Scarlet fever in children: symptoms and treatment (17 photos)
A skin rash, throat lesions and fever are symptoms of many childhood infections. One of these infectious diseases is scarlet fever. It is very common in childhood and can cause serious complications. And therefore, many parents are concerned about how a child becomes infected with scarlet fever and what a rash looks like during a given disease, how scarlet fever occurs in children and how this infection is dangerous, and many others.
What it is
Scarlet fever is called an acute infection, the causative agents of which are hemolytic streptococci belonging to group A. Such bacteria are able to have a toxic and septic, as well as an allergic effect on the human body due to the production of a special toxic substance - erythrotoxin.
It is this toxin and causes all the symptoms characteristic of scarlet fever. Due to the expansion of small vessels in children, a rash appears, and the erythrotoxin-induced loss of the epidermis causes a pronounced peeling of the skin.
How is it transmitted
Group A Streptococci from carriers and patients are transmitted to healthy children mainly by airborne droplets. Bacteria spread when sneezing or coughing, so people who are near a sick child are especially at risk. Pathogen transmission is also possible through clothing, contaminated toys or food.
From whom you can get infected
Streptococci can cause scarlet fever when ingested by:
- A person suffering from scarlet fever who is especially contagious in the first days of infection.
- A person suffering from pharyngitis or sore throat if these diseases are caused by group A streptococci.
- A newly recovered person, because bacteria continue to be released into the environment for up to three weeks after improvement.
- The carrier of hemolytic streptococcus, which has no symptoms of the disease. Bacteria can live on the mucous membranes of the nose and throat, and not to cause scarlet fever in their wearer, but to be dangerous to other people.

Incubation period
The first symptoms of the disease appear on average 3-7 days after infection. Most often, the incubation period in children lasts two to three days. Sometimes it is reduced to one day or even a few hours. In rare cases, the incubation period can be extended to twelve days.
How many days is the child contagious
The sick child begins to excrete scarlet fever pathogen into the environment from the moment of the first manifestations of the infection. An infectious period can have a different duration - both a few days and a few weeks. If scarlet fever is uneventful and the child is started on antibiotic treatment, then after 7-10 days, it ceases to be infectious to others.
Can an adult child get infected?
Scarlet fever is most often diagnosed in children from 2 to 10 years. The disease in most cases causes lifelong immunity, so if an adult has had such an infection in childhood, scarlet fever after contact with a sick child often does not develop. Repeated illness is possible with reduced adult immunity.
If an adult has not had scarlet fever before, it can become infected by a sick child by airborne droplets. In this case, the severity of scarlet fever in adulthood may be different. There are both erased forms and toxic scarlet fever with a very severe course.
Symptoms
The initial stage of scarlet fever in most children is short and lasts less than a day. The disease begins acutely with fever and sore throat. The main features of a typical form of scarlet fever in children are:
- Symptoms of general intoxication. The disease is manifested by headaches, fever, general malaise, agitated state (less lethargy), vomiting, aching muscles and joints, tachycardia.
- A ripple rash that appears on the first or third day of the disease.
- Angina, which can be more severe than with normal angina.
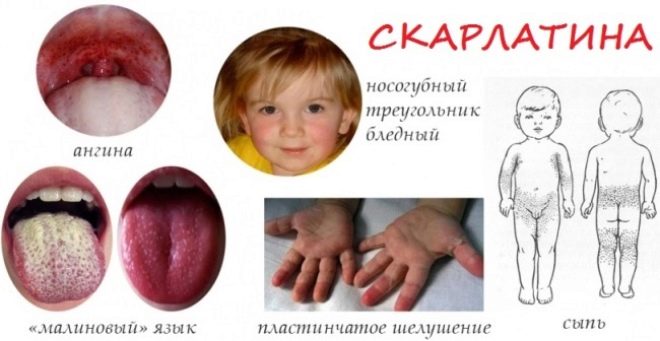
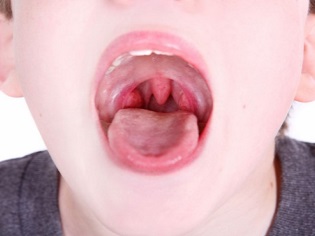
- A change in the language for which it is called "raspberry." The language for scarlet fever is first covered with a whitish bloom, but on the second or fourth day from the beginning of the clinical manifestations it becomes bright red. It shows grit as the size of the papillae increases.
