What is insemination and how is the procedure?
Among assisted reproductive techniques, a special place is given to insemination. It allows you to conceive a child in the case when fertilization by natural means for some reason becomes impossible. About how insemination goes, who is being carried out and what its effectiveness is, we will tell in this material.
Special features
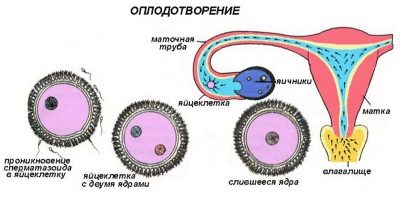
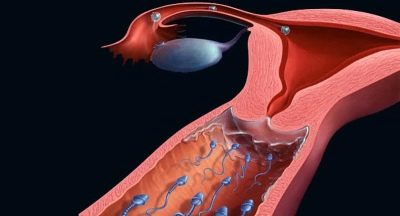
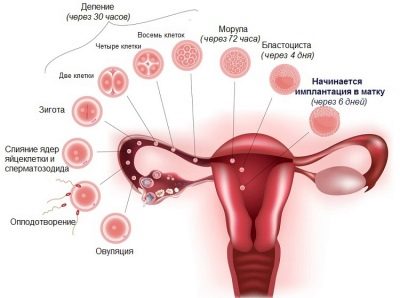
Insemination is the process of insemination. With natural intercourse, natural insemination occurs when the sperm enters the female's genital tract as a result of her partner's ejaculation at the time of orgasm. Next, sperm have a long way to go - to overcome the vagina with an acidic and rather aggressive environment, to overcome the cervix, cervical canal. No more than one third of the male sexual cells will reach the uterus.
In the uterus, the sperm environment is more favorable, but they still have to pass through the fallopian tube, in the ampullary part of which an egg cell ready for fertilization awaits them. If at some stage difficulties arise, then not a single sperm cell can reach the egg cell and then the pregnancy will not come.
In some forms of infertility associated with immune factors, with endocrine disorders, with male factors, with cervical pathologies, insemination is difficult in a natural way. Therefore, artificial insemination can be used. In this case, the husband’s or the donor’s sperm is injected into the woman’s cervix or into the uterine cavity with the help of special devices, that is, the procedure goes without sexual intercourse.
The first insemination experiment was carried out in Italy in the 18th century. Then the "baton" picked up the British. In the 19th century, physicians in many European countries actively used this method of help for infertility. In the middle of the last century, doctors learned not only to inject sperm closer to the cervix, but began to make intrauterine insertions and even introductions to the mouths of the fallopian tubes.
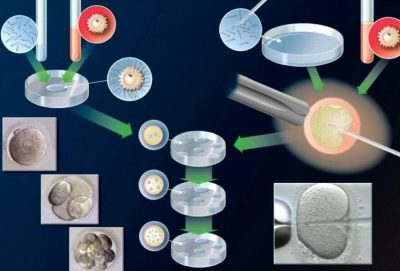
Insemination belongs to the category of methods of artificial insemination, but with IVF (in vitro fertilization) has nothing to do. The main difference is that in vitro fertilization, the fusion of the sex cells of a man and a woman occurs outside the female body. Ovum and sperm pass this stage in a laboratory Petri dish under the vigilant control of embryologists, and after several days the embryos are transferred into the uterus.
When insemination human intervention in the natural process is only that the sperm "help" to overcome particularly difficult areas - the vagina and cervical canal of the cervix. Thus, a greater number of male germ cells enters the uterus and fallopian tubes, and this increases the chances of pregnancy.
Fertilization itself takes place in the natural environment provided for by nature - in the wide part of the tube, from where the fertilized egg gradually moves into the uterine cavity. After about 8–9 days under favorable conditions, the implantation of the descending ovum occurs and the development of pregnancy begins.
Insemination differs from ICSI (intracytoplasmic sperm injection) the same as IVF in general.In ICSI, one selected sperm is injected with a thin needle under the egg shell manually. The whole process takes place outside the female body, in an embryological laboratory.
Quite often, intrauterine insemination is the first method that is assigned to couples for some forms of infertility. Sometimes her treatment ends, as the pregnancy begins.
