Rubella in children: symptoms, treatment and prevention
Rubella infection is one of the most common diseases in babies. According to statistics, every second child under three years old must have rubella. The disease is very common. In order to recognize a children's viral infection in time and to prevent complications, parents should know the main manifestations of the disease.
What is it?
Rubella has a viral cause, it is caused by the smallest Rubella virus, which survives extremely poorly in the external environment. However, without performing a special disinfecting treatment, the virus can remain in the air for a long time. Under the influence of external factors, he very quickly dies. It is detrimental to it: ultraviolet radiation, quartz treatment, exposure to high temperatures and aggressive chemical fluids (formalin or compounds containing chlorine).
The virus is well preserved at very low ambient temperatures. For this reason, more cases of rubella occur every year during the cold season.
The virus is very volatile, quickly transferred from a sick child to a healthy one. Children's body is very susceptible to this infection. According to statistics, the peak of the incidence of rubella occurs in the age of 2-10 years.
The reasons
The virus, after going through a development cycle in a child’s body, causes many unpleasant clinical symptoms in young children. The source of the infection is the sick child. It should be noted that not always kids can have acute manifestations of the disease. Approximately 15-20% of babies for a long time can only be virus carriers and infect other children. The disease in them usually proceeds in erased form.
If the baby is breastfed, he can easily get rubella from the mother. Viruses that cause disease, are the smallest size and perfectly penetrate into breast milk through the blood. If mom gets rubella, the baby also becomes ill after a while.
In more rare cases, doctors note a congenital form of the disease. If a woman contracted rubella during pregnancy, she passes the virus through the placenta to her unborn baby.
In closer groups the risk of getting sick is much higher. Scientists note that rubella occurs more frequently in large cities than in rural areas. Usually, outbreaks are recorded every 5-6 years. Doctors note that the incidence of rubella among pregnant women increases every year. This unfavorable and even dangerous situation is primarily associated with inadequate vaccination against infection.
Stages of the disease
In the course of the disease goes through several successive stages. After contact with a sick child, a large number of rubella infection pathogens enter the body of a healthy baby. In more crowded groups (kindergartens, schools, sports clubs) the risk of infection increases several times.
You can get rubella in several ways:
- Airborne. In this case, viruses are transmitted from a sick child to a healthy one during intercourse or personal hygiene violations. Susceptibility to the disease in children is very high. A small amount of time and microorganisms is enough to cause infection.
- Vertical. In this case, a pregnant woman infects her future baby through the placenta.Rubella viruses perfectly penetrate the placental barrier and with the blood flow reach the baby's organs. The baby may still be contagious after a few months after birth.
- Contact. Infection occurs when sharing common household items: bed linen and towels, mugs and tableware, toys, toothbrushes. Contact rubella infection is most relevant for children attending kindergarten. Insufficient disinfecting treatment of toys leads to massive outbreaks of the disease in preschool institutions.
On average, the incubation period of the disease is 2-3 weeks. This is the time from the moment the virus first enters the body until the development of the clinical symptoms of the disease. As a rule, after 7-10 days from the moment the pathogen enters the body, the child becomes infectious.
First, the virus invades the surface epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract. There he begins to actively multiply. After some time, it penetrates the lymph nodes and spreads through the blood throughout the body. At this time, the second week of the incubation period usually ends. If you make a diagnosis, it is during this period that you can still detect a large number of viral particles in the mucus of the nasopharynx and pharynx.
At the end of the incubation period, the amount of virus in the body already reaches a huge amount. With the flow of blood, the pathogen spreads throughout the body, penetrating virtually all internal organs. At this time, the babies show the first symptoms of rubella infection.
How to recognize: first signs
Making the right diagnosis during the incubation period is often quite difficult. The child practically does not bother. Skin manifestations are still absent. During the first three weeks after infection, the child may have a fever, and there is a slight general weakness. Children at this time become more capricious, their mood deteriorates. However, these signs are not specific and do not allow to suspect the disease in the early stages.
