Teething sequence in children
Any mother eagerly awaits the first tooth of her toddler, so knowing almost all the parents will erupt in what order the teeth will erupt. Besides, Knowledge of how teeth are crawling is also important for assessing the correctness of the development of the little one, because, having noticed some violations, it is possible to prevent dental problems in time.
Teething rules
- Teeth in an infant usually appear in pairs. When a mother notices one new tooth in a baby, she needs to wait for his eponymous “brother” to appear in the near future. It happens, at the crumbs, 2 or 4 teeth are simultaneously cut.
- In most babies, the teeth first erupt into the lower jaw. For example, first appear the lower central incisors, and then the same teeth at the top. The same situation occurs with the molars and canines, and only the lateral incisors climb differently (they are first cut at the top).
- The approximate number of teeth at a certain age is calculated on the basis of such a formula: "The age of the baby in months minus four." She suggests that on average, at 6 months, children have two teeth, and by the age of 24 months, all twenty teeth.
The opinion of Dr. Komarovsky about the first teeth and all the problems arising from their appearance, see in the video:
Symptoms
Although teething is a physiological and natural process, it still loads the child’s body, causing discomfort and such manifestations:
- Increased saliva secretion.
- Reduced appetite, up to a complete rejection of food.
- The desire to pull different objects in the mouth and gnaw them because of itching in the gums.
- Appearance in the place of eruption of swelling, redness and swelling.
- Capriciousness and irritability due to pain and itching.
- Disturbed sleep
Some babies add other symptoms to these symptoms:
- Increased body temperature (in most cases within + 37 + 37.5 ° С).
- Runny nose and cough due to excess saliva.
- Slight dilution of feces.
- Skin irritation on the chin and chest.
What teeth appear first?
The very first tooth that “hops” in an infant is called a chisel. He most of the tops appears on the lower jaw, and then quickly enough next to show another cutter. These teeth are distinguished by narrow crowns and are designed for biting food. Most often, they erupt at the age of 6-8 months, although in some karapuz the first incisor starts knocking about a spoon in 3-4 months, and some mothers have to wait for the first tooth to appear only by the age of one year old babies.
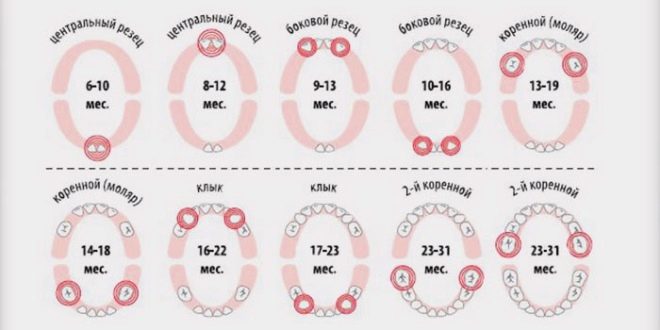
Teething sequence
Although the order of appearance of milk teeth is only approximate and may vary for each individual child, parents should focus on the following sequence:
- The first teeth of most babies, as we noted above, are central incisors called for their position in the dentition "edinichkami."
- Further, they are supplemented lateral incisors, which are called "twos".
- After the incisors comes the time of appearance first molars which in the dentition are "fours".
- The next step is eruption of canines between lateral incisors and first molarstherefore they are called "threes".
- The last among the milk teeth are the “fives”, which dentists call second molars.
The average terms of the appearance of milk teeth in the table
The process of eruption of each new baby tooth in different children takes place individually, However, if you look at the order and time of appearance of the first teeth in the majority of children, you can see the average time to which parents and pediatricians are oriented. Here is a table in which the averaged time for the appearance of teeth is noted with regard to the sequence of their cutting:
Name of teeth | In how many months on average erupt |
Central incisors | Below - in 6-9 months, Above - in 7-10 months. |
Side cutters | On the upper jaw - at 9-11 months, On the lower jaw - at 11-14 months. |
First molars | Lower - in 12-18 months, Upper - in 13-20 months. |
Fangs | Below - in 16-22 months, Above - in 17-23 months. |
Second molars | On the lower jaw - at 20-26 months On the upper jaw - at 26-33 months. |
In most children, the last milk teeth "hatch" by the age of 2-2.5 years.
When do baby teeth fall out?
The average terms for the loss of milk teeth will be:
- The central incisors begin to wobble and fall out at 6-8 years of age.
- Loss of lateral incisors observed in children 7-8 years.
- The term of the first molars is 9-11 years.
- Fangs most often fall between the ages of 9 and 12 years.
- The second molars stagger and fall out at 10-12 years of age.
