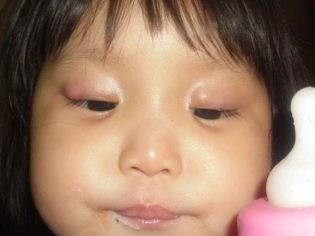
How to treat barley in a child?
Almost every parent at least once in his life faced such a problem as barley in a child. However, many will confirm that this disease can occur in different ways in different children. This also applies to the severity of clinical manifestations and the duration of treatment. In the Internet space, you can find a lot of advice from doctors and experienced parents on effective methods for treating barley in a child. Among them are quite relevant and obviously absurd.
What should be the tactics of parents when a child develops barley? What is the most effective treatment for this disease? Let's try to figure it out.
What it is
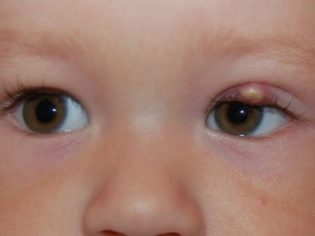
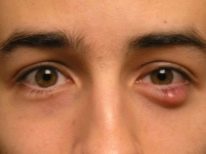
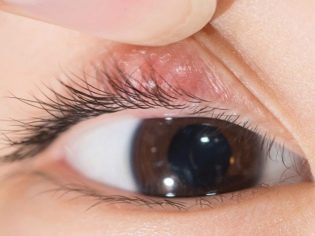
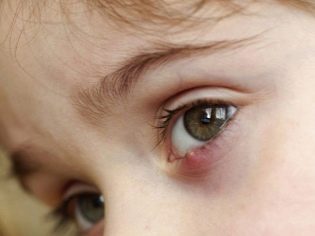
Barley is an acute inflammatory process with the formation of purulent exudate, localized in the thickness of the hair follicle of the century or the sebaceous gland located in the same place. Barley can appear in a child of any age (both in infants and in older children). Why do children suffer from this disease more often? The answer is obvious - The child’s immune system is more vulnerable to various kinds of harmful external and internal factors.
A child whose barley appeared in the upper or lower eyelids does not pose a threat to others, that is, the disease is not contagious and the child can go to kindergarten or school in the non-acute period of the disease.
How long you have to deal with this problem depends on various factors: the type of inflammation and the severity of clinical symptoms, the level of body resistance of the infection, the timeliness of treatment and the proper selection of therapeutic agents, the age of the child (newborn, preschooler or teenager), etc.
It often happens that parents inadvertently condone the progression of the disease, in which case the recovery time will be increased by several times, and the course of the disease will be more difficult for the child's body.
The opposite situation is when parents, relying not on the authoritative opinion of an ophthalmologist, but on prejudices and “tales” from the Internet, neglect conservative methods of treatment and try to self-cure the child with folk remedies at home and “grandmother” plots. Given the limitless imagination of some parents, it should be emphasized that such tactics can be not only ineffective, but also dangerous. Therefore, all parents strongly It is recommended not to resort to non-standard methods of treatment, without consulting with a doctor beforehand.
Causes
Among the etiological factors contributing to the emergence and development of barley, experts distinguish the following:
- Hypothermia In the autumn-winter period, the children's body is most susceptible to infection with a variety of infections. Therefore, you need to ensure that the child does not freeze from long walks and dressed for the weather. This also applies to children under the age of 1 year, who have not yet developed the mechanism of thermoregulation.
- Chronic diseases. It is proved that children suffering from diabetes and chronic inflammatory diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (gastritis, duodenitis, etc.) are more inclined to the appearance of barley in the eyelid.
- Hormonal imbalance. In children, this is most often associated with age-related changes that are accompanied by restructuring of the endocrine system.Therefore, in adolescence, boys and girls may suffer from the frequent occurrence of barley and other inflammatory diseases of the skin structures, such as acne.
- Genetic factor. It is known that in the DNA molecule there are certain areas that carry information about susceptibility to various pathologies. Therefore, there is a group of children who, without having other risk factors, still periodically suffer from this disease.
- Non-compliance with personal hygiene. This is the most common cause of barley in children. Children, especially at an early age, often neglect the need to wash their hands. It is enough to rub the eyelids once with dirty fingers to put a pathogen on the mucous membrane, which can later safely “settle” there.
- There is also a high risk of infection in the eye. in violation of the rules of wearing contact lenses. There is a direct contact of the hands with the mucous of the eyes, so before you put them on or take off, wash your hands thoroughly. If your child forgets about it, do not be lazy to remind him about it.
- Also, the infection can penetrate the mucous membrane of the eye. with a random speck. Therefore, if your child complains about the sensation of a foreign object in the eye, try to remove it as soon as possible, while also observing the conditions of sterility. If you yourself can not deal with this problem, then consult a doctor.
- Vitamin deficiency. Irrational diet leads to the fact that the child's immune system weakens, and the body during the attack of bacteria can not give them an adequate response. To avoid this, you need to make sure that your child’s diet is rich in vitamins and trace elements necessary for its full development. Among them are vitamins A and B, as well as ascorbic acid. They are found in fresh fruits, vegetables, herbs, seafood, legumes, rosehips, milk and dairy products, eggs.
