Hydrocephalus - dropsy of the brain in children
Hydrocephalus of the brain (dropsy) in children is a serious pathology, but this diagnosis cannot be considered a sentence. With the right approach and timely treatment, the child can lead a completely normal life - with minor restrictions, or even without them. About what constitutes a disease and how parents act, you will learn by reading this article.
What it is?
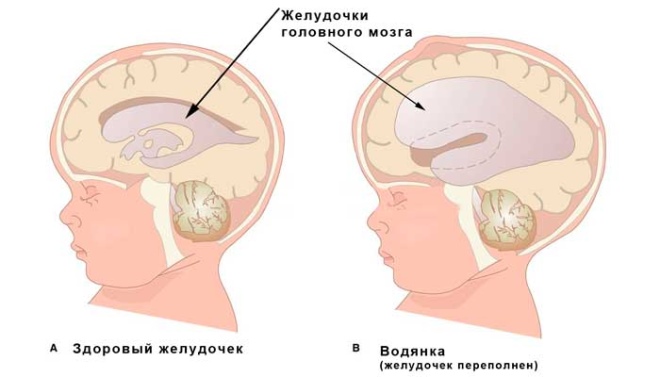
The disease is also called dropsy of the brain, and this definition very accurately reflects what actually happens in the body. Excess cerebrospinal fluid accumulates inside the skull, under the membranes of the brain, in its ventricles. In a healthy baby, this substance must flow to the spinal canal through the tubules (ventricles) and circulate freely.
The difficulty of this movement with a large amount of fluid leads to increased pressure, to partial or sufficiently significant leaching of the structures of the nervous system under pressure. The consequences of such exposure can be very diverse, they depend on the degree of damage and specific areas of the brain.
Liquor (this liquid) performs many useful and necessary functions for life. It protects the main human organ (brain), washes it, leukocytes in the composition of the liquid provide the necessary immune task. Cerebral fluid is produced continuously. In case of violation of circulation, stagnation appears, dropsy begins to develop.
If the disease is detected at the initial stage, the child quickly and competently received medical care, the consequences may be minimal or completely absent. In neglected and difficult cases, the child may experience problems with speech, development, psyche, neurological diagnoses, visual, hearing, vestibular and motor disorders. In the absence of assistance, the child’s death occurs.
This pathology is not as common, but not as rare as we would like. The statistics of the World Health Organization (WHO) show that hydrocephalus of varying degrees and varieties is found in one of 4,000 newborn babies.
In theory, hydrocephalus may well develop in an adult, but more often it affects children.
Types and causes
Cerebral edema can be either congenital or acquired pathology.
In the first case, the development of the disease is affected by unfavorable intrauterine factors: an infectious disease in acute form in the mother during pregnancy (most often a cytomegalovirus infection affects the child), malformations caused by genetic “errors”.
Acquired hydrocephalus most often affects children up to one year old, who were born much earlier than the allotted time, as well as toddlers who suffered a brain injury during childbirth.
The cause of the pathology can also be a traumatic brain injury or a previous infectious disease, a brain tumor. The most dangerous combination of risk factors is if, for example, meningitis, encephalitis or meningoencephalitis develops in a premature baby. The disease can develop after surgical procedures.
Dropsy is divided into several types – depending on where the cerebral fluid accumulates:
- outdoor;
- internal;
- mixed (combined).
With external dropsy, the accumulation of CSF is concentrated only under the membranes of the brain, it does not affect the deep areas. This condition usually occurs in newborns and children who have suffered a birth trauma.
Internal hydrocephalus - This is a situation in which the cerebral substance accumulates in the cerebral ventricles, which can not normally flow. Such a lesion may be a congenital abnormality, as well as acquired - in the toads over a year.
A mixed type of dropsy combines the signs of the first and second species, with the cerebrospinal fluid accumulating inside and outside the brain.
According to the assessment of the true obstacles that prevent the full circulation of fluid, dropsy is divided into:
- open (reported);
- closed (occlusal).
With the communicating form of the disease, there are no objective obstacles, the ventricles are sufficiently dilated, there are no mechanical barriers to the flow of cerebrospinal fluid. Occlusive hydrocephalus occurs as a result of abnormal development of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways themselves, pathologies in the structure of the ventricles, tubules, tumors in this system, tumors, adhesions. This form of the disease is almost never external, it is characterized by the accumulation of fluid inside the brain.
