What is azoospermia and how to treat it?
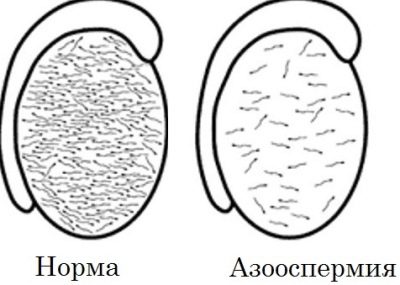
Azoospermia is a violation in the mechanism of seminal fluid production, in which it does not contain sperm. The presence of this pathology speaks of male infertility - absolute or relative. It depends on the cause of the disease. Suffer this disease can men of any age. What diagnostic methods make it possible to detect this reproductive dysfunction and cure it?
Sperm production disruption mechanism
First you need to know how the sperm production should normally take place. Spermatogenesis is the process of formation and maturation of spermatozoa. It begins in adolescence and may continue until old age. Sperm production is carried out in the convoluted seminiferous tubules of the testes. The mechanism of maturation of male germ cells includes three stages.
- Spermatogonia proliferation - stem cells that are located on the membrane of the tortuous tubules of the testes. About 1 billion spermatogonia are found in the thickness of one testicle. There are three types of spermatogonial cells:
- dark spermatogonia A;
- light spermatogonia A;
- spermatogonia B.
- Meiosis - a complex process of transformation of spermatogonia into cells with a haploid set of chromosomes (spermatids).
- Spermatogenesis - conversion of spermatids into viable spermatozoa.
Classification and etiology of azoospermia
Modern medicine has information about which diseases can trigger the development of such a violation. There is a classification of azoospermia depending on the etiological factors.
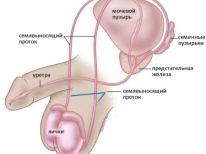
- Obstructive form. Due to the violation of the normal patency of the vas deferens. Because of this, the mature sperm, leaving the testicles, do not fall into the ejaculate. Therefore, the sperm cannot fertilize the female reproductive cell and pregnancy does not occur. An obstruction may occur in the epididymis, seminal vesicles or vas deferens.
- Non-obstructive or secretory form. Indicates the absence of sperm cells due to irregularities in the mechanism of their production or at the stage of maturation in the testicles.
- Transient or temporary form. Characterized by the absence of sperm in the ejaculate for certain time intervals, between which there is a probability of fertilization of a woman by natural means.
- Mixed form. It is a combination of impaired patency with a decrease in the functional activity of the testes.
There are special reasons for the formation of each of these forms of azoospermia. The occurrence of obstructive azoospermia can be triggered by a number of the following factors.
- Early injuries or various surgical interventions. For example, after undergoing vaseectomy, a procedure involving dressing or partial excision of the vas deferens.
- The reasons for the formation of obstructive azoospermia are considered complications of surgical manipulation of the scrotum, prostatectomy (removal of the prostate gland), removal of inguinal-scrotal hernia, extraction of the cyst of the seminiferous tubules, surgery in the posterior urethra.
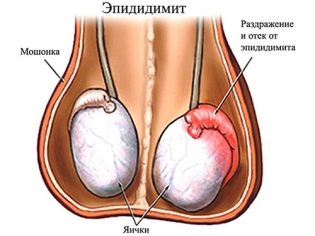
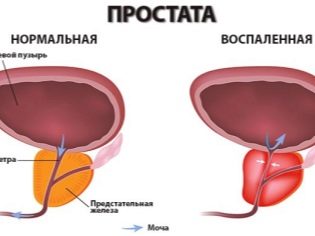
- The development of inflammatory processes of the epididymis (epididymitis).
- Congestive or infectious vesiculitis (inflammation of the seminal vesicles).
- Congenital anatomical anomaly, due to the complete absence of the vas deferens.
- Young's syndrome is a condition characterized by a symptocomplex (sinusitis, bronchitis and obstructive azoospermia).
- Congenital cysts of myeller ducts of the prostate.
- Violation of patency of the seminal ducts of the testes.
Non-obstructive azoospermia is formed as a result of a number of factors.
- A genetic abnormality characterized by the absence of the AZF-locus of the Y chromosome, which carries information about the mechanism of seminal fluid production.
