel so that the child grows up and does not hesitate to expose the stomach (this is especially true for girls).
You can also listen to useful tips from a professional doctor in the video below.
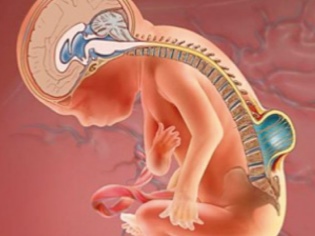
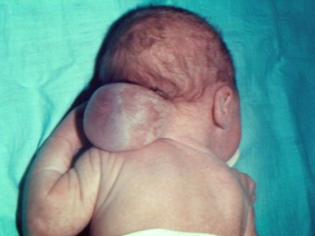
Cerebral hernia
Most often we are talking about spinal hernia, which is considered the rarest and most difficult in the treatment of pathologies of this kind. It is usually recorded in newborns and infants with disorders of the musculoskeletal system. Almost always, congenital cerebral hernia leads to disability. Hernia is congenital, but not inherited. This is a sign of irregularities in the formation and development of the fetus during pregnancy.
- The reasons. Experts believe that there is a direct link between the lack of folic acid in the mother’s body and the diagnosis of a newborn baby. About a third of cases are due to infectious causes associated with severe infection that a pregnant woman had in the first trimester.
- Symptoms Recognizing such a hernia is not difficult, despite the fact that not all types of ailment have an external bulge. Symptoms are noticeable even in the maternity hospital, less often - they become apparent already at the first visit to the pediatrician. A child may have paralyzed limbs, he does not control bowel movements and urination, he has multiple dysfunctions of various internal organs. Often this hernia accompanies brain hydrocephalus.
- Treatment. It is impossible to cure such a hernia completely, and even more so at home. Spinal hernial pathology is very difficult to treat in general. If the pathology of the fetus found on a planned ultrasound during pregnancy, the mother, it is possible to operate the child directly in the womb. Surgeons using high-precision equipment penetrate the baby’s spine and close the defect - the gap in the spine. The spinal cord returns to its place. Not all clinics in Russia today can afford to perform such operations, but this trend is developing, and will soon be able to cancel the need for a pregnant woman to raise funds and go for such an operation in Israel. After a baby with such a hernia is born, he needs a neurosurgical operation for several days. Otherwise, disability is inevitable.
What should parents do?
If any hernia is found in a child, you should remain calm and have the ability to sensibly assess the situation. Most hernias, with the exception of the spinal cord, are successfully treated, and some of the children in their first year of life pass by themselves to one and a half years.
If we are talking about common abdominal hernias (inguinal, umbilical, midline abdomen, femoral), then it is important to ensure that the child does not scream for a long time, since this causes an increase in hernia in size. It is important to avoid respiratory diseases that occur with a strong cough. Regular massage, light gymnastics, wearing a special orthopedic bandage will definitely benefit the baby. But to overfeed a baby with a hernia is not necessary, so as not to cause him indigestion or constipation.
It should be as best as possible to remember the signs of hernia infringement, because it can happen at any time:
- strong pain;
- vomiting, nausea;
- blanching of the skin;
- the hernia looks bloated, tense, it ceases to abate.
At the first similar symptoms, parents should immediately take the child to the surgical hospital or call an ambulance to do this.
What can not be done?
You can not try to reduce the hernia to a child by yourself and treat it with folk remedies instead of visiting a surgeon. This can lead to infringement with the development of very negative consequences.