According to the time of development of the pathology, there are three types of hydrocephalus:
- acute;
- subacute;
- chronic.
Acute develops rapidly, the pressure inside the skull rises literally in 2-3 days. Subacute pathology can develop up to six months, gradually, almost imperceptibly for parents. Its consequences can be more devastating. With chronic dropsy, the cerebrospinal fluid accumulates very slowly, for more than six months, which at first does not affect the baby’s well-being, because the pressure is growing at a very slow pace. And only then, when it reaches a critical level, the diagnosis becomes obvious.
Children's body has a very high compensatory abilities. If there is something wrong somewhere, the body tries in every way to compensate for this with other resources. Therefore, it happens so that with the established diagnosis of “dropsy of the brain,” the child has absolutely no deterioration of well-being, behavior change. In this case, talking about compensated hydrocephalus.
If the body does not have enough forces to compensate, the child’s well-being deteriorates, there are pronounced irregularities in his development, then they are talking about decompensated dropsy.
A minor compensated failure in the circulation of the liquor sometimes does not even need serious medical support, which cannot be said about decompensated disorders.
According to the degree of injury, doctors also divide the disease into stages. They are two:
- moderate;
- pronounced.
According to the dynamics of manifestations, hydrocephalus can be:
- progressive (with marked deterioration);
- stable (when new symptoms do not appear, but there is no improvement);
- regressive (with a gradual decrease in symptoms).
Risk factors
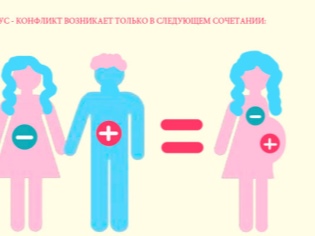
The probability of development of dropsy of the brain in utero affects a lot, but first of all - the unfavorable conditions for the development of the fetus. These factors include the Rh-conflict of the mother and the fetus.
In fairness it should be noted that not every Rh-conflict pregnancy ends with the birth of a child with congenital hydrocephalus. However, if the mother has a negative Rh factor, and the baby has a positive one, and the antibody titer in the woman’s blood is high, then doctors are sure to consider this probability.
Risk factors include infectious diseases that a woman can become infected during pregnancy.
The first trimester is especially dangerous in this respect. Such diseases include herpes sore throat, chickenpox, Coxsackie virus, sometimes problems arise because of infection with Toxoplasma, rubella viruses or measles.It is these ailments that can cause a disorder in the formation of the baby’s brain, and then the development of an occlusive cerebral dropsy is possible.
Often, hydrocephalic changes are closely associated with a concomitant diagnosis of genetic disorders in the fetus. Often children with Down syndrome, Turner, Edwards appear with severe congenital hydrocephalus.
Gestosis in the period of gestation is also dangerous, diabetes mellitus and severe anemia in the expectant mother can also play a role. When a child is pregnant with twins, the child has gross defects of the heart, circulatory system, kidneys, the risk of birth of hydrocephalus increases.
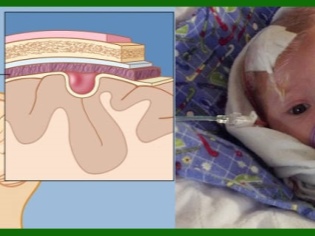
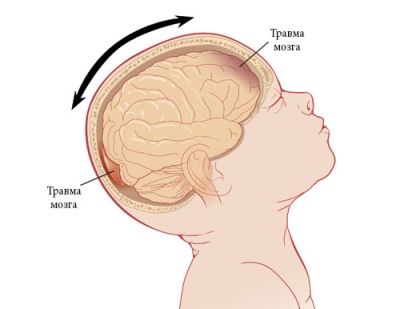
The postnatal period is also important for boys and girls in terms of the occurrence of hydrocephalus. Premature birth, a long anhydrous period, rapid delivery, in which the baby may have hemorrhages in the brain, are dangerous. Some birth injuries, infection in the early newborn age meningitis and encephalitis can also cause hydrocephalus.