- Peeling of the skin, which appears about 1-2 weeks after the initial manifestations of the disease (it replaces the rash). On the feet and palms, the skin is flaky in large parts, and on the body, ears and neck there is a small peeling, called scaly.
You can learn more about the symptoms that accompany the disease in the following video.
What a rash looks like
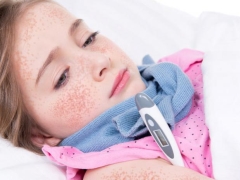
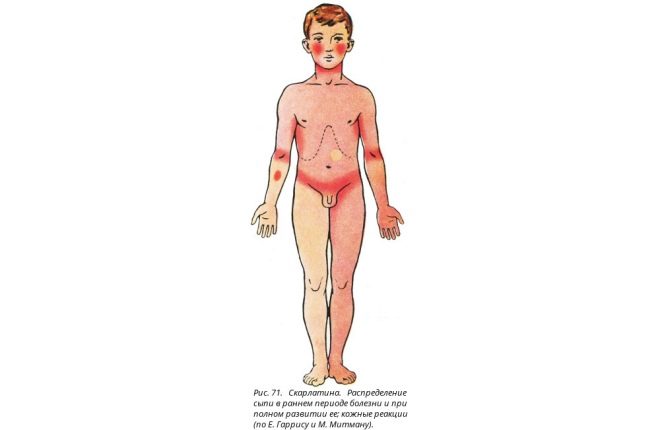
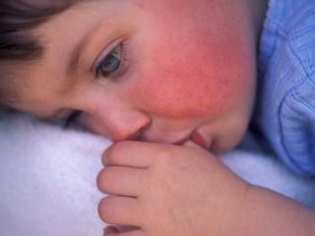
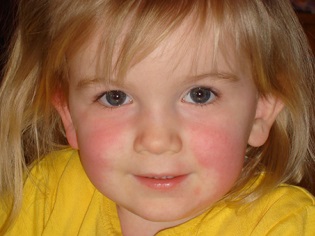
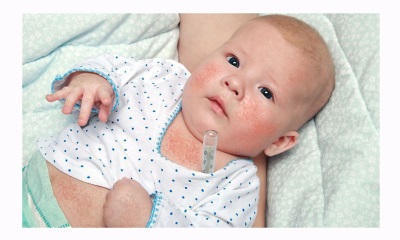
Rashes look like numerous dots of red or bright pink. Localization of rash represented mainly by the area of the face (on the cheeks), inguinal area, flexion surfaces of the extremities, as well as lateral parts of the body.
At the same time, in the area of the elbow folds, under the armpits and under the knees, the rash thickens, forming dark red stripes (this is called the Pastia symptom). In the area called “nasolabial triangle”, there is no rash with scarlet fever, and the skin of this part of the face will be pale (this is how Filatov’s symptoms manifest).
If you moderately press the rash with scarlet fever with a spatula, the spots become more distinct, but if you press hard with your palm, the rash disappears and the skin looks yellowish (this is called the "palm symptom"). To touch the skin of the baby with a rash is similar to sandpaper.
After 3-7 days after the onset of the rash begins to disappear, leaving behind a peeling. Especially pronounced peeling on the hands - the skin is removed from the fingertips in large areas, like gloves. Pigmentation after such a rash does not remain.
