Why does a child often scratch their ears?
If the baby frantically scratches and pulls his ears, it can not go unnoticed by the parents. And if this happens rarely, then there is no particular reason for anxiety, but if a baby does it all the time, and, worse, combing auricles into the blood, the problem is obvious. Only the reasons for such strange behavior remain hidden. In them we also will try to understand within the framework of this article.
When does this happen?
The infant cannot tell his parents what exactly is bothering him, but he is trying in every way to draw attention to his well-being. And the reason may not be in the ears at all. The kids are rather inquisitive and they like to get to know their own body. A child can pull their ears just out of curiosity, feel and explore them.
But not always everything is so harmless way. Most often, a child scratches his ears because he has uncomfortable or moderate pain in the hearing organs or somewhere nearby, because it is still difficult for a child to understand exactly where to scratch if it itches. Acute pain does not usually cause the desire to scratch a sore spot, and touches give a very unpleasant feeling. But prolonged sluggish irritation may well be the reason for this behavior. Let's look at the possible pathological and physiological causes that may be present.
Possible reasons
The desire to comb the ears occurs in a child for the following reasons:
- Violation of hygiene. If a child is rarely bathed, the reason why he tugs at the ears may be due to the banal pollution of the ears and skin folds behind them. Also, unpleasant sensations can cause excess accumulated earwax. Parents can deal with this problem on their own, without asking for help from a pediatrician.
- Parasitic disease. The cause of an itchy sensation in the ears can be parasites - lice, fleas, as well as skin and ear mites. In medicine, this is called parasitic otitis. It can be external when only the outer ear is affected, and maybe even the middle ear, when the middle part of the organ of hearing is involved in the process. A parasitic lesion can be recognized by a reddened and slightly swollen ear. As the number of parasites grows, the skin on the ears becomes drier, begins to peel off, small pustules may appear.
With similar symptoms, you should immediately contact the pediatrician, and it is better to an infectious diseases specialist, if there is such a doctor in the clinic.
- Otitis. Itching and itching can only external otitis, it is easy to recognize by the inflammation of the auricle. Quite often appear ulcers and boils. Otitis media does not itch, but hurts. However, the newborn and the infant cannot clearly communicate this, and simply rubs the ear, not understanding where and what is going wrong. Suspected otitis media can be characteristic of the discharge from the ear. They may be clear, yellowish or purulent. If it is easy to press with your fingers on the trestle (a small cartilage, located right at the entrance to the ear canal, the pain increases, and the baby begins to worry and cry.
Contact immediately with a pediatrician or otolaryngologist.
- Otomycosis. Fungal damage to the organs of hearing causes itching and a lot of unpleasant impressions. It is noteworthy that such a pathology develops very long, gradually and almost imperceptibly. At first there is a slight itch, then it increases. Scratching the ear of the baby will be attacks, as itchy sensations. Pain with otomycosis almost never happens.Suspecting such a disease is very difficult. A little edema in the area of the auditory canal can sometimes guard parents, sometimes whitish discharge (not always), as well as a possible decrease in hearing acuity with which the baby will react to a constant feeling of congestion. It is possible to establish an otomycosis only with the help of laboratory diagnostics, microscopic examination, which will detect fungi. It is necessary to be treated by an infectious diseases specialist and an otolaryngologist.
- Psoriasis. Itching and unpleasant burning causes the child and psoriasis, if it develops in the ear. Both the auricle and the middle ear can be affected by seborrheic psoriasis. In this disease, a red rash first appears. With her appearance, the child begins to scratch the ear. Then there is a strong peeling, the skin can become whitish, the scales of the epidermis are separated very easily. With suspicion of such a pathology of the child are taken to see a dermatologist and ENT doctor.
- Allergy. An allergic reaction may well cause itching in the ear. Usually, the skin is almost unchanged, sometimes a slight swelling can occur. It all depends on what type of allergic reaction began to develop. If it has caused allergic otitis, then there will be no discharge from the ear, as in otitis,. But the pressure on the tragus will show that the cause is still inflammation of the middle ear.
