What is artificial insemination and how is the procedure?
Most married couples in the process of their life together, sooner or later plan to have children. In some, this happens naturally, without medical intervention, and in others, as a result of problems with the reproductive system of one or both spouses, with the help of medical technology. One of the most effective methods for solving the problem of infertility in our time is artificial insemination.
Special features
Disappointing statistics show that every second married couple in the world is more or less experiencing problems with conception. And contrary to the popular belief that female infertility is much more common, only a third of these cases result from impaired reproductive function in women.
Currently, three main technologies of artificial insemination are used for the treatment of infertility:
- in vitro fertilization (IVF);
- intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI);
- artificial insemination.
The choice of the method of artificial insemination is carried out by an reproductive doctor individually. At the moment, according to numerous reviews, the most popular technology is IVF.
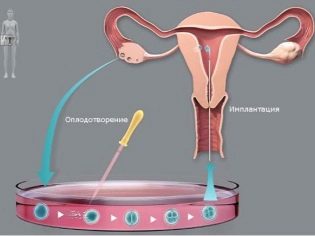
When IVF conception occurs outside the body of the mother, as it should occur during natural fertilization.
IVF is a rather complicated procedure, for the effective implementation of which it is necessary to use a large number of hormonal agents. Due to the intake of these drugs, the functional capabilities of the ovaries and pituitary gland are inhibited. During hormone therapy, it is important to closely monitor the changes occurring in the woman’s body.
After receiving all the data from laboratory studies and the final determination of the method of therapy, the woman is placed under the continuous supervision of a specialist. The dynamics of all changes in the endocrine system of the patient, occurring as a result of the constant use of hormonal drugs, is monitored using biochemical blood tests, which must be taken daily.
It should be noted that such careful control of physicians is not justified in all cases. Most often, the entire course of preparation for the IVF procedure occurs on an outpatient basis.
This is followed by the second stage of IVF - the cultivation and subsequent collection of female biological material. As was said, at the initial stage of preparation for the procedure, the drug suppresses the patient's natural hormonal background. After that, a specialist prescribes medications that can actively stimulate ovulation. As a result, in the ovaries can grow about fifty follicles in which there are eggs. Subsequently, they will become the biological material that will be necessary for this procedure.
Daily specialists record an increase in follicles. To do this, the woman is carried out an ultrasound of the ovaries. As soon as the moment comes when the follicles reach the size required for IVF, the woman is given a puncture. Of course, if the puncture site does not anesthetize the pre-collection site, then such a manipulation can be quite unpleasant.Therefore, in most cases, when taking a puncture, doctors use a mild form of general anesthesia. To do this, before the procedure, the patient is injected into the vein drug, and after a while she sinks into sleep.
Anesthesia an average of no more than half an hour, and the procedure of taking a puncture takes 5-10 minutes.
Carrying out this manipulation requires a highly qualified specialist, as if the needle is inaccurately inserted, the ovaries or fallopian tubes can be damaged (punctured). All manipulation is visualized by an ultrasound machine or laparoscopy.
After the cells are removed, they are placed on the medium most suitable for further work with them.
If the manipulation is successful, then the woman can return home on the same day.
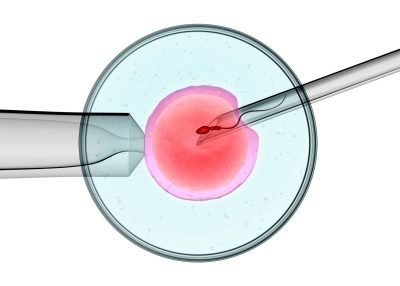
At the third stage of in vitro fertilization, the participation of the father of the unborn child becomes necessary - he needs to pass sperm in order to fertilize the female reproductive cell in an artificial environment. When the IVF specialist receives all the necessary biological materials, he proceeds directly to the fertilization procedure itself: the male and female germ cells are placed in special tubes, where they should merge.
When fertilization has taken place and the embryo begins to actively develop in the place of the mother cell, it must still be in the artificially created environment for several days.
The final stage of IVF is the transfer of a fertilized cell directly into the uterus. This manipulation also occurs under the action of anesthesia. In one procedure, a woman can be “planted” from one to four embryos.
Sometimes the concept of "cryo-transfer" is used. This term means the transfer of fertilized eggs from the uterus cavity to the external environment (in special conditions) or the transfer of “frozen” (“cryo” - freeze) embryos to the uterus cavity.