His opinion regarding the change of milk teeth to permanent ones, was expressed by the orthodontist, MD. Svetlana Vakhney:
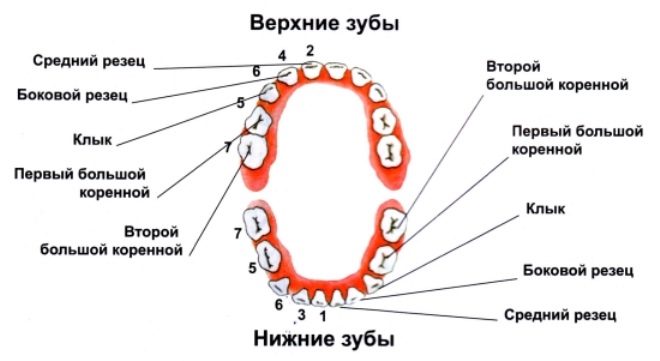
Permanent Teething Procedure
The first among the child's permanent teeth are the "six", that is, the teeth, which are located in the dentition immediately after the second milk molars. They are called the first molars, and the milk molars are replaced by teeth called premolars. The first permanent molars erupt in children aged 6-7 years, and this usually happens before the first baby teeth fall out.
Further, the procedure for “spitting up” permanent teeth is often as follows:
- At the age of 6 or 7 years, central incisors appear in the lower jaw.
- At 7-8 years of age, the central incisors are incised in the child and on the upper jaw.
- The bottom "twos" also erupt at the age of 7-8 years.
- The lateral incisors at the top are cut to 8-9 years.
- On the lower jaw, fangs grow into 9-10 years.
- Upper canines appear in children 11-12 years of age.
- The appearance of the first premolars in the upper jaw is observed on average in 10-11 years.
- The term for cutting through the first lower premolars is 10–12 years.
- The second premolars are cut at the top in children aged 10 to 12 years, and in the lower jaw at the age of 11-12 years.
- The second molars come out at the bottom in 11-13 years.
- The cutting of the second molars in the upper jaw is noted at 12-13 years of age.
- Third molars are cut at the top and on the lower jaw at the age of 17 years.
Possible problems with teething
The main problems that occur with teething, are in violation of the timing of their appearance, as well as in the wrong sequence. In addition, since the appearance of new teeth lowers the child’s immunity, a baby can develop:
- ARVI
- Otitis
- Pneumonia
- Caries
- Stomatitis
- Abscess (pharyngeal)
Why is teething lagging?
If the baby, by the age of one, has not yet had a single baby tooth, it is worthwhile to show the child to the doctor. and find out the reasons for this situation. They may consist of:
- The influence of hereditary factors. If mom, dad or other close relatives have teeth that erupt later than the average time, then the situation in the crumbs will be the same.
- Calcium deficiencywhich also provokes rickets.
- Lack of hormoneswhich produces the thyroid gland.
- Digestion problems and absorption of nutrients.
- Absence of rudiments of teeth.
- Baby prematurity.
- The development of an infectious disease.
Advice to parents on what to do and how to behave during teething, gives the Union of Pediatricians of Russia:
Gaps between teeth
Baby teeth appearing in a child under 3 years of age may be located asymmetrically or with gaps between them. This is a variant of the norm, if the entire dentition has not yet erupted. Once it is fully formed, due to active chewing all the teeth will fall into place. Further, by the age of 6-7, when the change of milk teeth begins, gaps will again arise between the teeth, since the size of the permanent teeth is much larger. The appearance of such intervals should not bother the parents.
When should you go to the dentist?
To show the baby to the pediatric dentist in such situations:
- Teeth appeared later than usual or not cut through.
- Teeth got out too early.
- There is no tooth.
- Disordered the appearance of teeth.
- The tooth was formed incorrectly.
- The tooth came out far from the arc of the dentition.
- A black band appeared on the neck of the tooth.
- There is a large gap between the permanent central incisors.
- Enamel has acquired a reddish, greenish or yellow-brown hue.
- The tooth is damaged.
How to prevent dental problems?
In order for both dairy and permanent teeth to delight the children and their parents with their strength and healthy appearance, you should visit the pediatric dentist every six months. In addition, the following measures are important:
- Do not try older food with a baby spoon.
- Do not lick an adult baby's pacifier.
- Reduce your child’s sugar intake.
- Do not give the child a sweet drink before bedtime.
- Teach your baby to rinse your mouth after eating or drink a small amount of water.
- Try to prevent trauma to the teeth.
- Pay attention to the diet of the baby - to strengthen the teeth in it should be cheese, cottage cheese, dried apricots, tea, raisins, seaweed.
- Ensure that the child brushes his teeth twice a day (cleaning before bed is mandatory).