Amblyopia in children
Amblyopia is a disease in which sharply reduced visual acuity without any organic pathology. Also in case of amblyopia disturbance of accommodation and contrast sensitivity is observed. Usually, the disease affects only one eye. Such a defect is not corrected by wearing glasses or contact lenses. How to recognize this pathology in a child and what methods of treatment of amblyopia are most effective, we will tell in this article.
What it is?
From Greek, the term "amblyopia" literally translates as "lazy eye." This is the essence of this pathology. Amblyopia is a functional disorder of the visual apparatus. Numerous studies on this issue indicate that amblyopia is one of the main causes of a sharp decline in vision in children and people of working age.
It is important to identify amblyopia at the earliest stages of its development, as this may contribute to the successful outcome of treatment, and if there are other concomitant favorable factors, vision can be fully restored.
In childhood, this pathology quite often occurs against the background of other visual disorders that prevent the full development of binocular vision.
In the medical scientific environment, there are many contradictions regarding the clear definition of indicators of visual acuity, under which it would be correct to make the diagnosis "amblyopia." This has introduced a significant error in the process of collecting statistical data showing the level of amblyopia disease among the population of different regions.
The most common types of amblyopia, found in world clinical practice, are considered to be dysbinocular and refractive.
Among the factors contributing to the development of amblyopia in childhood are the following:
- persistent strabismus;
- high degree of atopy;
- medium and high degree of prematurity or low birth weight;
- cerebral palsy;
- developmental delay;
- heredity (if one of the parents suffers from amblyopia, strabismus, incurred cataracts, anisometropia and other visual pathologies);
- Smoking and regular use of alcohol by a woman during pregnancy increases the risk of developing amblyopia and other functional disorders of the visual apparatus in the fetus.
Clinical manifestations
Amblyopia in a child is manifested by the following symptoms:
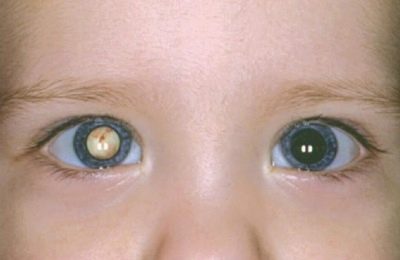
- a sharp decrease in visual acuity of one eye or both;
- deterioration of the three-dimensional perception of objects;
- if the child has a squint, then there is an increase in the deviation of the eyeball from the correct position;
- difficulties in learning associated with the deterioration of the perception of visual information.
Kinds
There is a classification of amblyopia on the etiological factors, according to which all types of diseases are divided into primary and secondary.
Primary types of amblyopia:
- Refractive. It develops against the background of any refractive errors in a child (mild, moderate or high myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism, etc.) that were not corrected in time by the constant wearing of glasses or contact lenses. Refractive amblyopia is one- or two-sided, symmetrical or asymmetric.
- Disbinokulyarnaya. Developed due to impaired binocular vision.Quite often, this type of amblyopia develops against the background of persistent squint.
- Mixed This type of amblyopia is a cross between dysbinocular and refractive amblyopia. There is a decrease in the severity of monocular vision. Usually, during therapy, the degree of influence of each of the causes changes.
- Hysterical. A sharp decrease in visual acuity in one or both eyes is due to any neurological pathology or severe psychological trauma.
Secondary species are characterized by the fact that they are the result of another organic defect in the visual system, which has been successfully corrected.
The following secondary species are distinguished:
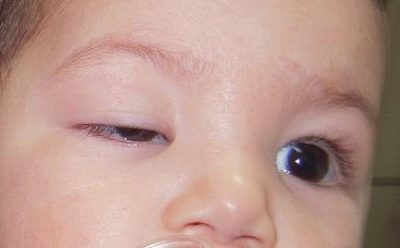
- Obscuration It appears when there is a certain defect in the visual apparatus, which is a kind of obstacle for focusing the light beam on the retina. The most common types of such defects are cataract or ptosis (omission) of the upper eyelid. Also, a variety of pathologists of the eyeball conductive media can cause the disruption of the normal image transmission to the retina. Obstructive amblyopia can develop on one eye or on both and have different degrees of difficulty.
- Neurogenic. Here, various degenerative and inflammatory processes of the optic nerve act as etiological factors. This type of amblyopia is characterized by a functional decrease in visual acuity even after the primary disease has completely cured.