How is angina manifested
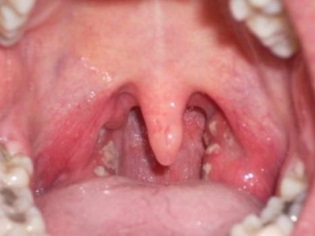
Streptococcus trapped on the mucous membranes of the nasopharynx settles on the tonsils and begins to release a toxin, which is the cause of angina with scarlet fever. A child’s throat acquires a bright red color (due to severe inflammation, such a picture is called “flaming throat”), and the tonsils are covered with purulent bloom.
Here are some photos of the baby's throat for scarlet fever:
How long does the temperature hold
Fever is one of the most frequent symptoms of the initial stage of scarlet fever. The temperature rises sharply to 38-40 ° C. In some children, febrile seizures are noted due to such a rise in temperature.Lowering the temperature in most babies is noted from the third to fifth day of illness.
Severity of illness
Depending on the age, state of immunity and the clinical picture of scarlet fever in a child, there are:
- Easy The symptoms of intoxication in this course are mild, the fever does not exceed + 38.5 ° C, the tonsils can be without plaque, and the rash is less bright and abundant. The mild form proceeds faster - by the fourth or fifth day the temperature returns to normal and all the acute symptoms disappear. In our time, this form in children is diagnosed more often than others.
- Medium heavy. The disease begins acutely, the temperature rises to + 40 ° C, the child complains of headaches, weakness, he noted vomiting, rapid pulse. The rash in this form is quite abundant, its color is bright, and the pharynx and tonsils are covered with purulent bloom. A decrease in temperature and the disappearance of acute symptoms are noted on the seventh or eighth day of illness.
- Heavy. At present, such a form develops rarely. Due to severe intoxication, such scarlet fever is called septic or toxic. In addition, the severe form of scarlet fever is necrotic, if the child has necrotic inflammation of the tonsils, and the lymph nodes are inflamed and suppurate. In severe forms, children must be hospitalized.
Atypical Scarlet Fever
Some babies have an atypical infection (a latent form develops). Doctors distinguish these forms of scarlet fever in addition to the typical:
- Wiped out. When it intoxication is mild, sore throat catarrhal, and the rash is pale, scanty and quickly disappears.
- Extrabuccal. With such scarlet fever, streptococci enter the children's body through the affected skin.
- Scarlet fever without a rash. With such an infection, all the symptoms of scarlet fever are present, but there is no rash on the skin.
How many times are sick
In most cases, after suffering scarlet fever, a person develops immunity to erythrotoxin produced by streptococci; therefore, children often suffer from such an infection once in a lifetime. However, although very rarely, cases of recurrent disease occur.
The transmission of antitoxic immunity from scarred mom to a baby after birth causes the rarity of scarlet fever in the newborn. A child within six months after birth is protected from such an infection by maternal immunity.
Treatment
Most children with scarlet fever are given home treatment. Hospitalization is required only in case of severe or complications, as well as in some other situations (for example, if a child is ill from a boarding school or in the family of a sick child there are people who work with children, but they cannot be isolated).
Mode
Until the moment when the temperature decreases, the child should stay in bed. In addition, in the acute phase it is important to stick to a diet and strengthen the drinking regime. Food is given to the child in a semi-liquid or liquid form, and protein products are limited. A child suffering from scarlet fever should drink a lot. It is best to give a warm drink, such as tea.
Drug therapy
Drug treatment of scarlet fever certainly includes antibiotics. Often, children are prescribed penicillin preparations in tablet form or in syrup, for example, amoxicillin, augmentin, amoxiclav, retarpen. The duration of use and dosage is determined by the doctor, but usually a course of antibiotic therapy lasts 7-10 days.
Additionally, the child is given vitamin preparations and antiallergic drugsand if intoxication is pronounced, infusion therapy is recommended (glucose and other drugs are injected intravenously). Chamomile extract, furatsilina solution, soda solution, calendula infusion and other antiseptics are used for gargling.