If insemination does not give a positive result, the possibility of IVF or IVF + ICSI is considered.
Kinds
Vaginal, intracervical and intrauterine insemination are distinguished by the depth of the ejaculate injection. Depending on whose sex cells will be used to fertilize a woman, there are two types of insemination:
- homologous - Insemination, for which the sperm of the husband or the permanent sexual partner of the woman is used;
- heterologous - Insemination, which is carried out using anonymous or other donor sperm.
The donor's sperm procedure is performed when the spouse or a regular partner's sperm is considered unsuitable for fertilization due to a violation of the sperm morphology, a small number of live and active sperm, and other serious spermogram disturbances. Also, insemination with a donor biomaterial is recommended when a man has severe hereditary pathologies that can be inherited by a child. A woman who wants a child, but lives alone, without a husband, can also be inseminated at her will.
The procedure with the husband's sperm is carried out if the quality of the ejaculate is good enough for fertilization to take place, but not sufficient for natural conception through sexual intercourse, as well as in certain female diseases.
Indications
Unlike in vitro fertilization, which theoretically can help a large group of infertile couples with a variety of reasons for reduced or lack of fertility, intrauterine insemination is shown to a rather narrow group of patients. These include:
- women without a partner;
- couples in which there is a male factor of infertility according to semen;
- couples in which a woman has minor pathologies of the reproductive system.
Male factors that may require the use of insemination by donor sperm can be caused by a lack of testicles from birth, or due to injury or surgery. Also, donor material, in consultation with the spouses, is used if the couple has a genetic incompatibility or the man has an extremely low sperm quality, which is not amenable to medical and surgical correction.
Insemination becomes a chance to become a dad for men who for some reason cannot perform a full-fledged act, for example, in case of paralysis of the lower body, if the spinal cord is damaged. Intrauterine sperm injection will help solve the problem of conceiving couples in which a man suffers from retrograde ejaculation (sperm enter the urinary tract as a result of disrupting the process of eruption).
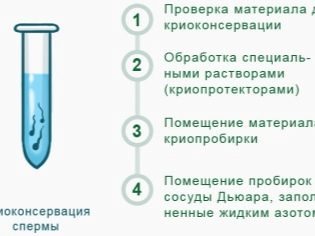
Delivery of sperm followed by its cryopreservation for insemination may be required for men who are going to undergo a course of treatment for oncology, for example, a course of radiation therapy. Own germ cells can suffer greatly as a result of cancer treatment, and frozen sperm will remain unchanged and can be used for insemination as desired by the couple.
Among the female pathologies that prevent the occurrence of pregnancy naturally, but can be overcome by intrauterine insemination, include cervical or cervical infertility factors, in which the passage of partner sperm through the sexual ways is difficult, with the immune factor of infertility, if a large amount of antisperm antibodies is produced, also with moderate endometriosis and mild forms of menstrual disorders.
Sometimes it is not possible to identify the true cause of infertility - according to the results of all examinations, both partners are somatically healthy. In this case, intrauterine insemination is also used as an experimental measure.
Insemination is recommended for women with vaginismus, in which penetration into the vagina causes a strong spasm, with scars on the cervix, caused by previous operations on it or ruptures during previous difficult labor.
Contraindications
For most assisted reproductive technologies and methods, the list of contraindications established by orders of the Ministry of Health is almost identical. As in the case of IVF, a woman who currently has acute inflammatory diseases or exacerbated chronic diseases will not be admitted to insemination. The ban applies to women with mental health problems who require regular or periodic use of psychostimulants.
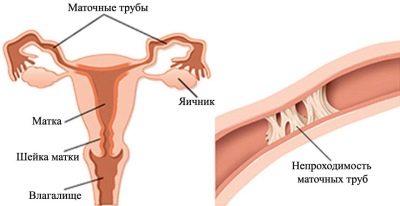
In the presence of cancer, any benign tumors at the time of the procedure, insemination will also be denied. If a woman develops malformations of the uterus and tubes, if she suffers from obstruction of the fallopian tubes, if she has congenital anatomical anomalies of the uterus, vagina, tubes and ovaries, insemination is also denied, because pregnancy in these cases can be life-threatening and dangerous. women.
