Symptoms and treatment of cytomegalovirus infection in children
Viral diseases in children are quite common. One of these pathologies is cytomegalovirus infection. How dangerous this disease can be, this article will tell.
What it is?
The causative agents of cytomegalovirus infection (CMVI) are cytomegaloviruses. These microorganisms belong to the group of DNA viruses. These microbes in their nosological affiliation belong to herpes viruses. This morphological structure also determines the peculiarity of the action exerted by microbes.
You can meet cytomegalovirus in a variety of biological fluids and secrets. The maximum concentration is noted in saliva and salivary glands. Quite often there is a carrier of viruses. In this case, viruses are present in the children's body, but no adverse symptoms develop. The maximum risk is noted in children with serious immunodeficiency states.
Some scientists say that a long-term carrier of a cytomegalovirus infection may result to the development of malignant neoplasms in the future. These data are very contradictory and are not recognized by all medical specialists. Cytomegalovirus is found worldwide. Even in economically developed and prosperous countries, there is a fairly high prevalence of these microorganisms.
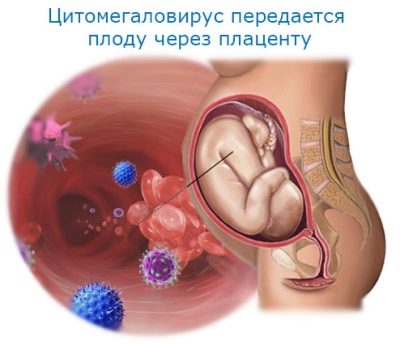
According to statistics, almost 3% of children have viruses in their blood. Quite often, these babies are carriers of the disease, but do not get sick themselves. There are also congenital forms of CMVI. In this case, the future baby becomes infected even during its intrauterine development. The first adverse symptoms of the disease may occur in newborn babies.
Scientists do note that the highest prevalence of this infection is found in economically developing countries. Many doctors believe that the high incidence of cytomegalovirus infection leads to an overall increase in mortality. The impact of these microorganisms on the immune system of babies leads to the development of acquired immunodeficiency states, which contribute to the acquisition of concomitant chronic diseases of internal organs.
There are several forms of this infection. Most common in children generalized version of the disease. According to statistics, it occurs in 85% of babies with cytomegalovirus in their blood.
There is also an asymptomatic form of the disease. In this case, adverse symptoms can only be noticed many years after infection.
The peculiarity of viruses is that they penetrate the cells perfectly. This leads to the fact that these microorganisms can be further found in a variety of internal organs. Once in the child's body and settling in the cells, they begin to actively reproduce and develop in them. As a result, the number of viral particles in a child’s body increases many times over.
In the end, damaged cells acquire their characteristic appearance. In appearance, they resemble "owl eyes." The large size of the nucleus and protoplasm pushed aside to the periphery of the cell cause the characteristic appearance of the damaged cells. Also noted during the illness lymphocytic infiltration. This clinical condition suggests that the immune system was already involved in the inflammatory process.
At the very beginning of the disease, the rate of spread of the formation of new viral particles is insignificant. This is largely due to the characteristics of the immune system, which is actively coping with viruses. After some time, the immunity of the infected baby begins to weaken. This leads to the fact that cytomegaloviruses begin to multiply actively, and the disease becomes active.
Symptoms
The incubation period of cytomegalovirus infection may be different. It largely depends on the initial state of immunity of the child’s body. Premature babies or babies with persistent anatomical developmental defects are at increased risk. Older children suffering from chronic diseases of internal organs are also susceptible to mild infection. In most cases The incubation period for CMVI is from 2 weeks to 3 months.
The adverse symptoms of this disease can be very different. The most common are:
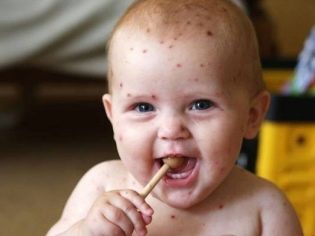
Skin rashes. The most common symptom. Manifestation of these skin rashes petechial rash. In appearance, they resemble small hemorrhages that are common on the skin. This symptom occurs in 75-80% of cases.
Petechial rash. Manifest thrombocytopenic purpura. This clinical condition occurs in 75% of cases. It is characterized by the appearance of multiple bruises that are located on different parts of the body. This symptom is extremely unfavorable and quite often occurs in children in 2-3 years.
Yellowing of the skin. The appearance of this symptom is associated with damage to the liver tissue. This clinical symptom occurs in 60-70% of cases.
Enlarged liver and spleen. This condition is associated with involvement in the inflammatory process of the immune system, as well as vital organs.