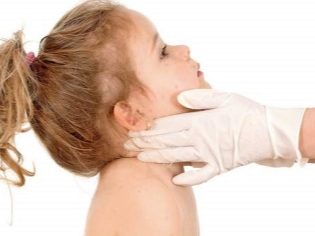
The first characteristic symptoms appear by the third week of illness. At this time, many groups of lymph nodes are greatly enlarged. The lymphatic groups in the occiput area are most strongly altered. They become so big that they even look and feel well. During the inspection of the neck, the baby does not feel pain.
The lymph groups of the nodes located in the axillary zone, in the groin and under the lower jaw are enlarged. When feeling, they are quite large, dense. In some cases, you can even see some redness over the damaged skin. By the end of the third week, the babies have a slight pain in the neck. It may increase slightly with sharp movements or turns of the head.
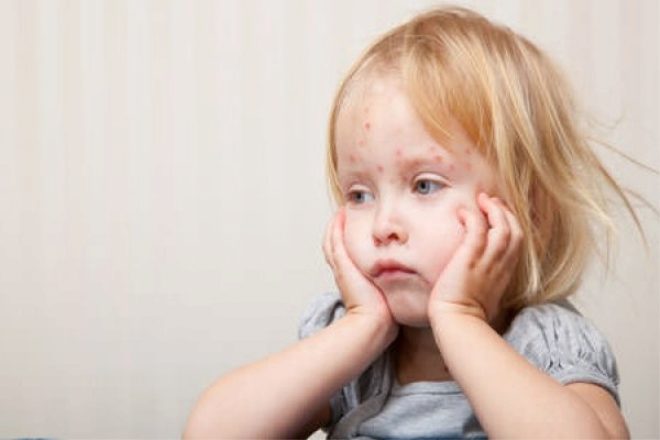
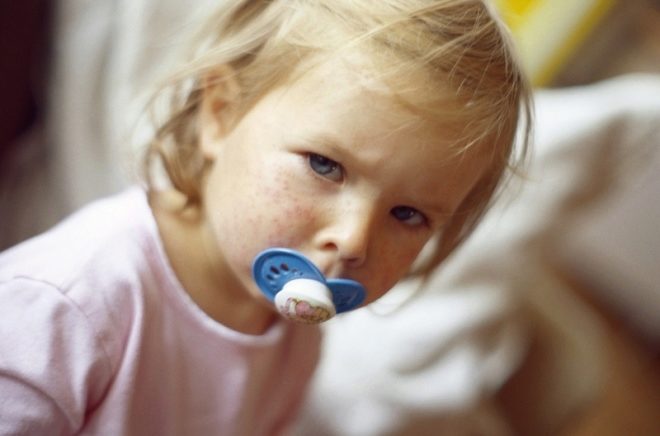
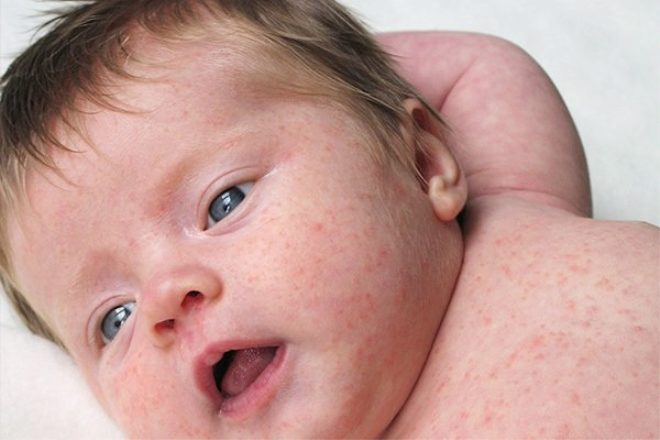
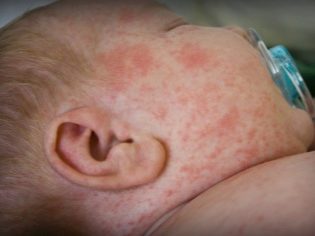
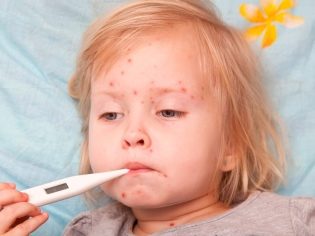
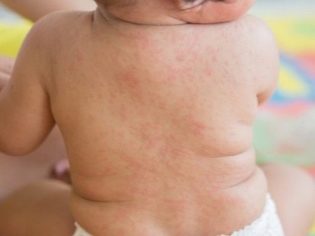
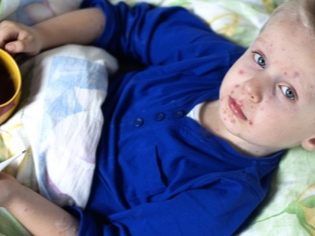
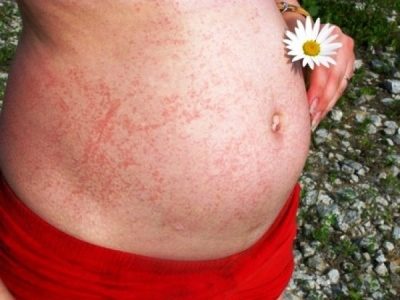
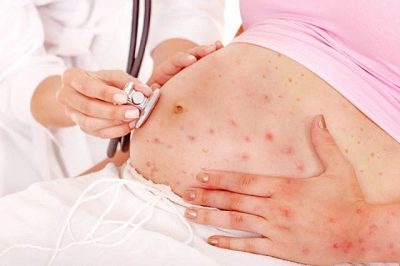
Typically, 2-3 days after the end of the incubation period, a rash characteristic of rubella infection appears. First, it appears on the scalp, neck, and also on the face. The rash consists of small red elements (from 2-4 mm). They can merge with each other, various patterns appear. The rash does not itch. It occurs due to the fact that the virus during its reproduction releases toxic products into the blood. They damage the blood capillaries and cause them to rupture.
The rash after 3-4 hours begins to spread rapidly throughout the body. Red elements can be seen in all areas, except for the palms and soles. This is also one of the characteristic clinical signs of rubella infection. After 4 days, the elements of the rash gradually begin to turn white, decrease in diameter. After another 5-7 days, it completely disappears, leaving no disfiguring scars or scars on the body.