It should be noted that insemination can be carried out with a single tube or with partial obstruction of the fallopian tubes, but only by individual indicators, that is, the decision on the expediency of the procedure is made taking into account the degree of obstruction and the chances of success.
Infectious diseases of the husband can also cause failure in the insemination procedure, since there is a likelihood of infection of the woman at the time of introduction of the spouse's biomaterial. That is why before insemination it is necessary to conduct a thorough examination and pass a rather impressive list of tests.
Training
If the couple was examined by a gynecologist and a urologist, and these specialists concluded that insemination is necessary for conception (readings are indicated above), then the woman’s doctor will give her directions for tests and examinations. Before insemination, a woman should be given general urine and blood tests, a biochemical blood test, sexually transmitted infection tests, a blood test for HIV, syphilis, a blood group, and a Rh factor.
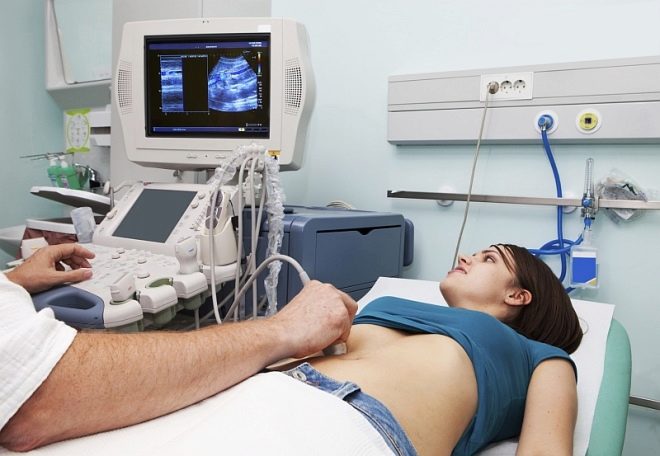
On day 5-6 of the menstrual cycle, she should donate blood from a vein to the main hormones responsible for reproductive abilities (prolactin, FSH, LH, testosterone, estradiol, etc.). A woman must perform an ultrasound of the pelvic organs, take swabs from the vagina and scraping from the cervix. Colposcopy and hysteroscopy are also shown (in case of suspected endometriosis). The patency of the fallopian tubes can be installed diagnostic laparoscopy or other methods.
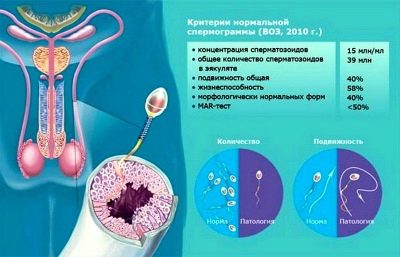
A man should make a spermogram with a mandatory extended test for antisperm antibodies and various types of abnormalities in spermatogenesis. In addition, a man undergoes general blood tests, urine tests, chest x-ray of the chest organs, blood tests for HIV, syphilis, genital infections, a smear from the urethra, blood for the group and Rh factor.
Intrauterine insemination is included in the program of state support for NRT (new reproductive technologies), and therefore it can be done both at its own expense and free of charge, according to the policy of the MLA. In the first case, with the conclusion of a doctor and analyzes, you can go to any clinic that provides such a service. In the second case, it will take about a month to wait until the documents submitted by the attending physician to the commission of the Ministry of Health of the region will be considered.
If a couple is allowed to make insemination at the expense of state or regional funds, she will be offered a list of clinics and hospitals that can carry out the procedure and have a corresponding license for it. It remains to choose one of them and go there with all the analyzes and documents for the quota procedure.