Homeopathy and folk remedies can be used in the treatment of scarlet fever as an auxiliary method, but only after consulting a doctor.
Is it possible to bathe a child
Washing with scarlet fever is not prohibited. On the contrary, children should be bathed, because it will reduce the itching of the skin and will prevent the scratching of the rash. However, it is important to follow some rules:
- The water in the bath should not be too hot or very cool.
- If the child has a fever, the bath is replaced with rubbing.
- The skin should not be rubbed with a sponge or sponge.
- For washing off the soap suds instead of the shower, it is better to pour douches from the dipper.
- After bathing, wipe the child with a towel is not advised. It is better to wet the water, wrapping the baby in a sheet or diaper.
Complications
When scarlet fever in children, such complications are possible:
- Glomerulonephritis.
- Purulent otitis.
- Inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Arthritis.
- Myocarditis.
- Pneumonia.
The risk of complications is significantly reduced with timely antibiotic therapy. In the development of lesions of the heart, joints and kidneys, the sensitization of the child’s body (its increased allergic sensitivity to erytotoxin) is of great importance.
Opinion Komarovsky
Famous pediatrician often faced with scarlet fever in my practice. Komarovsky focuses the attention of parents on such nuances:
- Streptococci are highly sensitive to penicillin antibiotics, therefore, after several doses of the drug, the condition of babies with scarlet fever is clearly improving.
- If a child has penicillin intolerance, this will also not be a problem, as streptococci are sensitive to many other antimicrobial drugs.
- Scarlet fever can be called a disease in which the timely administration of antibiotics ensures a successful outcome. If this infection is not treated, serious complications (damage to the kidneys and heart) are possible.
- Treatment should not be stopped as soon as the child's condition has improved. It is important to complete a course of an antimicrobial drug prescribed by a doctor.
- Due to the timely prescription of antimicrobial agents, sometimes streptococci die in the child’s body very quickly, and do not have time to develop immunity to their toxins. This is the cause of repeated diseases, which, according to Komarovsky, are easier than the first infection.
- Streptococcus can enter the child’s body not only through the throat. There are cases of infection through wounds on the skin. In this case, the child has all the signs of scarlet fever (there will be no sore throat). The treatment is prescribed the same as for ordinary scarlet fever.
- A child who has had scarlet fever for some time after an illness should not be in contact with other people, since a second hit of streptococcus threatens with allergies and other complications. Komarovsky recommends starting school or kindergarten after scarlet fever no sooner than after 3 weeks.
Mild forms and most of the moderate forms of scarlet fever in children are safely treated at home. The babies are isolated for 10 days, after which, in a satisfactory condition, they are allowed to walk.
Effects
At the present time, the prognosis for a child with scarlet fever is favorable in most cases. When a child has recovered, it is important to monitor their well-being in order to identify possible complications in a timely manner. Careful attention should be removed urine color (it changes with kidney damage, becoming like a "meat slop") and complaints of pain in the joints.
Physicians should monitor their condition after scarlet fever in moderate or severe form for one month. If after 3 weeks after recovery, the child is examined, blood and urine tests show no abnormalities, dispensary observation is stopped. Having identified any alarming symptoms in a child who has had scarlet fever, he is referred for examination by a nephrologist or a rheumatologist.
Prevention
It is known that vaccines that protect against scarlet fever do not exist. Protect from infection in children and adults who have not been sick before, such measures can be:
- In order to prevent the infection of family members in the room where the sick child is staying, it is important to conduct regular airing and wet cleaning.
- Caring for a child with scarlet fever should be dealt with by one person who is recommended to use specially selected clothing and a gauze mask.
- A sick child should be given a separate towel, his dishes, a handkerchief, toys and other items that healthy family members should not contact.
If the child has been in contact with a person who has scarlet fever and has not previously suffered from such an infection, it should be isolated from the children's team for 7 days. After staying at home for a week, such a child can return to school (it’s about primary school) or kindergarten.