- Disorders of hormonal balance associated with failure in the process of production of sex hormones.
- Pituitary neoplasm and blood cancer.
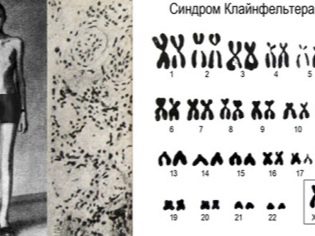
- Klinefelter syndrome is a type of chromosomal pathology, the main feature of which is the presence of one or several "extra" X chromosomes in the XY-karyotype. One tenth of men suffering from azoospermia, have this disease.
- Prader-Willi syndrome is a chromosomal mutation caused by damage to the genes that are on the 15th chromosome.
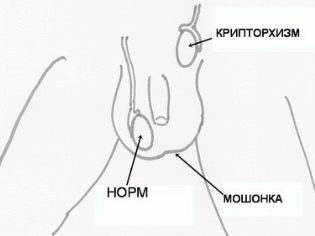
- Cryptorchidism is a congenital defect that is characterized by the absence of one or both testicles in the scrotum at birth. This anomaly is caused by a delay in their progress along the inguinal canal. This disease is manifested by an asymmetric scrotum, lack of testicle in it, pain sensations in the lower abdomen.
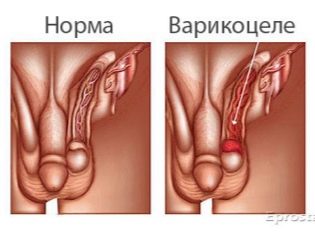
- Varicocele - varicose veins of the spermatic cord, due to which testicular trophic is broken, which leads to its dystrophy.
- The consequences of some past infectious diseases, for example, mumps.
- Radiation therapy or chemotherapy.
- Uncontrolled intake of steroid hormonal drugs.
- Consequences of mechanical injury and testicular torsion.
- The development of oncological process in the thickness of the testicle.
Temporary azoospermia is the absence of spermatozoa in seminal fluid for certain time intervals between which conception is possible.
Temporary azoospermia may be associated with the following processes:
- severe clinical course of some infectious diseases;
- excessive physical or psycho-emotional stress, as well as prolonged stressful states and professional sports;
- prostatitis (inflammation of the prostate gland);
- orchiepididymitis (inflammation of the appendages and testicles);
- unbalanced diet with a low content of vitamins and trace elements necessary for the male body;
- taking chemotherapeutic drugs, antibiotic therapy, hormonal treatment;
- sexual excesses, as a result of which sperm cells do not have time to be produced and reach sufficient maturity;
- endocrine imbalance;
- hypodynamia (limited mobility);
- systematic use of alcohol, drugs, smoking.
There is a so-called idiopathic azoospermia. In this case, the cause of the disease cannot be reliably established. There may also be a combination of several risk factors, such as obesity and age.
Symptoms of azoospermia
The main characteristic symptom of azoospermia is male infertility. In this case, the sexual function of a man may not suffer. Other clinical manifestations of this pathology indicate the presence of the underlying disease.
Diagnosis of the disease
An objective examination by a urologist is impossible to diagnose azoospermia. To identify this disease is necessary to conduct a series of studies.
- General clinical and biochemical blood tests. These are quite informative studies indicating the development of the inflammatory process, endocrine disorders in the body of a man.
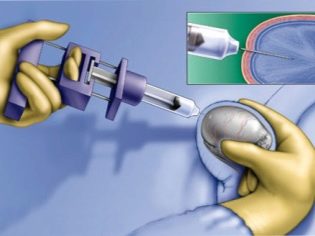
- Testicular biopsy. Conducted to study the functional activity of these organs, as well as to accurately determine the type of infertility. The essence of the procedure consists in taking the biomaterial (in this case, particles of the working tissue of the testicles) and its further detailed laboratory research.
- Genetic analysis on the presence of damaged chromosomes that affect the formation of the reproductive system.
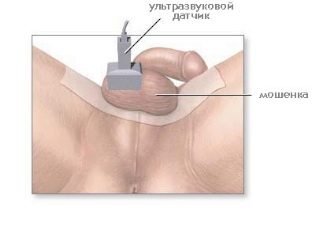
- Duplex scanning of the testicles and penis, representing the study of the venous system.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Using this diagnostic method, you can determine the causes of the disease, which are not related to the male sexual apparatus.