Order of conduct
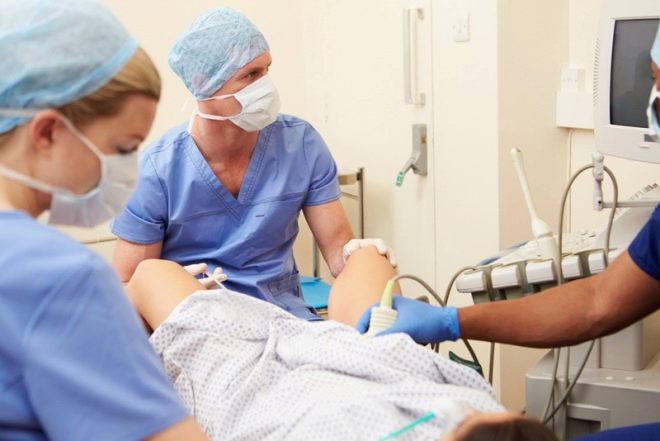
For intrauterine insemination, a woman does not need to go to the hospital. This procedure is quite simple and quick. It can be done in a natural cycle or with the use of hormonal drugs that should stimulate ovulation in a woman (if there are violations of the ovulatory cycle). Whether or not ovarian stimulation is needed, the fertility doctor will decide who will receive tests about the hormonal background of the patient.
In the natural cycle, a woman will not have to take any hormonal drugs, which sometimes cause unwanted negative effects in the female body. She will make the first visit to the doctor after the end of the menstrual period, donate blood for hormones and will visit the doctor every two days so that foliar ultrasound can be monitored by ultrasound. As soon as the dominant follicle increases to 18-20 mm, an insemination procedure will be prescribed.
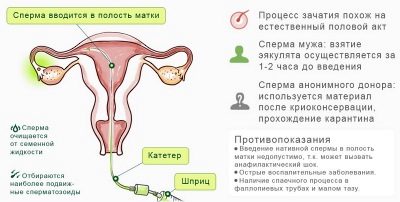
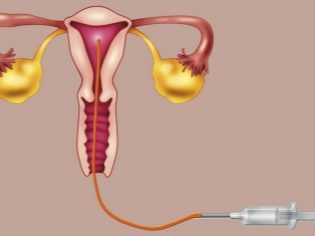
Immediately after ovulation, which is perfectly monitored and determined by ultrasound, the previously cleaned and prepared semen will be inserted into the uterus using a long and thin catheter and a disposable syringe. This procedure is painless, takes no more than five minutes, does not require anesthesia. For women with increased pain sensitivity, local anesthetics can be applied lightly.
If a woman has problems with her own ovulation, then the insemination protocol will be very similar to the IVF protocol. First, the woman will receive hormonal drugs that stimulate the maturation of the follicles. Up to 10-12 days of the menstrual cycle, growth will be observed by ultrasound. As soon as the follicle size reaches 16-20 mm, the doctor makes the patient a single hCG angle. This hormone stimulates the maturation of the egg and its release from the follicle approximately 36 hours after injection.
Immediately after ovulation, a sperm will be inserted through the catheter into the uterine cavity. During the ovulation period, the cervical canal slightly opens, which is why a thin catheter can be easily passed into the uterus without resorting to an artificial instrumental dilation of the cervix. That is why a woman does not feel pain.
After the introduction of sperm, a woman is recommended to keep her body in a horizontal position for at least 40 minutes, after which the doctor allows her to dress and leave the medical facility.
After stimulation of ovulation, from the first day, women are prescribed progesterone preparations, which contribute to the preparation of the endometrium of the uterus for the upcoming (possible) implantation of the ovum. To do this, more often use drugs such as "Duphaston", "Utrogestan". The doctor will tell you in detail how to behave after the procedure.
Sperm before the introduction is cleaned of seminal fluid and other impurities by methods of sedimentation, washing, passing through a centrifuge. As a result, only the concentrated ejaculate remains. Sperm is released from immature, defective sperm with poor morphology, from dead and sedentary cells. The remaining strong sperm should not live, therefore should be introduced as soon as possible. Purified sperm of the husband or donor is not subject to freezing, so cleaning is carried out immediately before the introduction.
Before taking sperm on a day of insemination, sexual abstinence is recommended to a man for 3-5 days, good nutrition, no stress. Alcohol, antibiotics and hormonal drugs are prohibited for 2-3 months before insemination. You should not take a hot bath, go to the bath or sauna. This will help prepare for the delivery of the biomaterial in the best possible way.
