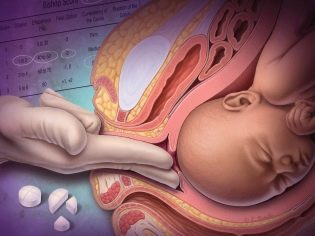
How many hours do contractions usually last?
Contractions will not be so terrible for a woman in labor, if you learn more about them. It is the fear and insecurity of women that sometimes make the period of labor so painful and difficult.
In this article we will tell you what stages to go through during labor, how many contractions will last, and how uterine contractions are felt at different stages.
What it is?
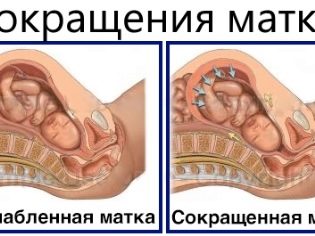
Contractions of the uterine muscles, which occur periodically and constantly dynamically, are called “contractions” for the nature of pain. She "grasps" the back, lower back and abdomen of the woman in labor, and then smoothly "lets go." Normal labor always begins with the appearance of such sensations. Of course, there may be several options. Some initially waste water, some have amniotic fluid and contractions occur simultaneously. But these options are considered complications and have no relation to the norm. The mechanism of contractions is very complicated. So, they can only begin if a number of important conditions are met:
- in the pregnant woman’s body, enough relaxin and oxytocin are produced, and the level of progesterone, which helped to keep the pregnancy, has decreased;
- in the cells of the uterine tissue accumulated a sufficient amount of protein - actomyosin, which provides contractile abilities at the cellular level;
- the cervix is quite “mature”, softened and elastic.
The contractions begin in one of the parts of the uterine muscle tissue and gradually spread to adjacent areas until the entire body of the uterus and the cervix are involved in the contraction.
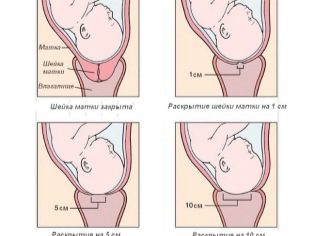
This tight and round muscle is very strong, and therefore its disclosure is a long matter. With each contraction, the cervical fibers become shorter and the cervix itself expands. When the disclosure becomes complete, the child’s exit from the mother’s womb will be possible.
Periods and stages
The woman cannot control the contractions. They begin and develop independently of her will.
The first uterine contractions are called latent (hidden). You can distinguish them from false ones by the frequency of repetition. False contractions that were present in the “forerunners” period, were repeated infrequently and were by and large not very painful. And if they brought inconvenience, it is more psychological.
Real contractions from the very beginning occur at regular intervals. Early contractions can be quite short and rare. One fight usually repeats every 30-40 minutes and lasts no more than 20 seconds. If this happens, there can be no doubt - the birth has begun.
But you should not panic and run around the apartment in search of a phone to call an “ambulance” at this stage either. The latent period of contractions is the longest, the woman has at least 4-6 hours to calmly get together and no less calmly go to the maternity hospital, not forgetting the documents and things important for hospitalization.
A woman needs to come to the maternity hospital when contractions are repeated every 10 minutes, and in the second or third births a little earlier, since each stage of labor with a second pregnant woman proceeds faster.
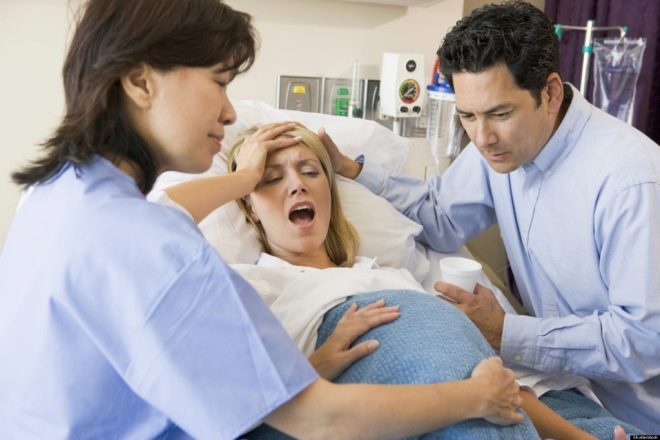
Continuation - the active phase of contractions. It usually takes place under the supervision of doctors. It is believed that it begins after the cervix opens to three centimeters.The contractions intensify, each lasting for at least 40-50 seconds, they are repeated every 4-5 minutes. After this period begins the stage of the strongest bouts.