For the longest time, rubella rashes can persist on the skin of the buttocks, as well as the forearms on the inside.During a period of rash, baby’s well-being often improves.. Despite the terrible look, the baby feels much better. At this time, body temperature returns to normal, breathing improves, and sleep and mood are restored.
During the period of skin manifestations, rubella infection is very similar to many other infectious skin diseases. The doctor must necessarily make a differential diagnosis. Other diseases can also manifest as a rash. Any expert knows how to distinguish a red infection from an allergy or other childhood infections that can cause the appearance of red elements on the skin. The rubella rash has many distinctive features that allow you to accurately enough to make the correct diagnosis.
Forms of the disease
Rubella infection can occur in several forms.
In a typical or common form of the disease, the child has all the classic symptoms of the disease (with the obligatory appearance of a rash). In some cases, there is an atypical option. In this embodiment, there are no manifestations on the skin.
The diagnosis of the atypical variant is much more complicated. This requires the use of special laboratory tests to help ascertain the result and identify the exact causative agent of the infection.
Rubella is often masked by many other childhood diseases, manifested by the appearance of a rash. With measles rubella, for example, skin manifestations also appear. However, at measles the child’s well-being suffers more. In children, the temperature rises strongly, there is no appetite. Elements of the rash do not merge with each other. In order not to make a false diagnosis, the doctor must necessarily monitor the baby from the very first hours of the disease.
Diagnostics
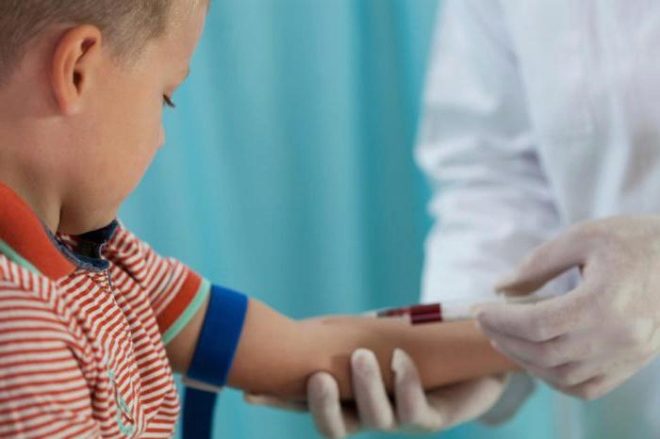
For differential diagnosis, doctors may prescribe additional laboratory tests. The most common test is the serological determination of specific anti-fume antibodies. Blood is taken from a vein, usually for 5-10 days from the onset of the disease.