Recommendations
A woman who has undergone artificial intrauterine insemination procedure is recommended to stay in bed or half-bed mode for the first two days, do not take hot baths, do not swim, do not go to the bathhouse and do not sunbathe. It should rest more, sleep well and eat a balanced diet. Diets will not benefit.
If a doctor prescribes progesterone, they should be taken in a clearly defined dosage and in compliance with the multiplicity and scheme. To skip the next pill or the introduction of a candle is unacceptable.
Influencing the probability of successful fertilization and implantation is quite difficult, or rather, almost unreal. These processes are still beyond human control. But to increase the chances of success will help calm psychological background, lack of stress, positive thinking.
If there is an unusual discharge after insemination - bloody, greenish, gray or abundant yellow, you should immediately inform your doctor.
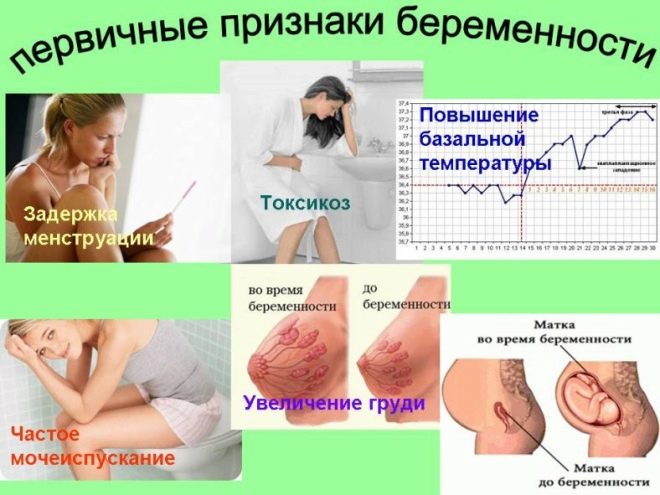
You should not be bothered by the search for early signs and symptoms of pregnancy - they may not be. Therefore, doctors recommend that you go to the diagnosis of pregnancy at the earliest a couple of days before the next menstruation is delayed. During these periods, a blood test can be made from a vein for plasma concentration of chorionic gonadotropic hormone - hCG. Pregnancy tests, which are dipped in a jar of urine at home, are most reasonable to start using only on the first day of the delay and later.
A week after the start of the delay, if the menstrual periods do not arrive, and the tests show signs of hCG, a confirmatory ultrasound should be done that will accurately determine not only the fact of pregnancy, but also its features - the number of fruits, the place of attachment of the ovum, the absence of signs of ectopic pregnancy other pathologies.
Feelings after the procedure
Objectively, sensations after intrauterine insemination are not much different from sensations of a woman who had unprotected sexual intercourse during the period of ovulation. In other words, there will not be any special sensations in the days that women expect and expect so much after artificial sperm injection.
On the first day, a slight pulling pain is possible, which is almost unnoticeable. These are the consequences of inserting a catheter into the uterine cavity.
If at this stage the lower abdomen is strongly pulled up, a high temperature has risen, you must call an ambulance, it is possible that the infection or air will get into the uterine cavity.
Approximately 7-9 days after the introduction of sperm, implantation may occur if fertilization has taken place. However, some women note a slight increase in temperature, the appearance of aching back pain and a small scanty discharge from the genitals of pink, cream or brownish hue. They are caused by blood entering the vaginal secretions from the damaged endometrium. The functional layer of the uterus is damaged when a fetal egg is inserted into it. This phenomenon is called implant bleeding.
It happens far from every woman, and therefore strongly rely on such a sign of pregnancy is not worth it. In addition, implantation is not always successful, and pregnancy, before it begins, can be interrupted for a great variety of reasons, not all of which are known and understood by medicine in general and gynecology in particular.
If the pregnancy nevertheless began, from the moment of implantation in the body, the level of the hCG hormone will slowly accumulate - it is produced by the cells of the chorion, which the fetal egg "clings" to the uterine wall. This does not mean that it will immediately begin to feel sick, as some people think. Toxicosis is also not all, and usually develops a little later.