Uterine contractions in the transitional period before attempts are repeated every 1-2 minutes and last for a maximum of 60-70 seconds. The cervix is fully open, the disclosure is 10-12 centimeters.
Then begins the attempts in which the baby "pushed" into the birth canal and passes through them. A woman can already partially influence this process, putting some efforts for a faster completion of labor. Need to push only at the command of an obstetrician. Childbirth ends not with the birth of a child, but with the birth of the placenta. Usually, the next stage of childbirth proceeds with less pain.
Duration
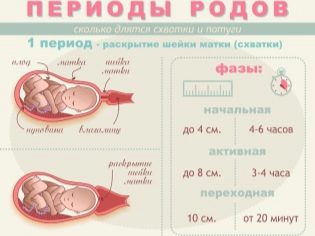
The main question is how long the fights last. It is definitely quite difficult to answer it, because much depends on the individual characteristics of the female body, on the number of births, on possible complications, which are difficult to foresee. On average (these are very averaged values) the contractions last so much in time:
Period of labor | First birth | Subsequent delivery (second, third, etc.) |
Hidden (latent) | 8-12 hours | 7-9 hours |
Active contractions | 3-5 hours | 2-3 hours |
Transitional fights | 1-1.5 hours | 15 minutes to 45 minutes |
Battles (attempts) | Up to 3 hours | 15 minutes to an hour |
The woman cannot adjust the duration. May not affect the length of uterine contractions over time and medical professionals.
In some cases, it is required to stimulate, speed up contractions if they are too sluggish, and cervical dilatation is slow. In this case, do catheterization of the bladder or amniotomy (mechanical opening of the sac of the fetus). After puncture of the bladder, the contractions sometimes “diverge”, and the subsequent period is somewhat reduced.
The contractions will continue until the fetus is released. After this, uterine contractions are activated only at the time of the expulsion of the afterbirth. This stage takes on average from 20 to 40 minutes, in primiparous women, the placenta is usually separated more quickly than during repeated births.
Sensations
The change of stages a woman can feel, focusing not only on the time frame. Initial contractions initially resemble pain during menstruation, and then they have a clear shingles. There is pain, according to women, somewhere in the middle of the back, quickly moving to the lower back and sacrum, in the very bottom of the abdomen and up the abdominal wall.
After a while the pain recedes. In the active phase of labor, uterine contractions are more painful, frequent, intense. The transition from contractions to attempts is characterized by sudden sensations of abrupt pressure below, the woman has a desire to push, to empty her intestines.
How to make it easier?
To ease the pain will help the knowledge and skills that a pregnant woman can get in the courses of expectant mothers, held in each antenatal clinic.
Thus, the correct breathing of the woman in labor will not only provide the born child with sufficient oxygen during the whole process, but also naturally reduce the pain. When the body, especially the brain, is saturated with oxygen, more endorphins are produced in the female body. These hormones not only give a feeling of happiness and mild euphoria, but also have a pronounced analgesic effect.
At the early stage of contractions, you need to practice deep and calm slow breaths and the same exhalations. At the same time, the expiration time should be approximately twice as long as the inhalation.
When contractions become frequent and painful, the woman needs to alternate calm breathing between contractions with frequent and intense breathing at the peak of pain.
In the attempts, a deep breath is used and the breath is held at the time of the attempt, while puffing up the cheeks and straining the head is not necessary to rule out hemorrhages, they are strained to the "bottom", and the chest filled with air as if pushes the baby away, promotes his expulsion from the womb.
The sacral area massage also helps. Make it a woman can herself, and can enlist the support of a partner, if you are supposed to give birth together.
There are also certain poses in which it is much easier to survive the contractions. They can also be designed for a single performance or for partner childbirth.
A warm shower helps to ease contractions; many modern maternity hospitals have such opportunities; women in labor are allowed to go into the shower in the initial and active phase of contractions for as long as they want.
Trying poses, perfecting your breathing and practicing self-massage should be done during pregnancy, before childbirth, so that later, when everything starts, you can reproduce all the necessary actions automatically.
Read more about how long the contractions last, the specialist tells in the next video.