Calcium for children
All parents know how important calcium is for growing children's bodies. But not everyone knows in what quantities and in what form the substance should be given to the child in order for it to digest and benefit. We will tell about it in this article.
Benefit
Calcium is useful for children in the first place because they are actively growing. For bones, teeth, nervous system, heart, it is very important that this substance is present in the body in sufficient quantities.
But by itself, calcium is of no use, its properties are revealed only when interacting with other substances - vitamin D, magnesium, phosphorus.
Only in the “bundle” with vitamin D can calcium be absorbed by the body, and only with magnesium does it provide protection for the heart and blood vessels. If phosphorus is not enough, then calcium will not be able to strengthen bones and teeth. Calcium is needed for a child not only at the turn. Without it, there will be problems with muscle contraction and blood formation, with the health of the thyroid and pancreas, sex glands. Calcium deficiency adversely affects the general well-being of the child, his ability to learn, the baby's sleep becomes not strong and calm.
But the body needs calcium in certain quantities, because an overdose can harm no less than a shortage. To calculate this amount, you need to know what the daily intake of this substance.
Daily consumption rate
The World Health Organization has calculated and proposed the most optimal age dosages of calcium for children. The calculation took into account the rate of renewal of bone tissue at each age, the body's costs of maintaining the balance of salts and minerals:
- newborns and infants up to six months - 250-300 mg per day;
- children from six months to 1 year - 400 mg per day;
- babies from 1 to 3 years old - 600 mg per day;
- children 4 years and up to 10 years - 800 mg per day;
- children from 10 to 13 years old - 1000 mg per day;
- adolescents from 13 years and older - from 1200 mg per day.
For babies up to six months or even a year, you can not worry, because while they eat mother's milk or adapted milk formula, they will not have a calcium deficiency.
Problems can begin when the child switches to a different diet, and complementary foods will be more than two-thirds of his daily volume of food.
Symptoms and signs of lack
With great accuracy to answer the question of whether the child has a lack of calcium in the body, only a doctor who pre-assigns the baby blood tests — a general and biochemical one — can show how much mineral is contained (in mmoles per liter), and also determine whether there is Are there any deficiencies in calcium, magnesium, phosphorus and vitamin D, which are important for calcium? Usually, the problem of the lack of this substance is greatly exaggerated by the parents themselves, who lead quite healthy and strong babies to doctors complaining of weak teeth or insufficient ones. nN growth.
The real, genuine calcium deficiency is called hypocalcemia.
And this state has quite independent expressed symptoms:
- Increased excitability of nerve structures and muscles. This can be manifested by twitching of the eyelids, trembling of the wings of the nose, the corners of the mouth. In case of a sufficiently strong shortage, seizures may begin.
- Nails and teeth become brittle, easily injured, nail plates become uneven, wavy.
- Growth is slowing.
- The child has a heart rhythm disturbance like tachycardia or bradycardia.
- The baby's sleep becomes restless.
- The child complains of a tingling sensation at the fingertips.
- Quite often, a child with calcium deficiency suffers from vomiting and diarrhea.
For a long time hypocalcemia can hide behind other "guises", and sometimes not at all give symptoms. Severe deficiency causes memory impairment, loss of consciousness, confusion and even hallucinations.
Causes of deficiency
A lack of calcium in a child can be for two reasons: either the mineral is chronically lacking in the food that the baby eats, or the calcium is poorly absorbed and leaves the intestines, and has not fulfilled its main purpose. That is why, first of all, the doctor will take an interest in the child's diet, correct it, advise what products should be given. If it is not nutrition, then the cause will be in a state of the thyroid gland, since with a healthy thyroid vitamin D, which helps calcium to fully digest, everything is usually in order.
Other possible causes of an inadequate calcium concentration can be found in:
- intestinal diseases in which the ability of the mucous membranes of the small intestine to absorb calcium and other substances is impaired;
- diseases of the pancreas, in which salts of minerals are deposited "in reserve" in the field of fat necrosis;
- tumors are quite large;
- an excess of phosphorus, which can "flush out" calcium. This usually occurs when feeding an infant with cow or goat milk instead of an adapted mixture;
- taking certain medications (the "washing out" of calcium is greatly facilitated by diuretics, anticonvulsants drugs and even some antibiotics).