Symptoms
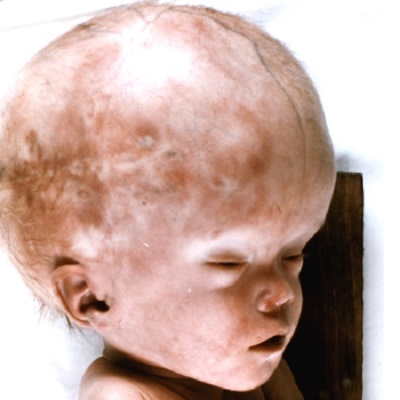
Not always excessive accumulation of liquor in the head can be determined immediately after the birth of the crumbs, sometimes the symptoms manifest themselves much later. The main visual symptom is an increase in the head. Normally, the newborn's girth is 1-2 centimeters more than the girth of the chest. These proportions should change diametrically by 6 months. If this does not happen, the head continues to remain larger than the breast and grows ahead of the age norms; this is the reason for the examination.
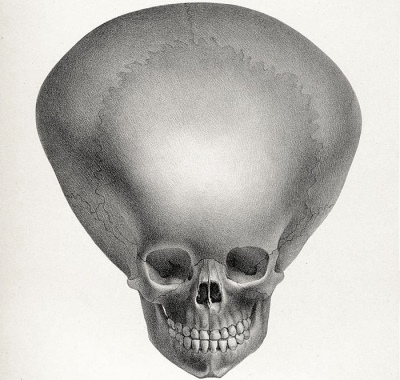
A characteristic hydrocephalic skull with prominent frontal lobes, an irregularly enlarged form, appears when the imbalance of body proportions reaches a maximum.
Each pediatrician on the table or in the office has a table with which doctors compare the age norms of girth. In a newborn, these values are usually in the range of 34-35 centimeters, and in a child at 3 months - 40-41 centimeters. You should not panic if the baby has a volume of 40 centimeters not in 3 months, but in a month. All children are different in height, and some have bigger head sizes, while others have smaller ones. Anticipating the age norm alone cannot speak of pathology.
What is important is the rate at which the head of the baby grows. Normally, it increases by a centimeter per month. An alarming symptom can be considered if the head has not grown by 1, but by 3-4 centimeters for a month.
The remaining symptoms should be assessed if the growth rate is abnormal.
A sick child usually has:
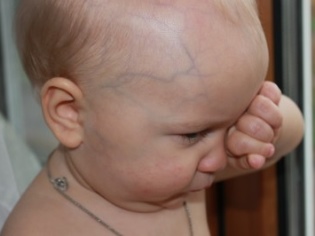
- On the forehead, temples and occipital part of the head clearly visible vein veins.
- The child does not hold the head (the symptom is only important if the baby is already more than 3 months).
- Baby is not smiling, even if he is already 3-4 months old.
- The skin over the fontanelle appears above the surface, visibly pulsing.
- The baby is constantly crying eating badly, sleeping restlessly, slowly gaining weight (an ambiguous symptom that cannot speak about anything by itself).
- Frontal lobes very largespeakers
- Pupils are not fixed on the subject, all the time finely “tremble” from side to side or from top to bottom (the symptom should be assessed only after 2 months of independent life of the child).
- The location of the eyes seems deep due to overhanging massive brow ridges.
- There are signs of strabismus by divergent type.
- Lost skills (the baby ceases to fix the gaze on the object, cannot hold his head in an upright position, even if he did it earlier, ceases to roar, sit).
- Convulsions, vomiting, and incessant monotonous weeping (these symptoms are usually accompanied by emergency conditions with cerebral edema).
In children older than one year, signs of hydrocephalus are usually somewhat different:
- spontaneous convulsions with loss of consciousness;
- frequent headaches (usually they get worse in the morning and almost disappear in the evening);
- frequent nasal bleeding due to headache, vomiting;
- frequent episodes of panicked night crying and crying - for no apparent reason;
- urinary incontinence;
- visual impairment.
It should be noted that most of the symptoms that can accompany the edema of the brain in a child after one year, in fact, is all that is usually noted by the neurologist. This is a trembling chin, and a scattered attention, and hyperactivity, and irritability, and even walking on the toes. The main thing here is not to evaluate each such symptom separately, you should not immediately “write” the baby into the rows of hydrocephalus.
