Is there always a cervical dilatation during contractions and can the process be painless?
Even during pregnancy, a woman is told that contractions that are waiting for her in labor should lead to the opening of the cervix so that the baby, when the time comes, can get out of the uterus into the genital tract and eventually be born. But does the contraction always lead to the opening of the neck? In this article we will try to understand this in detail.
Process and stages
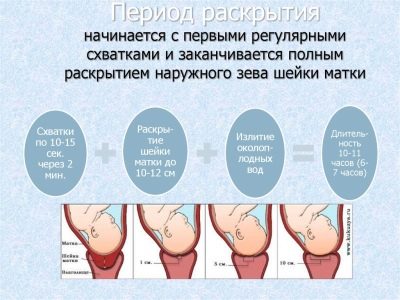
Normally, childbirth begins with the appearance of contractions. There may be other options, for example, the first to drain the water, but they are not considered the norm. The first fights are very rare: they last no more than 20 seconds and repeat approximately once every 30-40 minutes. Then the duration of the spasm increases, and the time between contractions decreases. With each contraction, the walls of this reproductive organ are involved, as well as the annular circular muscle, which is essentially the cervix.
During the first period of labor, which is called latent, the cervix opens up to 3 centimeters (or about 2 fingers, in the language of obstetricians). Disclosure within 8–12 hours of the latent period is rather slow. But already at the stage of active contractions, the uterus unfolds about an centimeter per hour.
The active period lasts about 4–5 hours, contractions are repeated every 4–6 minutes, spasms last for about a minute. During this time, the uterus expands to about 7 centimeters. Then within half an hour - an hour and a half, the period of transitional bouts lasts, the strongest, which last more than a minute and repeat every 2–3 minutes. But the disclosure at the end of the period is 10-12 centimeters, which is quite enough for the passage of the baby's head. The attempts begin.
In this way, normal labor pains are always associated with cervical dilatation.
If there are contractions, but there is no disclosure, they talk about generic weakness, childbirth is considered abnormal.
Causes of weakness
If there is no disclosure, or it goes at a very slow pace and is clearly not consistent with the periods of childbirth, the reason usually lies in the weak contractility of the uterus. If the contractions are weak, then the cervix cannot open. Moreover, the periods of relaxation between contractions usually exceed the norm in time, the woman “rests” more, the contractions themselves lag behind the required values. This complication is characteristic of approximately 7% of the parturient women, most often, primiparas face it.
The primary weakness of labor forces most often develops in women:
- with more abortions in the past;
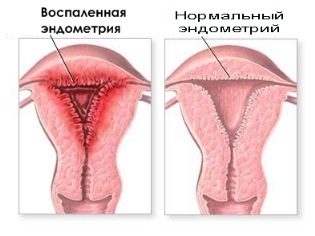
- with endometritis, myoma in history;
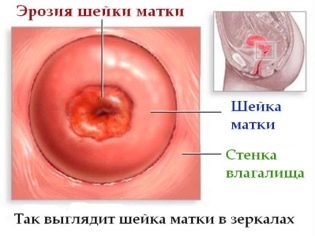
- with the presence of scars on the cervix after inflammation or erosion;
- hormonal imbalance;
- with preterm labor;
- during post-term pregnancy;
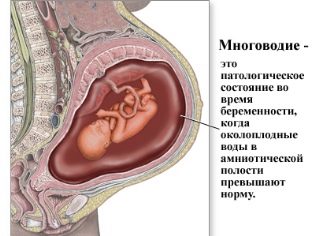
- at a lot of water;
- with obesity;
- in childbirth on the background of preeclampsia;
- in the presence of pathological conditions of the fetus: hypoxia, Rh-conflict, placenta previa, etc.
Such a reason as the woman’s psychological unpreparedness for childbirth deserves special attention. Often, doctors are surprised to encounter the weakness of labor forces when contractions go on, and the neck is not revealed in a healthy woman without pathologies of pregnancy. The wide pelvis, the normal weight of the fetus, all tests are in order, and the neck does not want to open.This may be due to a strong fear of the woman in labor before giving birth, unwillingness to give birth (unwanted child), if the woman was subjected to psychological pressure, conflicts in the family, she was tired, not getting enough sleep, she was very nervous or worried. Sometimes weakness becomes a consequence of an excessive amount of painkillers, which the woman tried to ease the contractions.
How does the uterus open up in this case? The excitability of the reproductive female organ is reduced. Periods of tension of the uterus are replaced by periods of "rest", which exceed the normal for a particular stage of contractions by 1.5-2 times.
What are they doing?
In order to speed up the opening of the cervix, it is sometimes simple enough to perform an amniotomy — pierce the membranes of the fetus and ensure the flow of amniotic fluid. A woman can be given a short medication sleep to replenish the spent forces. If within 3–4 hours after an amniotomy, contractions do not intensify, and the cervix does not open or the disclosure continues to go slowly, give birth-stimulating therapy.
Women are given hormones (oxytocin, dinoprost), which stimulate uterine contractions. At the same time, monitoring of the fetus is established using CTG.
If contractions under the action of drugs become faster and the opening has begun, childbirth is usually carried out. If stimulation has not brought the desired effect, the woman will undergo an emergency cesarean section.
About pain
Pain in the weakness of the tribal forces may be different. Contractions can be both painful and not painful. The weaker the smooth muscles of the female reproductive organ contract, the less pain the woman will feel, although even here everything is very individual.
In general, the period of labor is considered the most painful in childbirth. This statement sometimes scares women so much that they cannot cope with fear even after the first bouts begin.
Painless period of labor can not be. Neither anesthetic preparations, nor methods of natural anesthesia with the help of breathing and acupressure can guarantee that there will be no pain at all. But both drugs and alternative pain relief help reduce the intensity of pain, which allows a woman to give birth easier.
In order for the disclosure to take place at the right pace and reach 10–12 centimeters (at which the attempts begin), a woman needs to know from the very beginning how to behave, how to relate to what is happening. Proper breathing from the very beginning of contractions is deep and slow inhalation and exhalation, allowing you to relax as much as possible. At the stage of active bouts help a series of short and quick breaths and exhalations at the peak of the fight.
When the body is saturated with oxygen, the release of endorphins increases. These hormones have a certain anesthetic effect. In addition, proper breathing contributes to the saturation of all organs with oxygen, improves blood circulation, is the prevention of fetal hypoxia during childbirth.
With regard to the anesthesia of a drug, a woman has the right to decide for herself whether she needs it and wants to abandon the proposed epidural anesthesia if it considers it unnecessary.
The very mechanism of pain in childbirth is difficult to explain, because in the uterus there are no nerve receptors. Therefore, experts are inclined to consider pain as psychogenic, and, therefore, it will be possible to cope with it.
Prevention
In order to avoid non-disclosure of the cervix in childbirth, doctors recommend pregnant women to calm down, not be nervous, if necessary, visit a psychologist if there are problems or a strong fear of birth pain. In the later stages of pregnancy, a moderate but still motor activity is recommended for a woman. Lying on the couch is not much useful for the upcoming labor activity.
There is a popular belief that having sex increases the likelihood of successful disclosure. This is partly true: the semen contains prostaglandins, which soften the cervix, but they do not affect the contractility.
See the next video for more details on cervical dilatation.