If the allergy is manifested by the type of dermatitis, then the symptoms are unlikely to concern only the organs of hearing. Skin rashes will definitely be found in other parts of the body. With suspicion of an allergic reaction should contact a pediatrician, an allergist and ENT.
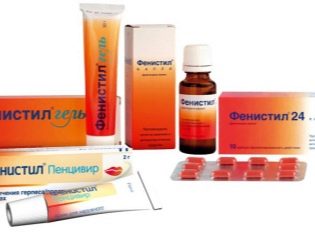
- Insect bites. If a child is bitten by a mosquito or other insect, then the itch in the area of the bite will not be particularly long. True, the child may begin to comb his ear in a dream, because insect bites not only itch by themselves, but also cause local inflammation, and sometimes a slight allergic reaction. Parents can cope with such a problem on their own without going to a doctor. If you managed to find a bite, it smeared "Phenystyle". Even without this, the bite will not disturb the baby for a long time, and within a couple of days the child will no longer scratch the ear.
- Foreign object. If a child gets something foreign in the ear, then it is quite reasonable it will bother him. If the parents were able to see a foreign body, then you can get it with a small forceps and independently. But if the subject is located deeply, in order to avoid injury to the hearing organs, it is better to seek help from an otolaryngologist, who with the help of special tools will be able to remove the subject without pain and the risk of injury.
How to inspect the child?
If the child began to scratch his ears, then it is necessary to conduct the first home inspection. To begin with, the child measures the temperature. Elevated temperature is usually characteristic of otitis, teething, inflammatory process in the organs of hearing.
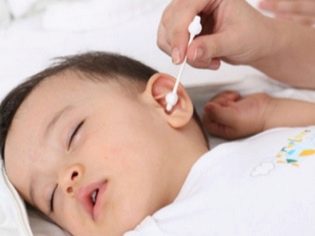
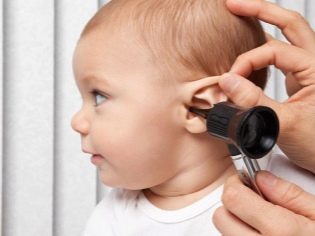
Then you need to explore the ear. For this you should use a small household flashlight. First assess the condition of the auricle - the size, the presence of puffiness, rash, ulcers, peeling. If nothing is detected, The auditory meatus should be examined with a flashlight.
Accumulation of earwax, discharge from the ear, a foreign body in the ear canal, as well as insect bites, in most cases, can be seen by all parents who are not even savvy in medicine. After inspection, a test is performed on otitis media, easily pressing on the tragus. In the absence of response to pressing, it is worth considering other reasons.
Strip the baby and inspect the skin for rashes and possible allergies. If the temperature is normal, the ear is visually healthy, it does not hurt, then you should watch the child, in what situations and how he scratches his ear, perhaps the reasons lie in another.
If no obvious reason found
If no pathology is found, then it is worth considering others. The reasons why a baby theoretically and practically can begin to scratch your ear:
- Syndrome of obsessive movements. If the child already has a year or more, then he may scratch his ears for psychological and neurological reasons. This may be a consequence of severe stress that the baby has experienced. Sometimes we are talking about the so-called syndrome of obsessive movements. In this case, parents may notice that the child does not always begin to scratch their ears, but in strictly defined situations related to anxiety and feelings. So, on the physical level, the peanut tries to sublimate his accumulated nervous tension. Contact should be to the neurologist, child psychologist and child psychiatrist.
- Teeth. An unpleasant and obsessive itching in the gum area can also cause the child to want to scratch his ear. This usually happens when the crumbs are 5-6 months old and older, when the period of teething begins. This version can be confirmed by swollen gums on the side from which the child pulls the ear. In the absence of pathological symptoms from the ears, it is worth considering this version of what is happening.
- Hunger or fatigue. From a medical point of view, it is very difficult to explain why a child scratches his ears when he wants to sleep or eat. But the fact remains that very often small children react in this way to fatigue and hunger. They not only rub their eyes and nose, but also pull at their ears.
If, after the child had fed from the heart, got drunk and put to bed, he stopped scratching his ear, then probably the parents were able to unravel the secret "signals" of the little man.
How to clean the ears of the child and the adult, see the following video.