Usually, one by one, these signs, even neurological disorders, can only be considered a stretch. For this reason, it is important to assess the totality of factors, signs and rely not on the fact that the baby is written and shouts at night, but on the results of medical examinations.
By the way, it makes no sense to measure the child’s head after a year. Even with severe hydrocephalus, it does not change in size, since the bones of the skull with the closing of the fontanel cease to be mobile, but intracranial pressure such babies are much higher.
Diagnostics
Very often, the diagnosis of the state of the brain is excessive. This means that moms and dads are announced the names of diseases that infants do not have. Quite often (about 3-4 crumbs out of a dozen) during the passage of magnetic resonance or computed tomography (and even on conventional ultrasound of the head) put hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome. Some neurologists even manage to make such a diagnosis without additional examinations.
The reality is that this syndrome is not very common, and not in 30-40% of children. The enlarged ventricles of the brain are sometimes just an individual feature of the brain’s structure in a given karapuz, therefore it is important not to rush to treat the child, and choose observation tactics, monitor the size of doubtful brain structures during the growth of the baby. To do this, regularly measure the circumference of the head and from time to time conduct a special study - neurosonography.
Hypertension-hydrocephalic syndrome is always associated with increased pressure inside the skull, which is caused by the accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Most parents have absolutely nothing to worry about.
However, to underestimate the danger can not be. Be sure to contact your doctor if the child has several symptoms from the lists above. And this doctor should be a pediatrician. The doctor assesses the overall well-being of the baby, “takes measurements” from the head, sets the chest girth, relates all this to the warning signs described by the parents and gives direction to the neurologist.
It is worth noting that children's neurologists love to find what is not and treat what they have found. That’s why parents should have a clear idea when a neurologist can suggest a disease, based on what research he confirms or denies such a serious diagnosis.
First, the neurologist evaluates the reflexes of the child. If he doesn’t like something, he sends the little patient to the eye doctor’s office, who assesses the state of the fundus using special devices. When a congestive disc, strabismus, and dilated pupils are detected, if there is no response to light, the eye doctor again sends the child to a neurologist, who at this stage can suggest hydrocephalus. But only to assume, and nothing more.
Ultrasonography of the brain, which is recommended by a neurologist, is also not a basis for diagnosis. The probability of overdiagnosis is too high. Although it is possible to examine the structure of the brain through a fontanel, it is impossible to estimate their size and correlate them with any norms, one needs observation in dynamics.
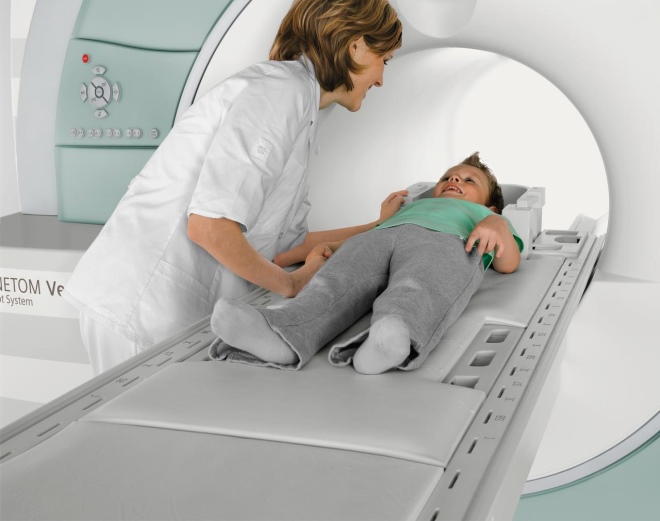
If the condition of the child inspires fear, and the neurologist finds it inappropriate to wait, he will refer the baby to an MRI. Magnetic resonance imaging allows you to get more detailed and reliable information about the state of each area and each layer of the brain. A doctor with such a picture with high accuracy will be able to determine not only the presence of the disease, but also its degree, location of dropsy, degree of damage to neighboring structures, volume of fluid in the ventricles of the brain and other important nuances.
This method, which is excellent in all respects, is not very convenient for infants, because during the study for quite a long time the child will have to lie still - in a special chamber with a huge magnet. Therefore, for young children, medical anesthesia is necessary to conduct research and obtain reliable results.