Hypotrophy. Quite well, this clinical sign is manifested in babies up to a year.
Prematurity Intrauterine infection of the fetus contributes to impaired placental blood flow and various pathologies of the internal organs. Ultimately, this contributes to the birth of babies much earlier.
Brain damage. This clinical sign is manifested, as a rule, by the development of encephalitis. It occurs in 15-20% of cases.
Inflammation of the retina and internal structures of the eye. As a rule, this is manifested by chorioretinitis.
Infection can occur in different ways. Quite often, babies are infected from adults. Also, children are infected from each other in organized groups. You can become infected through blood. Most often this occurs during various medical interventions - during blood transfusion or during the staging of injections and droppers.
A rather common form of the course of this disease is an isolated lesion of the salivary glands. Only in certain clinical situations is it possible for viruses to spread to internal organs. Generalized forms of the disease are accompanied by fever. Quite often, its values do not exceed subfebrile values.
A sick baby has a sore throat, which can be of very different intensity. The child has peripheral lymph nodes increase. Most often a group of cervical lymph nodes is involved in the inflammatory process. Over time, the child increases the liver and spleen. In some cases, this is manifested by yellowing of the skin.
Non-specific symptoms of intoxication include headache, dizziness, increase in general weakness, weight loss, loss of appetite and sleep disturbance. The long course of cytomegalovirus infection contributes to the child’s lagging physical development from his peers.Many children develop poorly enough and cope with daily loads worse.
When an oropharynx is infected, the child has symptoms that resemble pharyngitis. The mucous membranes of the mouth and throat become red. Quite often palatine tonsils increase in size and begin to hang over the mouth opening.
Generalized forms of the disease, accompanied by damage to the liver, can also occur with the development of other adverse manifestations of the disease. Various disorders of the gastrointestinal tract occur in infants quite often.
As a rule, these disorders are manifested by a speeded-up chair or, conversely, a tendency to constipation.
Severe forms of the disease are accompanied by a pronounced increase in body temperature. In some cases, it can reach values of 39-40 degrees. In the period of febrile, the child, as a rule, feels fever and severe chills. Against the background of high temperature, a sick baby may develop vomiting. For some babies, febrile can last for quite a long time - for several weeks.
Diagnostics
Clinical examination for cytomegalovirus infection is mainly auxiliary. Only a sufficiently experienced pediatrician can suspect the disease. Establish the correct diagnosis and carry out differential diagnostics is possible only with the help of laboratory tests.
Such tests allow you to identify an infection that is even in “sleep mode”.
The determination of specific antibodies to cytomegalovirus is the main element of diagnosis. Reviews of parents who conducted their kids these studies, the most positive. They note that only with the help of the tests performed was it possible to make a correct diagnosis. These studies are practically painless and can be performed on toddlers of very young age.
Elevated cytomegalovirus in the blood of a child is always a significant concern for parents. The appearance of Ig M testifies to the first meeting of viruses with a child’s body. In some cases, this may indicate that a chronic variant of the disease has been reinfected. Usually this condition occurs in children who have suffered a lot of stress or exacerbation of a chronic disease on the eve.
If, during pregnancy, a woman has high titers of immunoglobulins M to cytomegaloviruses in the blood, this may indicate that the intrauterine infection of her unborn child is also possible. It is possible to detect an increase in Ig M in 1-1.5 months from the moment of the first entry of viruses into the children's organism. A sufficiently high content of these protein molecules is noted for another 15-20 weeks.
With the development of this disease, other immune components appear - Immunoglobulins G. Their caption in different babies can vary considerably. As a rule, with some decrease in the activity of viral replication, the amount of these protein molecules begins to increase. A positive analysis on igG indicates that the child’s body is familiar with this type of virus.
Set the stage of development of the disease, relying only on laboratory tests, unfortunately, it is impossible. In the course of the disease, tests are constantly changing. In order to prevent the development of complications, it is imperative to carry out laboratory monitoring.
It is possible to detect microorganisms inside the cells using another modern diagnostic method, the PCR test.
Biological material for research can be very different. In most cases, venous blood or saliva is used for this. In some clinical situations, viruses can be detected in the urine. Quantitative determination of viruses using this test helps to establish the activity of the life process of microorganisms.
It is possible to identify functional disorders in the work of internal organs by biochemical analysis of blood. When liver inflammation is involved in peripheral blood, the number of liver transaminases, ALT and AST, increases. Much less frequently in a diseased baby, the indicators of total bilirubin increase. A decrease in platelets in the general blood test may be the first laboratory sign of thrombocytopenic purpura.
