All about late ovulation
When planning a pregnancy, women are usually more anxious about their state of health and signs of impending ovulation, since it is this period that allows a woman to become pregnant. And sometimes in the middle of the cycle, when an important day is expected, there are no signs of ovulation - and the basal temperature remains unchanged, and tests for ovulation persistently give out a single bar instead of the expected two.
Many at this stage believe that they have an anovulatory cycle, and they are trying to determine the time favorable for conception. And in vain. The most persistent and persistent women know that sometimes just before menstruation, the ovulation test suddenly becomes positive, and the egg output itself is late.
What it is?
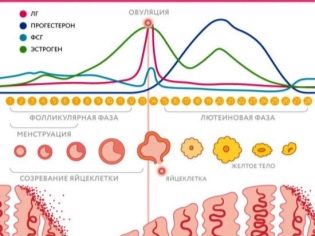
It is generally believed that female ovulation occurs exactly in the middle of the cycle, dividing it into two half-phases. The calendar method of its determination suggests to subtract from the cycle duration 14, to determine which day to expect the release of a mature egg from the follicle. If the cycle lasts 28 days, then ovulation is expected on the 14th day from the day of the beginning of the last menstruation, with a cycle of 30 days - on the 16th day, with a cycle of 26 days - on the 12th day of the cycle, and so on. But it would be simple if the calendar method was 100% accurate.
Ovulation is a complex process that can change under the influence of many factors, both external and internal. The follicle grows after the end of the next menstruation under the influence of hormones, and the hormonal background is known to be very sensitive to various factors.
The second phase of the female cycle after ovulation usually lasts more or less a certain time. It is usually considered to be two weeks (14 days plus or minus a day). This duration is due to the longevity of the corpus luteum, which is formed as a temporary source of progesterone in place of the bursting follicle from which the egg came out.
In the understanding of physicians, late ovulation is the late exit of the oocyte from the follicle, when a significant moment for those planning pregnancy is later than in the middle of the menstrual cycle. It is difficult to say how late the release of the egg is. Much here is related to the duration of the cycle of a particular woman.. When it lasts from 30 to 34 days, then it is considered late ovulation, which occurred after the 25th day of the cycle. If the lady’s cycle itself lasts for more than 35 days, the release of the egg in it always happens with a delay, which requires medical examination and treatment, since such a female cycle cannot be initially considered as normal and healthy.
With the standard cycle (the most common) in 28-29 days, late ovulation should be discussed when it is actually exercised after 16 days from the beginning of the first day of the last menstruation. Occasionally it also happens that the release of a mature oocyte occurs only on the 20th day of the cycle, that is, shortly before the menstruation. This phenomenon can be monitored by compiling a regular schedule of basal temperature, as well as conducting home testing with pharmacy ovulation tests.
The role of hormones
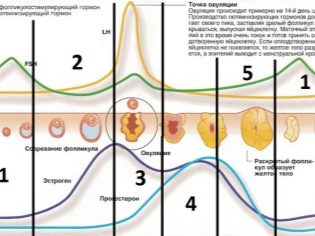
Late ovulation often requires the appointment of certain hormonal agents to a woman, since she is always associated with a violation of the hormonal support of the ovulatory process. To understand why ovulation is late, you need to clearly understand what processes lead to it. The mechanisms of hormonal regulation of oocyte maturation and release are five-step. They include the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, the limbic system and the amygdala.
The “commander in chief” of the ovulatory process is the hypothalamus. It produces liberins that stimulate the production of hormones necessary for the female cycle. Folliberin, for example, as a middle-level commander, triggers the production of FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone, in the body of a woman, and lyuliberin is responsible for the production of luteinizing hormone. FSH allows follicles to grow, grow, and LH provokes a rupture of the mature dominant follicle on the day of ovulation. Also, the hypothalamus produces a group of statin hormones, whose task is to slow down the production of other hormones that are not needed for ovulation.
The pituitary gland, obeying the command of the hypothalamus, produces FSH. Under its action, estrogen is increasing in the first half of the female cycle. At the right time, the pituitary gland switches to the synthesis of luteinizing hormone.
The gonads, the ovaries, produce progesterone in the second phase of the cycle and estrogen in the first. The duration of the female cycle, by the way, depends on the balance of these hormones.
All organs that have a natural sensitivity to hormones in general react to changes in the hormonal accompaniment on different days of the cycle. This chest and fatty tissue in the body, and bone tissue and even hair follicles. And, of course, there is a reaction from the side of the uterus - its task is to build up the endometrium. If conception takes place, then a sufficient layer of the endometrium will ensure successful implantation of the embryo; if it does not take place, then the enlarged cells will be rejected and brought out during the next menstruation.
After the completion of the menstrual period, the pituitary gland begins to produce FSH and in a low concentration luteinizing hormone. If progesterone levels are elevated at this stage, then ovulation may not occur at all. As you approach the middle of the cycle, the concentration of estrogen increases, which provokes a sharp release of LH - this is called a luteinizing peak. Usually after it, within 24 hours, the follicle bursts and releases an egg cell, ready for fertilization. And here the follicle is in a very dependent position - any imbalance of LH, androgen can lead to the fact that ovulation does not occur at the right time.
The concentration of progesterone in the female body begins to increase after ovulation. His task is to prepare the body for pregnancy. If it has not come, then progesterone level decreases 5-6 days before menstruation, estrogen levels rise and premenstrual changes begin, the body adjusts for menstruation.
It is possible to determine the ratio of hormones in a woman’s blood on any day of the cycle with the help of a laboratory study of venous blood, which allows the doctor to determine in which of the endocrine stages there is a “failure”. Correction is made by hormonal drugs that allow you to raise or lower the level of certain hormones so that ovulation is timely.