The computed tomography method is also good enough for diagnosing dropsy in the brain. Only MRI and CT are able to answer the main question - is everything in order with the baby? An important caveat: in order for the diagnosis to be reliable, an MRI scan is desirable to be carried out 2-3 times - with intervals of 2-3 weeks between studies.
Practice shows that doctors often prescribe other studies (echoencephalography, electroencephalography). However, according to the existing standards of diagnostics, these methods are not reliable in cases of hydrocephalus, parents may well refuse them.
The true cause of the development of dropsy (whether it is an infection or a birth trauma) in infants often remains a mystery to both physicians and parents. Only traumatic causes can be more or less accurately determined if a head injury was received.
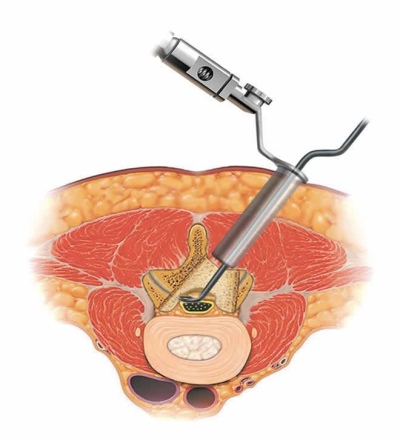
Last diagnostic "touch" - determining the level of cranial pressure. There are no devices that can do this, and therefore invasive procedures are used to clarify this factor. Most often, puncture of the cerebrospinal fluid is done - in the intervertebral space, in the lumbar region.
Further decisions will be taken together by two specialists - a neurologist and a neurosurgeon.
Treatment
Treatment (regardless of the cause that caused cerebral dropsy) is always carried out according to certain schemes and principles. The main method is surgical treatment, but sometimes neurosurgeons allow the use of drug therapy therapy - if they believe that there is no danger to the child, and the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is possible without surgery.
Conservative treatment
For conservative treatment, diuretics are commonly used, which can reduce the production of CSF and increase its circulation. In most cases, with open hydrocephalus, which is not complicated by severe symptoms, this is quite enough.
A drug "Diacarb"Is prescribed to children most often. It slows down the production of cerebral fluid and promotes more active urination. The medicine has a big disadvantage - it rapidly removes potassium from the children's body, which is so necessary for growth and development. Therefore, it is taken together with drugs containing this substance - "Panangin" or "Asparkam".
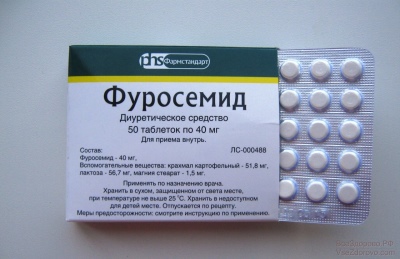
If a child has a high level of intracranial pressure, but neurosurgeons consider it appropriate to wait for the operation or see an opportunity to cope with hydrocephalus without a scalpel, the baby is prescribed diuretic drugs Mannitol or Furosemide. Moreover, in the second case, it is also necessary to take potassium preparations.
Additionally, the doctor may prescribe drugs that stimulate the work of neurons.. To relieve minor symptoms of cerebral edema (delayed speech development, diffuse attention), a tonic and adaptogenic drug is often prescribedKogitum". It is intended for children from 7 years.
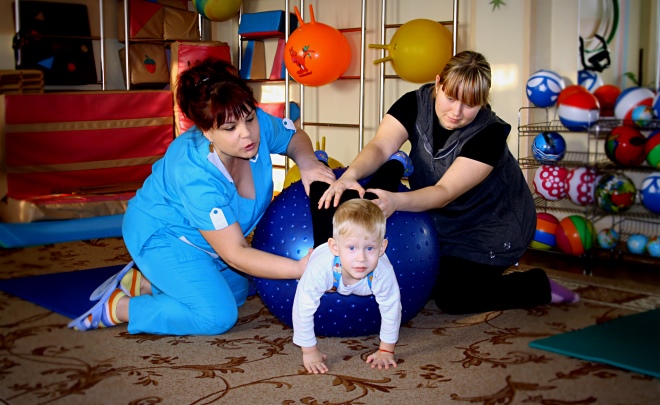
To increase the effectiveness of medicines, the child is recommended additional treatment, which includes massage, exercise therapy, microcurrent reflexology. The main thing is not to go to extremes and not to start looking for osteopaths who, for a "moderate" reward, promise to put the baby all the bones of the skull in place.
