What does degree 2 infertility mean in women and how to treat it?
Second degree infertility is diagnosed in women who have already given birth or have been pregnant, but the pregnancy was terminated for some reason. There are many different pathologies leading to the development of similar problems in the reproductive system.
What is second-degree infertility?
Gynecologists diagnose second-degree infertility in women who have already had pregnancies. In this case, it does not matter whether they ended in childbirth or for some reason were interrupted. In other words, the second degree of infertility occurs against a background of impaired reproductive ability.
It is possible to talk about secondary infertility when a couple has problems with childbirth, despite the fact that they follow the rules that increase the possibility of conception. These include:
- frequent sex, which falls on the 11-18 day of the menstrual cycle (if you count the days from the first day of bleeding);
- frequency of sexual relations (not more often than every other day, but not less than twice a week);
- the use of sexual positions conducive to conception;
- rejection of the use of lubricants, etc.
If some of these requirements have not been met, then there may well be no fruitlessness.
In general, according to statistics, approximately 10% of couples are considered fruitless. In this situation, it is necessary to examine both partners. According to reviews, in a third of such cases, the problem is found in a woman, in another third (according to some data - in half) - in men. The remaining third is made up of those couples where both partners have problems with reproductive health.
Classification
There are several types of fruitlessness (depending on etiological factors):
- physiological (period before puberty, menopause);
- congenital (anomalies of the development of organs of the reproductive system, underdevelopment of the genital organs - infantilism);
- acquired (a consequence of the transferred diseases of the sexual apparatus);
- voluntary (use of contraceptives of various mechanisms of action);
- temporary (due to psycho-emotional upheaval, depression, problems with immunity, starvation, abrupt climate change, as well as the period of breastfeeding);
- constant (resulting from the partial or complete removal of the genitals).
Risk factors
Factors contributing to the development of a woman's secondary infertility:
- the woman belongs to the age group over 35;
- a history of unhealthy pregnancies;
- in the patient, due to neuroendocrine pathologies, the menstrual cycle is disturbed;
- the woman had sexually transmitted diseases
- genital endometriosis in history;
- On the genitals of the woman, surgical manipulations were repeatedly performed (for ovarian cysts, inflammation of the appendages, ectopic pregnancy, tumors, as well as cesarean section or plastic of the fallopian tubes).
Women in risk groups need a detailed examination, even in cases where they seek medical assistance on a matter not related to infertility treatment (here we are talking about identifying potentially infertile marriages).
The reasons
For secondary infertility in women there are several reasons.
- Age group. The advanced age of a woman is a common cause of secondary infertility, because it is he who determines the activity of the reproductive system of the female body. Statistics show that after 25 years, a woman's chances of becoming a mother are reduced, and after 35, the probability of pregnancy decreases even more. At this age, up to 7 menstrual cycles can occur without ovulation, whereas in 20-35 years there can be only 1-2 cycles without ovulation. Approximately 25% of all clinical cases of second-degree infertility are in this age group.
- Psycho-emotional status. The psychological state of a woman affects her hormones. If she is subject to stress or nervous tension, then this can lead to disruptions in the functioning of the reproductive system. Dramatic weight loss or obesity for the body are a real stress, which can also cause secondary infertility.
- Somatic diseases of the reproductive system. Inflammatory processes of an infectious nature in the female reproductive system can cause problems with conception. Second-grade infertility may be due to complications of other pathologies, such as tubal adhesions or disruption of the ovaries. The presence of diseases of the reproductive system leads to a deterioration in the quality characteristics of natural lubricant (it may become excessively liquid or too viscous), which will interfere with the movement of spermatozoa toward the egg cell. In addition, the following diseases are common causes of infertility: endometriosis, polyps, hyperplasia, uterine fibroids, polycystic ovaries, the presence of tumors in the thickness of the uterus.
- Transferred abortion. This operation can provoke infertility, due to the development of the inflammatory process in the reproductive system.
- Violation of the thyroid gland. All organs and systems in the body are interrelated. The production of sex hormones is influenced by the hormones that the thyroid gland synthesizes. Among the main causes of second-degree infertility, experts distinguish hypothyroidism (a decrease in the functional activity of the thyroid gland). This leads to inhibition of ovulation and disruption of the menstrual cycle. Malfunctions of the thyroid gland can be caused by iodine deficiency.