Consequences of shortage
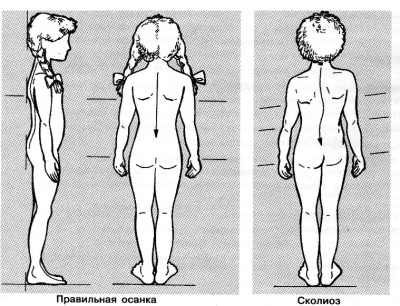
A child who suffers from a lack of this mineral will be slower than his peers to grow. And not only physical growth will suffer, but also mental activity. Another consequence of the lack of babies is rickets. In addition, a child may develop scoliosis of varying degrees, curvature of other bones in the body.
Children deprived of the necessary amount of calcium, are more susceptible to allergic reactions, they are disturbed by blood clotting, the kidneys and the cardiovascular system are affected. But the most severe blow hypocalcemia inflicts on the nervous system of the child. If time does not eliminate the calcium deficiency, then changes in its work may be irreversible. Such consequences include, in particular, multiple sclerosis.
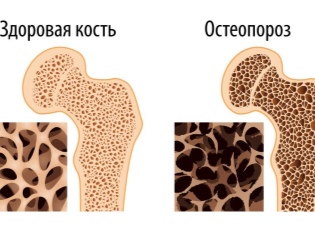
Baby gums begin to bleed heavily, teeth are destroyed and fall out. With a pronounced deficiency, bone softening can occur - osteoporosis, and this is fraught with brittle skeletal fragility and frequent and complex fractures.
Mineral oversupply
Parents, frightened by the prospect of a calcium deficiency in the children's body, often rush to buy drugs that contain this substance as soon as possible and start giving their babies.
This tactic is fundamentally erroneous, because the uncontrolled and unreasonable intake of such drugs may lead to another problem - hypercalcemia, that is, an excess of calcium.
Symptoms of such an oversupply can also go unnoticed for a long time, and only at the "finish" the state is complicated by vomiting and prolonged diarrhea, renal colic, high blood pressure. The child will begin to consume a huge amount of fluid due to a strong constant thirst, urination will become frequent.
Such a condition is dangerous for its complications, among which acute renal failure is the most “harmless” echo of the disease. Hypercalcemia can lead to cardiac arrest, coma.
Medications
Calcium preparations should not be given to the child for prevention, "just in case." They are needed only when the doctor on the basis of laboratory tests made a conclusion about the presence of hypocalcemia (lack of substance).
Quite often, the very fact of deficiency is detected when other diagnoses are established, but in this case also calcium preparations are prescribed. Such illnesses include rickets, thyroid abnormalities, a severe allergic reaction (both acute and chronic), various skin diseases, and bleeding disorders.
All preparations containing the desired mineral are sold without a prescription. In the form of solutions for injection, these drugs are used by doctors of hospitals and ambulance teams to provide emergency assistance in emergency situations - they are injected into a vein during anaphylactic shock, with severe convulsions and bleeding (especially with large blood loss), with an acute allergic reaction, which is life threatening.
For the correction of calcium deficiency in a child with diseases that do not require urgent hospitalization, usually tableted drugs are used. There are a great many of them today. Let's try to talk about the most popular.
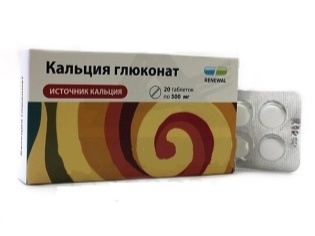
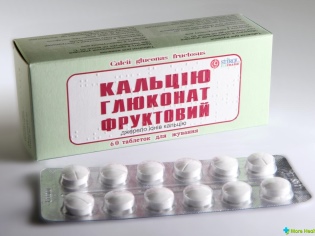
- Calcium gluconate. Tablets of this drug can be bought in two versions - hard and chewable, but the dosage they have today is one - 500 mg. The tool effectively restores the deficiency of ionized calcium and is the most prescribed for pediatric patients. Children do not need ampoules with calcium gluconate, although they can also be seen in the pharmacy, since their use is allowed only in adults and only in urgent cases.