Such procedures can be extremely dangerous for the life of the child, and therefore without the recommendation of a neurosurgeon you should not visit osteopaths. The benefits of their massage in medicine are not documented, in contrast to the unfortunate consequences of unsuccessful manipulations.
Usually, a conservative treatment is given no more than 3-5 months. If the condition of the child has not improved, and intermediate studies using MRI and CT showed deterioration and ineffectiveness of drug therapy, the decision is made to conduct the operation.
Surgical treatment
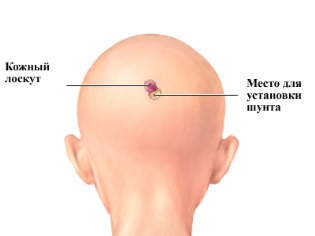
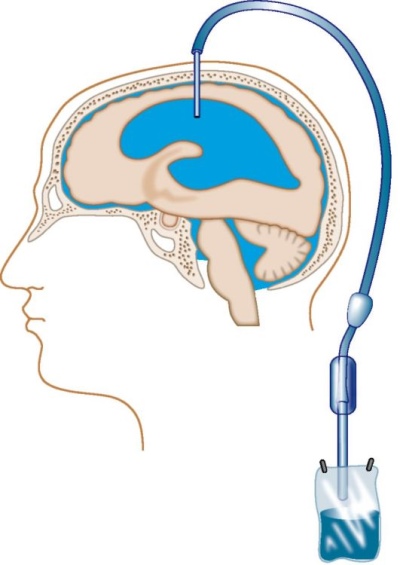
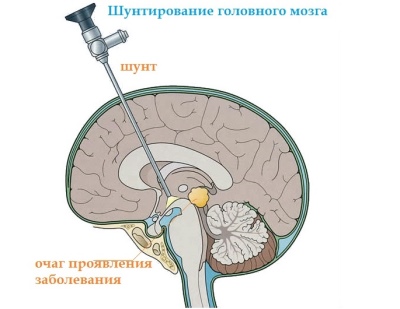
The most common surgical method of ridding a child of excessive cerebrospinal fluid in the head is shunting. After the craniotomy of the skull, special silicone tubules, shunts, are introduced into the brain's ventricle expanded from the fluid, by which excess fluid is discharged into the abdominal cavity. One end of the shunt resides in the brain, and the other is inserted into the abdominal cavity. The middle of the tube passes subcutaneously.
The risk of complications in shunting (despite the high qualification of the surgical team, or the excellent quality of the shunt) is quite high. It is about half of all cases.
In 40-60% of cases within six months or a year complications develop, which require another surgical intervention associated with the replacement of a shunt or a certain part of it.
It should be understood that as the child grows older it will take several more such operations. Shunts need to be replaced, because there is nothing eternal. They can become clogged, bend over, fray. In the planned mode, they change due to age-related changes in the child's body.
Otherwise, the life of “shunted” children is no different from the life of their peers - unless, of course, hydrocephalus did not cause any other disturbances in the nervous system during the period preceding the operation. There is one more factor that cannot be ignored: shunt addiction. While the child is small, his parents will worry about this, then he himself will understand that his life directly depends on the state of the silicone tubes inside his head.
In search of an alternative, medicine considered draining operations, when the liquor was taken out after trepanning and inserting a catheter. First, it did not eliminate the true cause of the disease, especially with malformations of the brain structures, and the fluid began to accumulate again. Secondly, the danger of brain infection during drainage increases tenfold. Therefore, this method is the place to be, but it is used extremely rarely - as a “gesture of despair”, when only urgent drainage can save the baby’s life at this stage.
The last 40 years in medicine are practiced and endoscopic surgery. They are considered a priority way to combat hydrocephalus. With the help of an endoscope, neurosurgeons can not only install a shunt, if necessary, but also “fix” some of the defects that led to closed deep hydrocephalus.
In fact, doctors create outflow pathways for cerebrospinal fluid. If it is impossible to eliminate the defect, they make these ways "workaround". When carrying out endoscopic surgery, you can remove some tumors that interfere with the normal outflow of CSF, eliminate the blockage of the ventricle. Surgical manipulations usually last no more than 20-30 minutes.