Detection of Ig class M and an increase in their number several times indicate the presence of an acute disease. The appearance of class G immunoglobulins in the blood indicates a past infection or a vaccination course.
Treatment
In its development, rubella in young children is much easier than in adults. Only in infants with reduced immunity or with chronic diseases can life-threatening complications arise.
However, the occurrence of adverse effects after rubella infection is quite rare.
Not everyone knows whether it is difficult to cure rubella at home. If the disease proceeds in a typical and fairly mild form, then the treatment is carried out at home. The need for hospitalization in an infectious children's hospital is only in difficult cases when the disease develops in a severe form. The decision about treatment in a hospital is made by the treating pediatrician. All babies with severe manifestations of the disease or having adverse complications are hospitalized in the hospital.
Antivirals or antibiotics are not prescribed for the treatment of rubella infection.. All therapy is reduced to the observance of non-specific methods of therapy. These include:
- Compliance with bed rest. For the entire period of acute manifestations of the baby is better to stay in bed. With the appearance of a rash, you can allow the child to get out of bed (but not earlier than a week after the appearance of the first skin rashes).
- Obligatory cleaning and disinfecting of all items and toys that are in the baby’s room. Rubella viruses die very easily after exposure to such chemical agents. If there is a bactericidal or quartz lamp at home, it can also be used to disinfect the room.
- Enough drinking. To relieve the intoxication symptoms, the baby must be given more fluid.It can be any drink up to 40 degrees. More hot liquids can damage the oral mucosa and even cause ulcers. Choose compotes from dried fruits and berries, as well as various fruit drinks.
- Therapeutic diet. During a viral infection in a baby, the need for many vitamins and trace elements increases. There is a need for additional energy that may be needed to successfully combat the disease.
- Symptomatic treatment to eliminate the main symptoms. With a cold, apply various drops in the nose. To improve the general condition of the doctors prescribe antihistamines. They will reduce drowsiness and even somewhat reduce skin manifestations. When the temperature rises to 38-39 degrees, antipyretics can be used. All drugs to relieve the main symptoms of the infection should appoint a doctor, after a full examination of the child.
- Enough sleep. For quick recovery during infection, the baby must sleep at least 10 hours a day. During this rest, the body's defenses are restored, additional energy appears to fight infection.
Diet
To quickly recover from rubella and recuperate, you need a special therapeutic food. A diet for a viral infection must include all the necessary substances (in sufficient quantities). Medical nutrition, which is prescribed to children in the acute period of the disease, includes:
- Separation of meals at equal intervals of time. Toddlers should eat every three to four hours. Infants are applied to the chest every 2-2.5 hours. All servings should be approximately the same size.
- Sparing type of food processing. In the acute period it is strictly forbidden to fry foods or bake them to form a coarse crust. All solid food particles can damage the inflamed oral mucosa and increase soreness.
- Semi-fluid consistency. The more products are ground, the better for the baby. More liquid food is quickly absorbed and nourishes the child's body with energy, without a sense of gravity.
- All dishes should be at a comfortable temperature. Too hot or cold food irritates the oropharynx and increases inflammation. Before serving, soups and hot dishes are best cooled to a temperature of 35-40 degrees. For washing down food you can make a warm compote or morsik.
- Mandatory inclusion of protein products. For the excellent work of immunity, the child needs to eat high-quality protein. At each meal try to include foods containing different amino acids. For this, veal, lean bird or fresh fish is perfect. You can complement the dish with a side dish of well-cooked cereals. For babies of the first year of life, vegetable mashed potatoes are perfect.