- Maculopathic. It develops as a result of a previously transferred disease of the central and paracentral zone of the retina.
- Nystagmic. Here, amblyopia develops against the background of nystagmus (uncontrolled periodic symmetrical movement of the eyeballs).
- Combined. As an etiological factor may be all or some of the above reasons.
Diagnosis of the disease
Without a doubt, amblyopia, detected at the earliest stages of development, is much more effective in treating than neglected cases. To do this, regularly carried out prophylactic ophthalmologic examinations, starting with the first months of the child's life. Children with the presence of factors that predispose to the development of amblyopia are shown to undergo similar tests more often (at least 1 time per year) of children who do not have additional risks. There are several types of objective examination for amblyopia:
- Visometry - the main diagnostic method that allows to identify amblyopia in a child. Using this diagnostic method, you can determine the maximum level of visual acuity with and without correction. Naturally, during the manipulation the age norm of visual acuity for a particular child is taken into account.
This diagnostic procedure is carried out using tables to determine visual acuity. The child is no closer than 5 m from the table, and alternately closing either the right or the left eye tries to name the pictures or letters that the optometrist is showing him. The whole procedure takes place under certain lighting conditions (approximately 700 lux).
Before carrying out visometry, it is important to make sure that the child knows the pictures depicted on the table, or the letters, when it comes to school-age children. For this child, you must bring to the table and ask him to name pictures. During the diagnostic procedure, the specialist needs to create a trusting atmosphere between himself and the child, especially when it comes to children of early preschool age.
Getting into an unfamiliar environment, the baby can get lost or be afraid of the doctor, because of this, he will not be able to answer his questions, which, of course, distorts the results of diagnosis.
If such a study is carried out for the first time for a baby and its results show a decrease in visual acuity, then in such cases it is recommended to reapply visometry after some time.It is necessary to start a survey with a worse seeing eye, as it often happens that low rates are associated with elementary fatigue or a quick loss of interest in the “game”.
During the procedure it is necessary to ensure that the child does not squint and does not look at them with another eye.
- Determination of eye refraction. This diagnostic study is carried out using special devices for objective analysis (refractometer and keratorefractometer). You can also determine the true refraction with a simple skiascopy, although the data will not be as accurate as with a refractometer. It is important that the refractometry is conducted by an experienced diagnostician who takes into account all the nuances of the procedure, since the accuracy of the observance of all conditions depends on how true the results of the study are.
Before refractometry, it is necessary for the child to bury the eye with a drug that dilates the pupil. At this time, the baby may complain that the vision has become blurred. Calm him, explaining that this phenomenon is temporary, which on average does not last more than a day.
In order to determine the refraction of very young children who are difficult to persuade to sit motionless for at least a few seconds and fix their eyes on one point without stopping, the ophthalmologist usually resorts to skiascopy. If a specialist has sufficient experience, then with proper execution of manipulation skiascopy can give no less accurate data than a refractometer.
Skiascopy is an objective method of studying the refraction of the eye. Its essence lies in the observation of the movement of shadows in the pupillary zone. During the manipulation of the eye should be illuminated by a beam of light directed by a mirror. Using this technique, it is possible to identify any refractive error in a child at a fairly early age, as well as to determine its type (myopia, hyperopia, astigmatism) and degree.
In ophthalmology, the term "shadow test" is used for such research.
- Objective assessment of the functioning of the oculomotor system. This type of examination is very important for the detection of amblyopia. The ophthalmologist conducts a cover test and a cover-ankaver test, a convergence study is also conducted, as well as the identification of a possible micro-consistency, imperceptible to the naked eye.
- Definition of fixation. The results of this study have a huge impact on the further determination of the tactics of treatment of amblyopia. Fixation is usually determined by resorting to direct and inverse ophthalmoscopy, as well as makulotester.
- Other types of instrumental diagnostics. Conducted to confirm the presence or exclusion of organic pathology of the visual apparatus, which could provoke the development of amblyopia.
Treatment
Treatment of the "lazy eye" involves the use of several therapeutic techniques:
Optical vision correction
This method is an integral part of the whole plan of treatment of amblyopia (especially refractive). If a child has a high degree of ametropia, then when prescribing a prescription for glasses, the doctor must convince parents to purchase products with high quality lenses (for example, high-index, aspherical design, with an antireflection coating).
Also, as an alternative to the constant wearing of glasses, contact correction can be applied here.