- Ultrasound examination of the scrotum (ultrasound). It is used to exclude the presence of a malignant neoplasm in the thickness of the testes and other structural changes.
- Spermogram Through this study, sperm fertility can be determined (the ability of sperm to fertilize the female reproductive cell).
- Urine analysis after ejaculation. The cause of infertility may be the wrong mechanism for the withdrawal of seminal fluid, for example, in the bladder.
Using this analysis, you can exclude or confirm the existence of such a violation.
All of these diagnostic methods are able to give the most complete information about the causes of azoospermia.
Treatment
Drug therapy of azoospermia is carried out with the correction of both the secretory form and obstructive. In addition, the patient may be prescribed drugs that reduce the intensity of the inflammatory process and restore the endocrine balance.
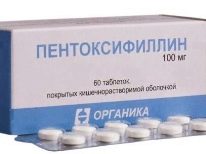
Stimulation of seminal fluid production can be done by taking the following drugs: Pentoxifylline, Tribestan, Menogon, Spemann, Proffertil, and other similar drugs containing "l-carnitine."
Among the main positive properties of these drugs are the following therapeutic effects:
- normalization of the spermatogenesis mechanism;
- creation of optimal conditions for the maturation of germ cells without disturbance;
- improving semen quality indicators;
- stimulation of sufficient blood supply to the genitals.
In the presence of endocrine disorders, a man may be prescribed the following medications: Humegon, Klostilbegit, Pregnil, Andriol.
There are several types of hormonal therapy for azoospermia:
- substitution (in this case, the introduction of hormonal drugs is carried out to neutralize the deficit of certain male sex hormones and normalize the endocrine balance in general);
- overwhelming (aimed at suppressing the production of certain hormones that prevent the implementation of normal spermatogenesis);
- stimulating (stimulation of the production of male sex hormones, which have a positive effect on the production of seminal fluid).
Stimulating hormone therapy is most commonly used for azoospermia. This treatment also helps to strengthen the immune system. Cryptorchidism is amenable to correction through orchippexy, an operation in which the surgeon artificially “lowers” the testicle into the scrotum.
Removal of the inguinal hernia is carried out by open or laparoscopic method. The difference between these techniques lies in the method of introducing surgical instruments.
If the cause of azoospermia is obstruction of the vas deferens, then surgical correction of the defect can be applied to such a patient. Such operations are carried out using microsurgical techniques.
With varicocele, a man shows a special Ivanisevich operation, the essence of which is the dressing of the testicular vein.
If the permeability of the sperm-tracts is not possible to be restored by the methods listed above, then a direct microsurgical aspiration of the sperm from the testicle, followed by IVF, is indicated for such a patient.This technique allows women to become pregnant, whose sexual partner suffers from even the most complex forms of azoospermia.
Use of folk remedies
If a man was diagnosed with azoospermia in the initial stages of formation, then in addition to the main treatment, you can try several means of traditional medicine. Numerous reviews indicate a fairly high therapeutic effect of non-traditional means. These methods are used in the secretory form of the disease.
- One teaspoon of seeds of wormwood pour 200 ml of boiling water. Drink the infusion is recommended during the day.
- One tablespoon of plantain seeds is poured 200 ml of boiling water and infused for half an hour. Take the resulting infusion is recommended for 2 tbsp. spoons 4 times a day. The course of treatment is 3 months.
- One tablespoon of hawthorn fruit is crushed and poured a glass of boiling water. Drink cooled infusion should be 50 g 3 times a day.
It is believed that the popular alternative method of treatment of various diseases - hirudotherapy (treatment with leeches) in the correction of pathologies leading to the formation of azoospermia, does not have sufficient effectiveness.
Important Tips
The question of whether azoospermia is treatable concerns every man to whom this diagnosis has been made. The success of the therapy depends on how timely the request for medical care was. Treatment should be carried out immediately after identifying the causes of the development of pathology. If therapy is started on time, a man will have much more chances to experience the joy of fatherhood.
If azoospermia is not treated at all, the risk of complications increases several times. You should not hope that this disease can go away on its own. Late therapy reduces the likelihood of complete recovery.
All about azoospermia and chances of pregnancy, see the following video.