Clinical picture
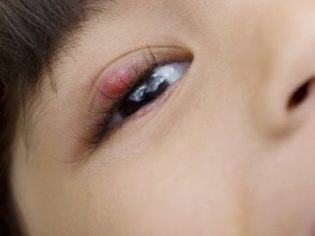
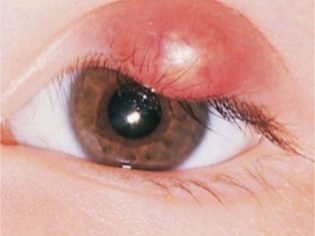
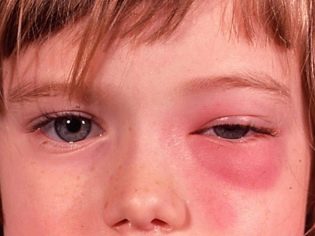
The initial symptoms of barley are the standard "satellites" of any inflammatory process - eyelid redness, swelling, pain on palpation. Itching may occur. In severe cases, symptoms of general intoxication are observed, which are characteristic of purulent inflammatory processes, such as headache or dizziness, muscle aches, fever, chills, and an increase in regional lymph nodes.
After 2-3 days, a lump with purulent content forms at the site of swelling. If during these days the treatment was carried out correctly, then approximately on the fifth day the abscess breaks through and the child's condition improves markedly. At this time, it is important to pay special attention to the personal hygiene of the child, or rather, to monitor the cleanliness of the hands to avoid secondary infection. Also during this period, it is advisable to take care that he has personal towel for the face.
After the barley breaks through, signs of inflammation should gradually subside. In no case should you try to open the pustular cavity yourself! With such an intervention, there is a high risk of bacteria entering the bloodstream, which can result in the development of much more serious diseases, such as meningitis (inflammation of the meninges) or sepsis (generalized infection). Barley must break spontaneously without active external intervention. In extreme cases, the doctor can perform the dissection of barley under sterile conditions.
Cases are quite common when barley disappears without a trace in a few days after appearance without specific treatment. However, this does not happen to everyone.
Treatment
With proper therapy barley passes, leaving no trace in the form of a scar. Of course, the first step that the responsible parent must take when barley occurs in a child is to seek qualified help from an ophthalmologist.After the initial examination and, if necessary, collecting tests, the doctor will determine the tactics of treatment, depending on the manifestations of the disease and the physiological characteristics of your child’s body.
Even with mild symptoms, one should not self-medicate.
If a child too often suffers from this disease, then an additional consultation of an immunologist may be given to him in more detail to identify the cause of the barley’s frequent occurrence and to give it a comprehensive treatment.
Drug treatment
The tactics of treatment of barley depends on the stage of the inflammatory process. When the barley is just beginning to ripen, apply some means, and after opening the pus - others.
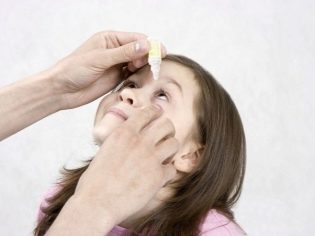
At the initial stages of the development of the disease, when the abscess is just beginning to form, the affected area is treated with an antiseptic solution (ethyl alcohol, green paint, calendula tincture, iodine, etc.). An UHF course may also be assigned at this stage. But any physiotherapeutic procedures can be prescribed only in the absence of fever in the child. Also during this period, the appointment of antibacterial drops is appropriate:
- «Levometsitin"- 5% solution is used for these purposes, it is necessary to drip 4-5 times a day for 1-2 weeks.
- «Cypromed»- use eye drops as instillations 3 times a day, five drops in each eye, before use, the drops should be warmed to room temperature.
- «Floksal"- drip 2-3 times a day, the course of treatment up to 14 days.
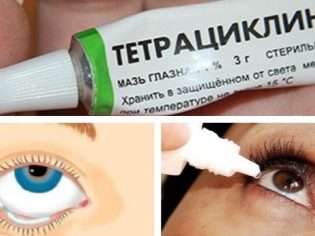
- Tetracycline ointment - To lay under the lower eyelid 2 times a day.
- Hydrocortisone ointment - To lay under the lower eyelid 2 times a day.
If a child gets barley too often, he may be prescribed drugs that stimulate the activation of immunity. In more detail this question should be discussed with the immunologist. If all therapeutic methods of treating barley have been tried, and the improvement has not come, then the ophthalmologist may recommend a surgical opening of the abscess. This manipulation does not require stitching, therefore, if the procedure is carried out correctly by a doctor, the child will not have any aesthetic defect in the eyelid area.
In a severe clinic, the child may be treated with inpatient therapy. There is antibiotic therapy aimed at the destruction of pathogenic microflora, and drugs are used to improve the general condition of the child (antipyretics, vitamins, etc.).