- The inclusion in the diet of foods rich in vitamins and microelements. To enhance immunity, be sure to add fruits and berries to your child’s diet. In the acute period, it is better to give preference to fruit puree or smoothie. They are easily digested and charge the body with all the necessary trace elements and vitamins.
Possible complications
Rubella proceeds relatively gently, without causing dangerous adverse effects in most children. Even in boys, the risk of developing serious post-infectious complications is much lower (compared to mumps).
Rubella causes the most adverse complications in pregnant women. If the expectant mother did not deliver vaccinations in time, then her baby may still have developmental abnormalities in utero. In the early stages of pregnancy, there is even a threat of miscarriage or fetal death.
The rubella virus has a particularly toxic effect on the organs of the nervous system and the brain. The child may experience anencephaly, hydrocephalus, violations of bookmarks of the organs of vision. In some cases, underdevelopment of the hearing organs occurs.
Congenital heart defects and malfunctions of the heart valves can be quite frequent consequences. In children, intrauterine defects of the heart valves, dislocation of large blood vessels develop.
Rubella virus is very dangerous for the future baby. It literally inhibits the development of vital organs and systems in the fetus. In many cases, pregnant women can not even inform, there are miscarriages. The virus also has a toxic effect on the formation of the immune system in the fetus. Underdevelopment of cells of the future immune protection leads to the birth of children with congenital immunodeficiencies.
From the very first days of their lives, such children are very susceptible to any (even the most innocuous) infections and require the obligatory supervision of doctors.
The most favorable period of pregnancy is the third trimester.. If a pregnant woman becomes infected with a rubella virus at this time, then such pronounced negative effects as in the first six months of pregnancy should not be expected. The laying of the vital organs of the fetus by this time, as a rule, is already completed. When infected at this time, the future baby may experience congenital immunodeficiency or chronic diseases of the nervous system. In rare cases, hearing impairment occurs.
Prevention
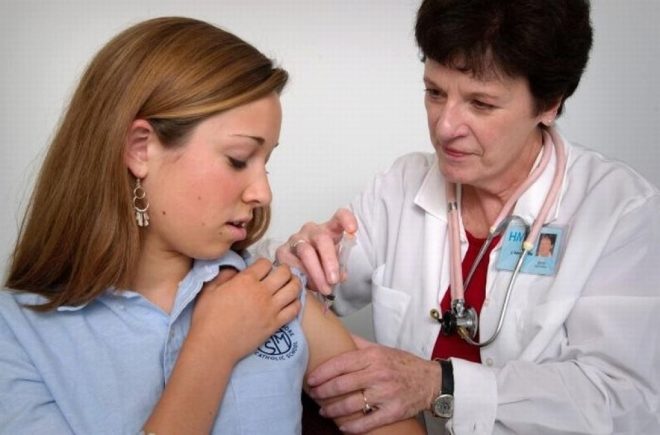
The most appropriate and reliable preventive measure is vaccination. All children (beginning with the year) must be given vaccination against rubella. The first vaccine put in a year and a half. When the child reaches the age of five to seven years, they conduct revaccination.
After vaccination, babies are reliably protected from the adverse course of rubella infection. The course of the disease in vaccinated and unvaccinated children is significantly different. Babies who have all vaccinations affixed can also become infected. However, they are not unfavorable to life complications.
Infected by a vaccinated person can not.
After the second vaccination (revaccination), the children form a very strong and strong immunity to the rubella virus.
All future mothers who are planning a pregnancy, doctors recommend to be sure to put rubella vaccinations. Between vaccination and conception a child must pass at least three months. This time is needed to develop a sufficient level of protective antibodies.
Toddlers receive a comprehensive vaccination against measles and mumps (simultaneously with rubella vaccinations). In all countries of the world, vaccination against these infections is mandatory and is included in national vaccination calendars. Vaccination is desirable before the child goes to kindergarten.
Rubella infection is a very frequent visitor. Infection usually proceeds quite favorably, but the course of the disease must be carefully monitored. Timely diagnosis ensures proper observation of the baby during the whole illness.
See below for details on Dr. Komarovsky’s transfer of a baby rash.
The program "Live Healthy" tells a lot of nuances about rubella.