Occlusion
This type of treatment consists in closing for a certain period of time a well seeing eye in order to make the eye work better with reduced vision.
For children suffering from amblyopia, without concomitant strabismus and while maintaining the correct binocular nature of vision, the healthy eye is blocked with an occluder for a certain time (not more than 3/4 of the entire wakefulness period).
There are several options for wearing the occluder, depending on the difference in visual acuity on the left and right eye, which can effectively treat amblyopia in a child at home.
If in both eyes vision is reduced to equal indicators, then the child wears an occluder on the right eye on the even days of the month, and on the even eye on the even days of the month.
If the difference in visual acuity on the left and right eye is significant enough, then here it is possible to use several techniques:
- one day they close their eyes for a while, which sees worse. After that, from 3 to 12 days in a row, a better seeing eye is closed for the same period of time. In this order, the occlusion is performed until the difference in visual acuity in both eyes is minimized;
- the occluder is worn every day alternately on each eye, while the worse seeing eye is closed for no more than 2 hours a day, and the best seeing eye is about 3/4 of the total wakefulness of the child.
The duration of wearing the occluder depends on the level of visual acuity of the eye and their difference between the two eyes.
If a child is diagnosed with amblyopia with improper visual fixation, then he may be assigned reverse occlusion, which means a permanent overlap worse than seeing the eye. This is done to reduce the competition of the non-central fixation site of the retina compared to the weakening from non-use of the central fossa fossa (foveola), whose main function is to ensure maximum visual acuity.
Successful therapy with this method will be indicated by a decrease in visual acuity in the eye with amblyopia. During the reverse occlusion, the child is taught to properly examine objects using foveola. When the baby has mastered it, direct occlusion is assigned (closing is better than the seeing eye) or alternating (alternate closing of both eyes within a certain mode).
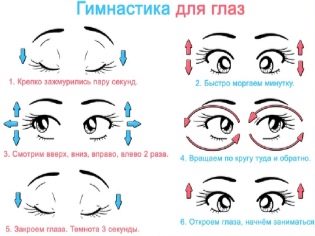
In parallel with this, the ophthalmologist usually prescribes the performance of special exercises that influence the formation of correct fixation, improvement of visual acuity and improvement of accommodative abilities of the eye with amblyopia.
In some cases, the constant wearing of the occluder can cause the following side effects:
- deterioration of eyesight in a healthy eye as a result of a violation of the mode of wearing an ocder;
- strabismus formation;
- the occurrence of diplopia (double vision);
- the emergence of various kinds of aesthetic problems;
- local irritation in places of contact of the skin with the occluder.
Occlusion is a mandatory method for the treatment of amblyopia. In drawing up the regime of occlusion, the doctor proceeds from the difference in visual acuity in different eyes of the child.
It is important to remember that the occluder should not change the position of the glasses on the face.
Pleoptika
This is a complex of methods that provide active stimulation of neurons of the retina of amblyopic eye.
Among the main means of pleotika distinguish the following therapeutic methods:
- use of special medical computer programs. With them, you can achieve full recovery of the binocular nature of vision, as well as improve visual acuity in the amblyopic eye. Usually, a complex of exercises is carried out in the form of a game, therefore it is suitable for treating the youngest patients with amblyopia;
- hardware treatment. It is a system of physiotherapy methods that contribute to a better blood supply to the visual system, stimulate the neurons of the retina, and also contribute to the accurate transmission of nerve impulses along the optic nerve.
It is possible to proceed to pleoptic treatment only after the etiological cause has been removed. A pleoptic treatment plan is drawn up depending on the type of fixation.
With a central fixation in a patient, it is quite possible to use the entire methodical complex of pleoptics (the use of glares, laser, magnetic and electrical stimulations, visual gymnastics, including a set of exercises for accommodation training, etc.).
If a child has an off-center fixation, the treatment focuses on correcting it into the central one, otherwise the whole therapy aimed at restoring normal vision in the amblyopic eye will be ineffective.
Non-central fixation is of two types: intramacular and extramacular. To correct intramacular fixation using makulotestr. With extravascular fixation, a reflex-free ophthalmoscope is used. When the fixation becomes central, it will be possible to proceed to treating the patient with a standard “set” of pleoptic therapeutic methods.
After successful completion of the treatment of amblyopia, the child remains in the clinic with an ophthalmologist.
For more information on the treatment of pediatric amblyopia, you will learn from the following video.