As a screening during pregnancy, a special pp65 test This study helps to identify microorganisms, even in pregnant women at different stages of pregnancy. Also, this examination is actively used to control the specific treatment prescribed for cytomegalovirus infection. This test allows you to identify the causative agent of the disease even a week before the first adverse symptoms. Of the drawbacks of this study is quite high cost.
In some clinical cases, it is required to take material several times. In this case, pathogens can be detected quite accurately in sera. Usually biological material is taken with a difference of a couple of weeks.
If a child has severe adverse symptoms, then blood can be collected at almost any time.
To identify lesions of the internal organs, additional consultations are conducted by different doctors. In this case, the pediatrician may refer the sick baby to a consultation with a urologist, gynecologist, gastroenterologist, or ophthalmologist. Quite often, with the active form of the inflammatory process, an ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed.
Effects
The development of the disease can be very different. Involvement in the inflammatory process of the internal organs is very unfavorable. The prognosis of the disease in this case is noticeably worse. The long course of the disease, especially in a generalized form, is accompanied by a change in metabolism. Ultimately, this contributes to pronounced lag of the sick child in physical development.
Many children who have a long-term cytomegalovirus infection may be significantly different in appearance from their peers. They are usually smaller in weight and height, their muscular tissue is not sufficiently developed. Even minor physical exertion can lead to quick fatigue of babies. At school age, these kids learn less well and get tired quickly even after 2-3 lessons.
As a result of cytomegalovirus-induced encephalitis, the child may experience some impaired memory and attention. Quite often, this is manifested in the difficulty of memorizing specific numbers or events. The inability to adequately shift attention is also found in babies who have had cytomegalovirus encephalitis.
Choreoretinitis, which occurs in 10-12% of babies with cytomegalovirus infection, can lead to the development of a child persistent visual impairment. In some cases, the decline in the work of the visual analyzer develops gradually. Any visual impairment arising in a child after undergoing cytomegalovirus choreoretinitis should be necessarily identified and treated.
Child neurologists also note that some babies may develop mental disturbanceswhich are also manifested by various deviations in mental development. Quite often, these manifestations occur in conjunction with cardiovascular abnormalities. Some babies are found and speech disorders. These dangerous complications can develop in children whose cytomegalovirus infection is asymptomatic.
Treatment
The whole therapy of cytomegalovirus therapy can be divided into two major areas. This is a specific antiviral treatment and symptomatic medical care.Drugs that have a devastating effect on viruses include "Ganciclovir". This drug can be taken both orally and administered parenterally. This drug has a pronounced therapeutic effect that allows you to achieve a good result.
This drug is well accumulated in the cells. The distribution in the body is very moderate. The drug penetrates well into various internal organs.
It is important to note that the intracellular content is several times higher than in the peripheral bloodstream. This clinical feature helps not only to achieve a good result, but also to reduce the risk of unwanted side effects.
The accumulation of drugs can be in a variety of biological materials, including in the liquor. The vast majority of drug metabolites are excreted through the kidneys. The average half-life in this case is 3.0-3.5 hours. If a child has chronic kidney or urinary tract diseases, then the drug can accumulate in the body much longer.
Foscarnet - Another drug used to treat this infection. This tool is introduced only parenterally. Metabolites of this drug are also excreted through the kidneys. Taking this medication may contribute to the development of adverse side effects. These include a pronounced decrease in immunity, impaired excretory function of the liver and kidneys.
When using these drugs necessarily carried out laboratory monitoring of blood tests several times a week.
If, against the background of medication in a child, the content of platelets and neutrophils has significantly decreased in peripheral blood, then the use of these chemicals is completely stopped. Selection of further treatment in this case remains for the treating physician.
By their basic mechanism of action, these drugs are cytostatic. In this case, the appointment of immunostimulating agents is required, which will allow preserving and replenishing lost immunity. The scheme of drug therapy is quite complicated and requires mandatory monitoring by doctors.
Do not use these medicines yourself! The risk of adverse side effects is high, which can affect the frequency of developed abnormalities in the work of internal organs.
"Cytotect" - This is a drug used in immunodeficiency states. In its composition, this tool contains cytomegalovirus immunoglobulins. The prescription of this medicinal product is carried out by the attending physician with the obligatory establishment of the required dosage. Quite often, taking the drug is accompanied by the appearance of many different side effects. The most frequent of these include headache, dizziness, nausea and tenderness in the abdomen, severe sweating.
In some cases, drug resistance occurs. As a rule, this condition occurs with a long course of the disease.
To eliminate drug resistance requires the correct selection of specific therapy. A protracted course of the disease requires the mandatory prescription of supporting immunostimulating treatment. This specific therapy is prescribed by a child immunologist.
For information on how to defeat cytomegalovirus, see the following video.