Why measure D-Dimer after IVF and what to do in case of deviations?
Monitoring the status of women is carried out at each stage of in vitro fertilization. Doctors monitor the laboratory parameters of women and in preparation for the puncture of the follicles, and after it.
In the post-embryo transfer period, certain tests are also assigned that will help the doctor to better understand what is happening in the patient's body. One of these tests is a blood test for D-dimer. Why is it recommended to do after the IVF protocol and how to act if deviations from the norm are detected, we will look at this material in detail.
What it is?
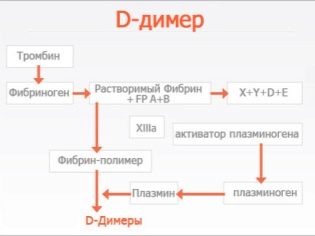
The success of the protocol depends on a lot of factors, including how well the patient’s circulatory system works. A blood test for D-dimer allows you to understand what are the features of hemostasis processes. This complex term is understood as more understandable - blood clotting. The ability of blood to coagulate quickly if necessary and stop blood loss due to the presence of platelets.
After the formation of a blood clot, it is important for the body to prevent the clogging of blood vessels with this thrombus, and therefore the natural stage of fibrinolysis starts, during which specific substances dissolve the clot and clean the vessel. An important parameter of this process and says such an indicator as D-dimer.
By itself, D-dimer is a protein fragment that remains after the process of fibrin breakdown during fibrinolysis.
The analysis is not assigned to everyone, but only to women who have preconditions for problems with hemostasis or those who have such problems were identified even at the stage of preparation for the IVF protocol. The results of laboratory studies allow us to conclude how thick or, conversely, the blood is liquid. Both are undesirable for successful completion of the IVF protocol.
It should be understood that the direction to such an analysis will be received only by the woman who has confirmed the pregnancy by laboratory and with the help of an ultrasound. Up to this point, a blood test for D-dimer is not considered informative, although it is quite often prescribed before and after embryo-transfer for about five days.
The most active will be to monitor the concentration of the substance in women who have previously experienced unsuccessful IVF attempts, have a history of strokes in women aged 35+, as well as in women prone to high blood pressure.
For women who previously suffered from miscarriage or had experience of preterm birth after IVF, such an analysis is considered mandatory and highly necessary.
Rates and deviations
The onset of pregnancy after IVF is in itself a good reason for changing the qualitative and quantitative indicators of blood. The interpretation of the results of the analysis is fairly free, because there is no uniform density norm for D-dimer in the blood.
By default, a concentration of 500 ng / ml is considered normal. Everything below this value is the norm, all that is higher is a deviation from it.
In women who managed to become pregnant through IVF, D-dimer is always somewhat elevated. The longer the gestation period, the more this indicator is increased.
In the first trimester, it increases about one and a half times relative to the base rate, in the second - two times, and in the third, the figure is increased three times. After IVF, the level of D-dimer may be somewhat higher than after conception in a natural way.This is due to the peculiarities of the treatment cycle: the woman was stimulated with hormones, the procedures were traumatic for her body, for example, the follicles were punctured to receive eggs.
Normal D-dimer after IVF protocol.
Obstetric term | The value of D-dimer, ng / ml |
4-13 week | 280 and less |
3-21 weeks | 700 or less |
21-29 week | 850 and less |
29-35 week | 1000 and less |
35-40 week | 1550 and less |
If a multiple pregnancy occurs after transplantation, the density of this indicator may be even higher.
Causes of deviations and action plan
With a high D-dimer, women in the IVF protocol and after it are encountered quite often. Therefore, it is required to pass this analysis in order to be able to correct the condition of the woman in time and eliminate the threats of gestation and the upcoming delivery.
The natural reasons for the increase are processes that begin in the pregnant woman's body almost immediately after implantation of the implanted embryos. Figures indicating increased concentration indicate that the body has already developed a large-scale preparation for the future process of childbirth. Since it is always closely associated with blood loss, the body begins to “reserve” resources for the future, increasing the viscosity of the blood itself.
Pathological causes may be thrombosis, DIC syndrome, liver disease, early toxicosis, as well as the threat of miscarriage associated with placental abruption. Certain pathologies of the cardiovascular system in women, as well as age, may well serve as a valid explanation of the increase in the amount of D-dimer.
The reduced D-dimer is an alarming situation only when it is combined with an increase in blood clotting time. In this case, they talk about "liquid" blood, it is fraught with bleeding and loss of pregnancy. It is required to consult a hematologist.
The action plan for detecting abnormalities is quite simple: first, you will need to undergo additional examinations, visit if necessary, a cardiologist, a hematologist, a therapist. If a coagulogram (a comprehensive study of hemostasis) does not reveal coarse pathologies, doctors choose the waiting and control tactics of D-dimer over time, the woman will simply have to do this analysis more often.
Depending on the degree of deviation, hemostatic preparations can be used. They are prescribed only by a doctor and only as a last resort. Usually, a pregnant woman after IVF is advised to go to the hospital or visit a day hospital, where she will be given drugs under the supervision of a doctor.
All women who have successfully overcome IVF treatment, but are faced with the problem of liquid or thick blood after it, are required to strictly follow the recommendations of the doctor and more often go to the consultation.
The correct drinking regimen helps to normalize the parameters of hemostasis: the expectant mother should drink 1-1.5 liters of water per day. Useful walks in the fresh air, in the park and square, located away from the roads. A reduction in salt in the diet also allows blood clotting parameters to be brought close to the “pregnant” rate.
For women, vitamins are recommended. This may be multivitamin complexes, and individual vitamin preparations of group B, C, and vitamin K. The dose of folic acid can be doubled, which the expectant mother was recommended to take at the preparatory stage for entry into the protocol. Insufficient folic acid content often causes an increase in D-dimer.
The strictest ban is imposed on substantial exercise. In no case can not sleep in fragments: a full eight-hour sleep at night allows for a fairly short time to normalize hemostasis.
Stress, quarrels and depression should also be completely excluded from the life of a pregnant woman who has gone such a long way to achieve her goal.A woman is recommended to eat a balanced and correct diet, not to miss the planned visits to the doctor, to take all the necessary tests for gestation, and after IVF they are always a little more than during pregnancy, which occurred naturally.
See what the high D-Dimer is about in the next video.