- Lack of progesterone. This hormone provides the onset and the normal course of pregnancy. With its deficiency, the woman cannot become pregnant or she will have frequent miscarriages in the early period of gestation. Determine the lack of this sex hormone by passing the appropriate analysis or measuring the basal temperature.
There are many reasons for the occurrence of secondary infertility in women, so this pathology requires careful diagnosis, based on the results of which the attending physician will be able to select treatment methods taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient.
Diagnostics
If pregnancy does not occur in a couple who do not use contraceptives for a year, the diagnosis is “second-degree infertility”. This is followed by a detailed examination of the pair.
The main study for a man is spermogram (semen analysis). This survey can determine the possible causes of problems with conception or exclude any.
The list of diagnostic procedures for women is much wider.
- Gynecological examination. This is the initial stage of diagnosis. During the visit, the doctor will conduct a survey, collect obstetric history and perform an examination of the patient. Based on the obtained data, the specialist will conduct differential diagnostics and set the direction for further actions.
- Tests for infections. To identify their presence in the female body will help a comprehensive examination, including a study of the composition of a smear from the vagina and a blood test.
- Analyzes on the content of hormones. A woman takes them if there is a violation of the menstrual cycle, hair appears in unusual places, there is a sharp weight gain. The specialist in this case assigns a series of tests that are taken on certain days of the cycle.
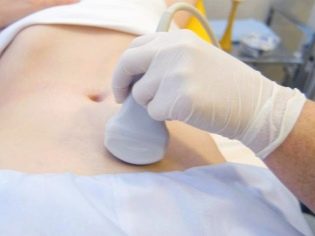
- Ultrasound examination of the pelvis. The study of the pelvic organs is carried out several times during the cycle, which allows to evaluate the work of the ovaries (to determine whether ovulation occurs), the activity of the uterine mucosa and the condition of the pelvic organs as a whole. Sometimes an ultrasound of the thyroid gland is prescribed.
- Detailed examination of the cervix. Diagnosis helps to identify the presence of atypical cells on the mucous membrane of the cervix, which is not always noticeable during a routine examination.
- Endoscopic examinations. This list includes procedures such as:
- hysteroscopy (examination of the uterus);
- hysterosalpingography (determination of tubal patency);
- ovarian examination using laparoscopy (a diagnostic procedure that is carried out through small incisions in the anterior wall of the abdomen using special optical instruments).
- Postcoital test. The study allows to determine whether the body of a man or a woman has antisperm antibodies produced by the human body to sperm antigens.
Treatment
The process of treating infertility of the second degree is rather complicated and time consuming: it can take several years. The treatment will be successful, provided that the patient exactly fulfills all the prescription and recommendations of the attending physician.
In inflammatory processes in the reproductive organs, antibacterial therapy, antiviral and antifungal agents are used, in some cases immunomodulators are used.
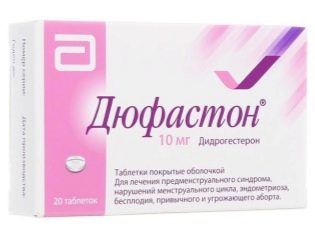
Due to the risk of dysbacteriosis, prebiotics, probiotics and enzymatic preparations are often prescribed. Restoration of the disturbed hormonal background is carried out with the preparations “Duphaston”, “Utrogestan”, “Clomid”, etc.
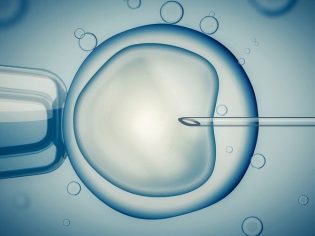
Surgical correction is prescribed in the absence of positive results from drug treatment. Sometimes the results of surgery also do not lead to a long-awaited pregnancy. Then the doctor raises the question of artificial insemination (IVF), where the introduction of spermatozoa occurs directly into the uterus.
In the next video, you will learn more about grade 2 infertility in women.