During IVF, an average of 1-4 fertilized eggs are administered to the patient to increase the chances of successful conception. All of them or several of them can successfully be implanted in the mucous layer of the uterus, but it is possible that all of them will leave the uterine cavity during the next menstruation. In this case, the woman will have to repeat the IVF procedure.
But if the pregnancy nevertheless occurred, and several embryos, or even all four, were successfully implanted into the endometrium, then according to the testimony of a specialist or at the request of the patient, several of them can be removed from the uterus and placed in artificial conditions specially created for them. which they will be in a frozen state according to a certain method.
The process of extracting embryos back into the external environment is called embryo reduction. This is done with the aim that in case of an unsuccessful IVF attempt there was a possibility of implantation of frozen embryos. Thanks to the cryo-transfer technique, in case of unsuccessful transplantation, it will not be necessary for a woman to once again undergo stimulation of the reproductive system for the onset of ovulation - she will not need to take multiple injections and drink pills. Also, a potential father can avoid re-passing the sample of sperm.
As already mentioned, there are cases where all embryos injected into the uterus have taken root, in this case the decision to leave all or remove the “extra” belongs to the woman. This nuance becomes the main argument of opponents of IVF, who consider this bioethical aspect unacceptable both from the point of view of religion and in the human right to life.
In the frozen form, fertilized eggs are stored in a special cryostorage, where optimal conditions are maintained for their viable state. You can store them in such a way from several months to several years depending on the desire of the biological parents. This service is paid.Its cost depends on the duration and storage conditions of the embryos.
After embryo transfer, the patient needs to be completely rest for a certain time, after which she can go home.
The attending physician prescribes a woman who has previously undergone this procedure, taking medications that have a positive effect on the condition of the endometrium (uterine lining). In addition, she may be recommended to take sedatives, as well as drugs that reduce the contractility of the uterus.
In the next two weeks, it is extremely important for a woman to pay special attention to her physical and emotional state: avoid excessive exertion and stressful situations, and also walk more. It would be ideal in this situation to take a vacation or go to the hospital.
After two or three weeks after implantation of a fertilized egg, a woman is undergoing an ultrasound study, which can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of the procedure, that is, to confirm or deny the occurrence of pregnancy. With the successful outcome of IVF, the expectant mother should continue to take the drugs prescribed to her, but if none of the “inserted” embryos could implant into the endometrium, these cells will leave the uterus with the next menstrual flow.
ICSI
This technology is an improved principle of in vitro fertilization.
When it occurs, the germ does not occur arbitrarily in a test tube, but through an instrument similar to a long cannula.
ICSI is used in case of reduced or lack of sperm motility. In addition to this nuance, the ICSI procedure is an absolute repetition of IVF.
Intrauterine insemination
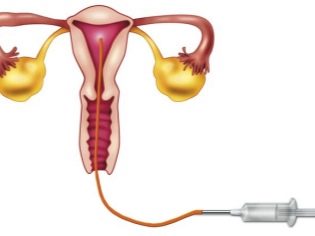
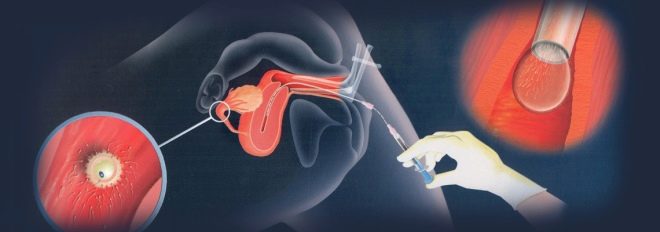
During intrauterine insemination, seminal fluid is injected directly into the uterine cavity of a woman in the ovulatory period using a special catheter.
This method is used when male sex cells for some reason do not have the opportunity to reach the uterine cavity (for example, with low sperm motility or with excessive viscosity of the mucus of the cervical canal).
Indications
The procedure of artificial insemination can be carried out in case of problems with conception both in one of the partners, and in both. The reasons for the emergence of such difficulties a great many.
So, those couples who have had regular sexual relations for a year without using any contraceptive pregnancy did not come to be infertile. This state of affairs undoubtedly requires an appeal to specialists in the field of reproductive health for subsequent examination and treatment. Of course, the fact that pregnancy does not occur for a certain period of time is not an absolute indication for IVF.