The reasons
The five-step hormonal process can be disrupted by any external and internal factors.
The most common causes of late ovulation are the following situations:
- the woman is in a state of chronic stress, nervous, suffered a heavy loss, shock;
- there was a change of climatic or time zones;
- preceded by an abortion;
- a woman was protected by oral contraceptives before planning, canceling OK causes a hormonal “disorder” in the body;
- the installation period of the menstrual cycle after childbirth - up to a year;
- breastfeeding with a restored cycle;
- transferred infectious diseases - influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, as well as colds and other diseases that occurred with an increase in body temperature;
- premenopausal period;
- gynecological diseases occurring with elevated levels of estrogen in the blood - endometriosis, endometrial hyperplasia of the layer, cancer of the breast;
- diseases that occur with an increase in the level of male sex hormones in a woman’s blood are polycystic ovaries, impaired functioning of the adrenal cortex.
If the woman as a whole has a normal duration cycle (28 days), but ovulation is late, this may be a sign of a latent inflammatory process in the uterus, fallopian tubes, in the ovaries, and can also be practically the only manifestation of infections such as chlamydia, ureaplasma.
Late ovulation can occur in women with any disease of the pituitary, hypothalamus, ovaries. Often, the delayed release of the oocyte is a consequence of obesity, since adipose tissue is also capable of producing hormones, and therefore the balance necessary for the correct cycle is disturbed.
Features and indications
Late ovulation has almost the same signs as the timely exit of the oocyte from the follicle.
- The amount of cervical secretion increases. Vaginal discharge becomes more abundant, resembling viscous raw chicken egg white. With late ovulation, the appearance of small bloody veins in the cervical secretions is not excluded, and the discharge may also become yellowish.
- Basal temperature drops sharply, and then rises sharply - The day of this decline is the day of ovulation.
- There are pulling sensations in the lower abdomen - not a mandatory feature, not peculiar to all.
- Breast becomes more sensitive, the nipples react more quickly to touch.
- Emotional state changessexual desire is increasing.
Pharmacy ovulation test systems show ovulation, even late, with fairly high accuracy, and it is also possible to do an ultrasound of the ovaries and donate blood for LH and FSH.
Conception and features of pregnancy
Can I get pregnant with late ovulation? Yes, this is possible, but only when the very fact of the late exit of the oocyte is not associated with polycystic ovaries or other diseases that in themselves can cause infertility. Also, a woman should be aware that with late ovulation her chances of conception are reduced. With timely - the probability of conceiving is in the range of 11-30% (should take into account the age and state of health). When late - about 7-15%. But the likelihood of pregnancy is still there.
If the monthly did not begin in the expected time, it is possible that you are pregnant. But a pregnancy test on the first day of delay, as recommended by the manufacturer, oriented to normal ovulation periods, should not be performed. After ovulation and fertilization, the embryo needs about 7-8 days to complete the implantation of the ovum into the endometrial layer of the uterus.
If the ovulation itself was late, then the implantation will be late.
Pregnancy tests respond to the hormone hCG, which is produced by chorionic villi after implantation. The level of human chorionic gonadotropin increases every two days. Therefore tests with high sensitivity will show a positive result on the 7-8 day of menstruation delay. Prior to this, tests may be negative due to the small amount of hCG in the urine, which the test systems do not catch.
Features of the course of pregnancy, which occurred in the cycle with late ovulation, lies in the fact that doctors will occasionally “frighten” the future mother with the possible lag of the child from the developmental norms.All obstetric formulas will imply a standard cycle, with standard ovulation, and in fact your baby will be younger in terms of gestation for a week, or even more.
There may also be questions when determining the expected date of delivery - doctors will consider that it should occur earlier. But the time of the onset of ovulation does not affect the sex of the child, this question does not depend on the egg cell at all. You will have a boy or a girl, depending on whether the spermatozoon with which genetic set the fertilized oocyte is XX (girl) or XY (boy).
Well, if you know for sure that ovulation was late, then misunderstandings during pregnancy are not terrible for you, you can always explain to the doctor that the output of the oocyte was late. That is why those who plan pregnancy and are advised to control their basal temperature, as well as conduct pharmacy tests or use symptothermal fertility recognition methods.
If conception occurred in a cycle with late ovulation, a woman may be threatened with spontaneous abortion due to a reduction in the second phase of the cycle and insufficient readiness of the endometrium for implantation. Often, on this occasion, women are advised to take progesterone drugs to maintain pregnancy during the first trimester.
The gestational period, which became possible in the oocyte late cycle, is determined by the standard, obstetric formulas, from the first day of the last menstruation, but in the exchange card the doctor may indicate that late ovulation has occurred, which will imply correction of the timing with an eye to that . The requirements of a woman to count pregnancy from the day of her ovulation, even if she knows exactly her date, can not be a reason for revising the term.
Do I need to undergo treatment?
If late ovulation has happened once or twice - this is not a reason for treatment. It is necessary to analyze whether factors of influence have taken place - flights, travel, stress, cold, weight fluctuations and the like. But when repeating late ovulation for three cycles in a row or more, consultation with a doctor is necessaryand only the specialist knows the exact answer, whether therapy is necessary in each specific situation.
In most cases, according to reviews, if the phenomenon is not associated with diseases, it is enough to establish a normal night's sleep, eat properly and balancedly, it is enough to move, have a regular sex life and give up bad habits. Late ovulation is dangerous only when a woman does not control her, does not know the features of her cycle. She may experience miscarriages, lack of implantation, even with a complete conception.
You can learn more about the women's cycle in the video below.