Most often, endoscopy is prescribed for mixed hydrocephalus, occlusive form, and pathology resulting from severe injury.The operation is less traumatic than shunting, it causes complications much less often, it does not impair the patient's quality of life, because he does not have a foreign object in his body, and there is no dependence on him. Do not think that endoscopy is expensive. With all its advantages, it is also the most cost-effective option for medical institutions, which does not require cost.
Unfortunately, the method is not effective with every hydrocephalus. If a neurosurgeon does not recommend endoscopy due to the individual characteristics of the child’s illness, then only bypass surgery remains.
After surgery, children who underwent endoscopy are registered with a neurologist. They can be removed from it if their condition has improved, and there are no violations. After shunting dispensary registration with a neurologist is for life, to remove a child from him there is not the slightest possibility.
Forecasts
There are no universal predictions for hydrocephalus in children. Everything is individual, and there are as many predictions as the patients themselves. The most positive prognosis with great caution is given to children with associated hydrocephalus. With occlusive dropsy, healing without consequences does not happen as often.
Congenital hydrocephalus, if identified in time, is faster and easier to treat than an acquired disease. Hydrocephalus first degree less often leaves irreversible effects than extensive and severe cerebral dropsy. The prognosis is all the more positive the earlier the doctors revealed the ailment, the sooner the medical aid was provided.
Unfortunately, a large number of children who have suffered severe forms of hydrocephalus, later still manifest debility, mental retardation, mental and personality disorders. Among the lesions of the nervous system leading cerebral palsy, as well as the lack of coordination. Vision and hearing suffer. Do not write off and postoperative complications - inflammatory processes, infectious and non-infectious brain damage, epileptic seizures.
Children who are treated diligently and consciously by their parents live much longer than abandoned children with congenital hydrocephalus. Cerebral edema is treatable. Only the consequences of the disease can be total.
Rehabilitation
Even after successful treatment, the child will need several years for rehabilitation.
Do not neglect the opportunity to attend a rehabilitation center with your baby. There are such institutions in every region.
Speech therapists, neurologists and massage therapists deal with the child there. Excellent results in treatment and rehabilitation show Chinese clinics in which practice laser therapy sessions. Rehabilitation centers are in Israel.
There are quite a few sanatoriums in Russia and abroad that are ready to accept children from 2–3 years old - after undergoing bypass surgery or endoscopic plastic surgery of the ventricles of the brain.
Courses in rehabilitation centers and trips to sanatoriums do not cancel daily intensive activities with such children, because they require much more attention and patience.
The child must eat properly, do not allow the intake of excess fluid, do not eat too much salted, pickled and smoked to avoid fluid retention in the body.
Useful tips
- If the child is diagnosed with hydrocephalus, do not despair. After all, the baby in this difficult period needs a strong, sensible and seasoned mother, who will help him overcome the disease. There are many forums on the Internet for parents whose children have successfully recovered from hydrocephalus, and for those who still have to.
- Do not look for the guiltySometimes this ailment does not depend on the parents and their right or wrong actions.
- During pregnancy should be required attend female consultation. Many studies and analyzes that are prescribed to expectant mothers will help to learn about risk factors in advance.
- Before pregnancy, a woman should visit the infectiologist at least once, to find out, having donated blood, what diseases she suffered, and antibodies to what dangerous infections she has in her body.
- If during pregnancy (especially in the early stages), a woman will have rubella, measles or another infection, she should definitely agree to additional research on the condition of the fetus, visit the geneticist to make a further (very painful) decision to carry the child. You need to know about the risks of pathologies, about the treatment during pregnancy.
- If the child was born before term, it is impossible to miss a single compulsory medical examination and a scheduled visit to the doctor.
- Children older than a year should be protected from head injuries. If you bought him a bike, be sure to donate a helmet. If a child is being carried by car, then by all means you need to use the car seat.
- All viral infectious diseasesthat infects a child, cannot be treated independently - according to grandma's recipes, viburnum and burdocks. Be sure to contact your doctor, take tests, take medication should be exclusively prescribed by a qualified doctor.
You will learn more about this disease from the video below.