As for the most common cases in which IVF is really indicated, these include:
- Polycystic ovary. This is a pathological change in the structure and function of the ovaries resulting from disturbances in the cycle. The impetus for the development of this disease is a failure in the production of estrogen and follicle formation and an increase in the concentration of androgens - male sex hormones, which leads to the appearance of many small cysts in the structure of the ovaries and, as a result, infertility.
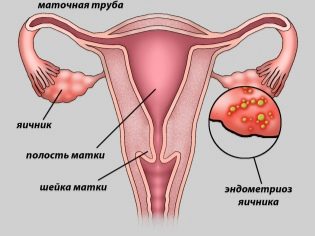
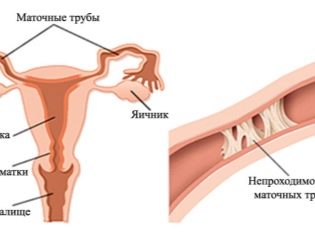
- Obstruction or lack of fallopian tubes.
- Endometriosis. The disease in which the cells of the endometrium, the mucous layer of the uterine wall, expand beyond it.
- Pathologiesaffecting male sperm quality.
- Infertility unexplained etiology.
Not so long ago, in world clinical practice, it was decided to conduct infertility therapy (which sometimes took many years) to women by various conservative methods: drug treatment with hormonal preparations, physiotherapy, massage, spa treatment, etc.
Artificial insemination in such a situation was regarded as an extreme option, so women turned for help to specialists in this field as being quite mature ladies (in terms of childbearing function). Such an approach is absolutely erroneous, since at this age the probability of a successful outcome of the procedure is reduced several times.
In our country, there are enough highly qualified specialists dealing with problems of infertility, to which sometimes childless spouses make appointments a few months in advance.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main task of artificial insemination is the birth of a healthy child, so if this goal is achieved, then all the disadvantages of such manipulation are leveled. According to statistics, more than a third of cases of artificial insemination result in pregnancy. However, it should be borne in mind that this is a rather complex technology, which may also have consequences for the patient's health. A woman should have the fullest possible idea of possible risks in order to consciously, after weighing all the pros and cons, she could make a final decision on the expediency of such a manipulation.
In the case of successful embryo grafting, there is a high proportion of the likelihood that several embryos are implanted into the uterus mucous membrane and a multiple pregnancy will develop. Therefore (at the request of a woman), “extra” embryos can be reduced, which, in turn, can cause spontaneous abortion. If you leave all the embryos, then the risk of hypoxia (oxygen starvation) and premature birth increases.
What influences a successful outcome?
The percentage of the likelihood of pregnancy as a result of artificial insemination is influenced following factors:
- age of potential parents;
- the cause of infertility of a childless couple;
- the results of ovarian puncture (characteristics of eggs and their number);
- seminal fluid quality of a potential father;
- the number of embryos resulting from the fusion of male and female germ cells in laboratory conditions that are capable of development;
- the futility of the couple;
- the state of the uterine mucosa at the time of embryo grafting (the presence or absence of scars, inflammatory processes, etc.);
- the number of previous attempts of the IVF procedure;
- degree of qualification of doctors in a particular medical institution;
- the correctness of the preparatory phase;
- the presence of hereditary diseases;
- lifestyle of potential parents and their bad habits;
- the presence of acute inflammatory diseases or not fully treated chronic at the time of embryo grafting
Ethical and legal aspects
In addition to the medical limitations of artificial insemination, there are laws requiring compliance. For example, being in a formal marriage, the consent of the spouse is required for IVF, especially if donor sperm will be used as male biological material. This is due to the fact that children born in wedlock are automatically acquired as the father of their mother’s spouse. However, the father is fully responsible for raising this child, regardless of true kinship.
Therefore, if, due to ethical, religious or any other considerations, the husband protests against artificial insemination, the solution of this problem will be the spouses' refusal of the procedure, if the wife fails to persuade her soul mate.
In the extreme case, a woman can get a divorce and participate in this program in the status of free ladies.
A man who has become a sperm donor cannot obtain personal information about a woman who has been artificially fertilized using his biological material. In relation to the child who was born in this way, he does not bear material obligations.
Some childless couples for a long time do not dare to resort to the procedure of artificial insemination due to religious and ethical considerations. Leading world religions (Christianity, Islam, Buddhism) accept this “immaculate conception” as the most extreme measure. In addition, the use by spouses of donor sperm, the conception of a single woman and the reduction of embryos in the case of multiple pregnancies is considered unacceptable. Also, Christianity categorically does not accept surrogate motherhood.
How the IVF procedure works, see below.