Children are advised to give the drug before a meal or one and a half hours after it; pre-crushed tablets should be taken with plenty of liquid. It is important to observe the age dose, as well as adhere to the WHO recommendations on the daily calcium intake of children. Analogs - “Calcium gluconate - Lect”, “Calcium gluconate stabilized”.
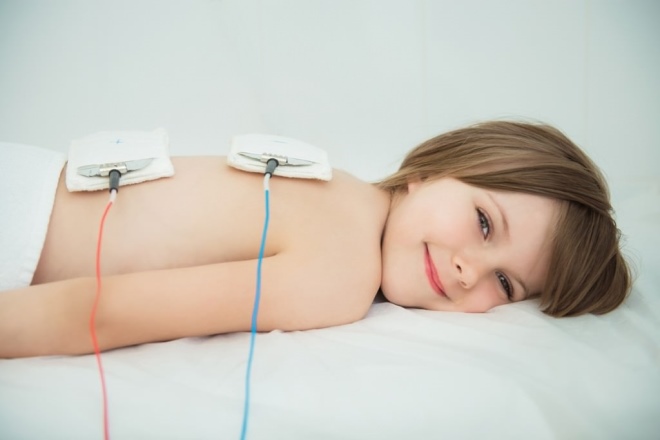
- Calcium chloride. In general, this drug is more familiar to adults under the popular name “chloride”. And do it intravenously for a variety of diseases. For children, the drug exists in the form of a solution for drinking, the concentration of a macro element is 5%.
By itself, the drug is not suitable for all children, because it causes irritation of the stomach in particular sensitive patients.
But quite often, doctors prescribe this tool to babies for electrophoresis procedures. In this case, liquid chlorinated calcium has a safer effect.
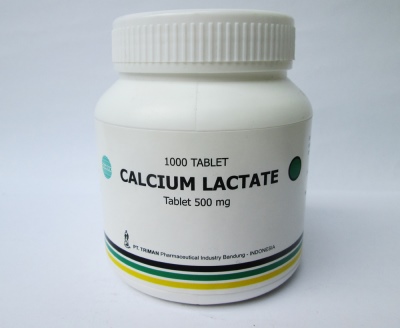
- Calcium lactate. This is a preparation of calcium, which is available only in pills. It is much better tolerated by children than calcium chloride, and therefore it is the preferred treatment for eliminating calcium deficiency. From side effects possible small heartburn.
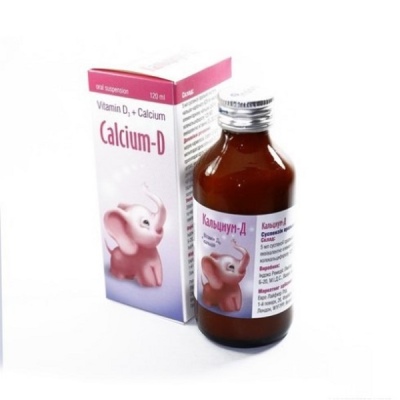
- Calcium D. This combination drug is used to treat children of all ages, including infants. Syrup, containing in addition to the main substance, vitamin D, can be given to children from 1 month. It is convenient to take syrup, it is not necessary to calculate the dosage of calcium separately, since the instruction prescribes not more than 2.5 ml once a day for children over 6 years old and 7.5 ml (for three doses) per day for children from 6 months to 6 years. Children under one year are given the same dose, also three times a day, but diluted with breast milk or water.
- Complite "Calcium D3" (for kids). It is a powder from which it is quite easy to prepare a pleasant taste and smell suspension at home. The advantage is that it is not necessary for the infant to crush and crush the tablets, mix them with milk or water, simultaneously calculating the dose of calcium in the resulting mixture. Parents will simply add water to the vial of powder and measuring spoon to measure the required amount of suspension for a single dose.