In turn, parents are required closely monitor that the baby touches the boil as rarely as possible, as it may unwittingly provoke a secondary infection. If the child is old enough, try to clearly explain why such actions can harm him. An unargumentated ban will most likely not convince him. If we are talking about a small child, then nothing remains but to make sure that the baby does not scratch and rub the sore eye.
Treatment by folk methods
Before you experiment with the health of your own child, trusting in questionable folk methods, think carefully. You should not treat all sorts of "grandmother's" recipes as something harmless that does not harm. You do not need to blindly trust the advice of relatives and friends, and perceive all sorts of unconventional methods as an alternative to qualified medical care.
In no case should barley be heated, be it an egg or a compress, since exposure to an abscess with high temperatures can turn into not the desired relief, but the spread of inflammation on nearby tissues.
Before resorting to any popular method of treating barley in a child, it is necessary to discuss its feasibility with an ophthalmologist. Perhaps he will allow you to use a home remedy as an adjunct to the main treatment.
The following recipes can be attributed to the barley-approved folk remedies for doctors:
- 2 tablespoons of fennel must be poured a glass of boiling water and cook for 15 minutes in a water bath. The resulting decoction must be filtered and used chilled as cold compresses.
- Mix in the same bowl in equal proportions St. John's wort, chamomile and calendula. Mixture pour boiling water. Cover with a clean towel or napkin. After cooling down, add a couple of drops there. propolis tincture. In the resulting solution, moisten a cotton swab and treat the sore eyelid.
- 2 teaspoons of hot eyes pour boiling water. Leave for 10-15 minutes. Strain broth and chilled to use for compresses.
- Aloe grind until a slurry forms, pour 200 ml of cool water over it, cover and leave in a dark place for 8-9 hours. This mixture is used for setting lotions to the patient's eyelid. The duration of the procedure should not exceed 20 minutes.
- 1 tablespoon of cornflowers flowers pour a glass of boiling water. Infuse the solution during the day. After that, dip a cotton swab there and attach to the century affected by barley for 15-20 minutes. Next, wash the eyelid with boiled water.
Using these recipes, you can not only speed up recovery, but also prevent the recurrence of the disease.
Complications of the disease
It should be noted once again that self-medication by dubious methods can aggravate the situation (especially for children under one year old) and provoke complications such as:
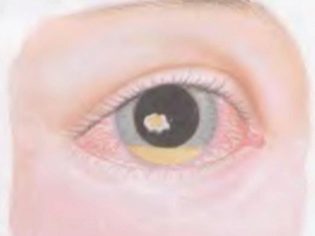
- conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye);
- keratitis (inflammatory process localized in the thickness of the cornea, which is clinically manifested by its clouding, appearance of ulcers, pain and burning on its surface);
- abscess formation (fibrous capsule filled with pus) or cellulitis (spilled purulent tissue inflammation).
The above pathologies are more difficult to treat and are more difficult for patients to tolerate. The spread of purulent inflammatory process can threaten not only the normal functioning of the entire visual apparatus, but also the life of a child.
Disease prevention
One of the main preventive measures to prevent the occurrence of barley is the observance of the rules of personal hygiene. Of course, a small child is a creature extremely restless, therefore even the most scrupulous in matters of cleanliness cannot be constantly monitored so that the hands of the child are perfectly clean. However, you can try.
As soon as the child enters a more conscious age (from about 2-3 years old), try to gradually accustom him to frequent hand washing.
Children are small conservatives, it is easier for them to get used to performing some actions if they are tied to a specific time of day or before other manipulations (after using the toilet, before eating, after walking, etc.). Show a personal example. Wash your hands with your child for several days in a row. To captivate him, buy soap in the shape of an animal or a towel with a bright pattern.
You can tell your baby about germs and why washing your hands is so important. Just do not need to clothe your story in the form of horror stories, so that the child does not fall into another extreme, and the love of purity does not turn into a phobia. It is also important that the child has his own towel for the face. This will reduce the risk of infection in the eye.
It is important to maintain the immunity of the child. The following measures can contribute to this: a diet enriched with vitamins, hardening of the body (within reasonable limits), regular walks in the fresh air, timely rehabilitation of other foci of infection.
What is different from the chaliasion?
Quite often, barley is confused with a chalazion. This is not surprising, since the symptoms of diseases in the early stages look very similar: redness of the eyelid, swelling, and further education in this place of clearly palpable compaction. However, barley is a closed cavity with purulent contents, and chalazion is simply a painless compaction that tends to gradually increase, quite often appears in children under the age of 1 year.
Barley is localized at the very edge of the eyelid, affecting the eyelash growth zone, and chalazion is located at the eyelid itself. This is due to the fact that barley occurs due to acute inflammation of the hair follicle or sebaceous gland, and chalazion occurs with inflammation of the meibomian glands, which are located in the stratum of the eyelid.
The pathogenesis of the formation of chalazion is that the duct of the meibomian gland is blocked, which is why the secret does not come out, but begins to accumulate directly in it. The immune system responds to this "failure" either by inflammation or by forming a connective tissue capsule around the focus. Despite this, iron continues to produce a secret, which leads to its uncontrolled increase.
How to treat barley in a child, see the following video.