- Tiens. Powder, which consists of calf bones, eggshell, milk powder and some vitamin supplements. Their powder is not a drink, but an additive for food. The diluted drug can be added to the baby porridge, in the cottage cheese or in the milkshake. Officially, "Tiens" is not considered a drug, it has the status of a dietary supplement.
- Calcium glycerophosphate. It is a drug in pills that effectively compensates for the deficiency of both calcium and phosphorus. In order for both substances to reach their destination, it is not recommended to give the child to drink his milk. In pharmacies, the product is sold in tablets and granules. Together with the drug in order to achieve greater success in treatment, it is recommended to give the child separate vitamin D and vitamin C.
- Calcium Gopantenate. This is a drug that contains calcium along with magnesium. This combination makes it a tool that has a beneficial effect on blood circulation and blood supply, including the brain. That is why the medicine has the status of a nootropic drug, and is prescribed to children not only with calcium deficiency, but also with associated depression, sleep disturbances, and neurosis and hyperactivity. It is usually prescribed by child neurologists. Feedback from parents about the drug is generally positive, but some emphasize that in children who are predisposed to allergies, it sometimes causes an undesirable skin reaction.
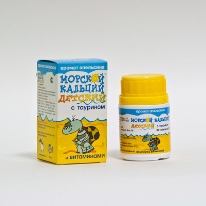
- Sea children calcium. This is a dietary supplement that is available in various forms - with iron, with magnesium, with taurine. It is not recommended as a complete therapeutic agent in cases where the child needs exactly dosages of calcium. It is good to add to the food of the child as an additional source of nutrients, vitamins, trace elements and minerals.
- Finnish calcium Weleda Aufbaukalkki. This is quite an expensive vitamin complex from Finland. It differs from all existing calcium preparations and vitamin preparations with its additives in that it offers a differentiated intake of the mineral. One tablet with certain excipients in addition to calcium is taken in the morning, and the other is different in composition - in the evening.
Features of calcium-containing drugs
The features of all drugs that have this mineral in their composition are that they must be taken in conjunction with meals. Some drugs - strictly before meals, others - only after.
This nuance plays a large role for more efficient absorption of the substance in the body. It is better to drink with plain water, not milk, preparations that contain auxiliary vitamins (D3, for example), as well as combined drugs with magnesium or phosphorus.
In order to prevent overdose, it is important for long-term use it is necessary to take a bio-chemical blood test several times to determine the calcium concentration. How to properly dilute tablets and suspensions is written in the instructions for use for each specific drug. Violate these regulations are not worth it.
List of foods rich in calcium
It is a mistake to think that only milk is rich in calcium, and it is wrong to give them a baby who for some reason does not tolerate dairy products at all.
Cow's milk, like goat's, by the way, is a rather insidious product. If they are given to infants, the risk of calcium deficiency increases, contrary to all expectations. After all, the amount of phosphorus, which is contained in whole milk, is able to “wash” even a sufficient amount of calcium from the intestine in its original form. It is for this reason that earlier, when there were no milk formulas, and the artificialists were fed cow's milk, such a large number of children with rickets were observed.
Today there is no urgent need for cow or goat milk, besides, it is possible to draw calcium reserves in other products that contain this mineral in large quantities.
In the child's diet must be:
- sea fish (especially sardines) and seafood;
- sea kale;
- dog rose;
- cabbage;
- potatoes;
- dried apricots and figs;
- spinach;
- garlic;
- beans;
- sesame;
- Greens - mint, thyme, dill, parsley.
Calcium-rich foods can be cooked on your own. Cottage cheese with calcium chloride is very popular. His recipe is pretty simple. It will require milk and the usual pharmaceutical preparation “Calcium chloride” in ampoules (at a concentration of 10%). Half a liter of milk take no more than a spoonful of solution. Milk is heated, poured into him the pharmaceutical preparation. After the contents of the saucepan is “coagulated,” a thick portion is thrown back onto the sieve, and the whey is drained.
Doctors often recommend such curd to give to children after fractures, as it allows the skeletal system to recover more quickly. Children who have difficulty tolerating ordinary cottage cheese will be able to digest calcined more easily, since less digestive enzymes are required to digest it.
The doctor will tell you how much calcium you need to consume daily. Komarovsky in the next video.