Among the earliest signs of pregnancy, even before the delay, breast sensitization can be mentioned, a brief but daily increase in body temperature in the afternoon or in the evening to 37.0-37.5 degrees.A woman may think that she has caught a cold because a feeling of nasal congestion and frequent urination may well be added to the increase in temperature, though without pain (as in cystitis). This is how progesterone acts in the body, which begins to “accompany” the pregnancy from its first hours and “protect” the embryo.
There are women who have all of these signs are missing, even with the onset of pregnancy. And there are more sensitive women who intuitively feel that everything in the body now “works” in a new way. Before the objective data of blood tests and ultrasound is better to stop worrying and relax.
Efficiency
Most gynecologists rightly believe that regular sex life (at least 2-3 sexual intercourses per week) has exactly the same chances of conception as a single injection of sperm through a catheter. If sex life is irregular, the procedure still increases the chances of pregnancy, but only slightly - by no more than 11%.
The lower the probability of a successful procedure in women over 35 years old, since their oocytes are already in a state of natural aging, which implies a reduction in the quality of germ cells. Even if spermatozoa get to such eggs, they sometimes cannot fertilize them, and if the intercourse does take place, the probability is that the implantation will not occur or the ovum will be rejected.
According to the WHO, the percentage of a positive result from the first time intrauterine insemination does not exceed 13%. In the second attempt, the probability of becoming pregnant increases slightly - up to 20%; in the third and fourth, the maximum percentage of positive results is observed - 25-27%. And then the increase in positive dynamics is not observed. The probability remains stable at 20-22%.
In gynecology and reproduction, it is believed that after the fourth attempt at artificial insemination, the further application of the method is inexpedient - most likely there are other reasons that prevent pregnancy, the couple needs another examination and, possibly, IVF.
Cost of
The average cost of an intrauterine insemination procedure in Russia starts from 20 thousand rubles and can reach 60 thousand. The final cost depends on the region, on the protocol, on the need for donor sperm. If you plan to stimulate ovulation, the procedure can rise in price three times the minimum value.
Is the procedure at home real?
There are special kits for insemination at home. A man and a woman will be enough to get the sperm (by interrupted act or masturbation), and enter it. But such insemination cannot be considered intrauterine. With home use, only vaginal insemination is possible.
The kit includes a syringe with an extension cord, which allows you to enter the semen as deep as possible into the vagina so that the concentration of spermatozoa is as high as possible. However, with cervical infertility or low sperm motility, this will not help.
In addition to the syringe, the kit includes tests with high sensitivity to hCG. They can be applied about 10 days after ovulation.
Doctors are quite skeptical of such sets, because all the manipulations that the couple is invited to do are easily carried out during natural sexual intercourse.
Important questions
Many religions look at donor sperm fertilization with disapproval. In Orthodoxy and Islam, this is considered a violation of the sacrament of marriage, in fact, treason. Before agreeing, think carefully about whether you will then experience moral difficulties. The spouse who agrees to the insemination of the wife by donor sperm should know that the child will not be his family by genes and blood. A woman should know that it is impossible to choose a donor, all sperm in cryobanks is stored as anonymous.
But patients will be able to receive general information about the donor - age, eye color, height, hair color, occupation, level of education. This will help at least approximately pick a type close to the appearance of the spouse, who will have to raise the baby.
Unlike IVF, intrauterine insemination does not make it possible to ensure that the fetus does not inherit genetic diseases, that it does not have chromosomal abnormalities, because the selection of embryos is not done, as it happens during in vitro fertilization at the preimplantation diagnostic stage. The insemination procedure also does not allow to know the sex of the unborn child.
Pregnancy, if it occurs as a result of intrauterine injection of sperm, proceeds without features. It is no different from pregnancy, which occurred as a result of natural sexual intercourse. A woman will not need to go to the antenatal clinic more often, as well as to undergo additional examinations beyond the generally accepted ones, as is the case with women after IVF.
Childbirth can occur both naturally and by caesarean section. Insemination history is not an indication for cesarean section, it can be assigned for other reasons and indications.
Reviews
There are not as many positive reviews about successful intrauterine insemination in thematic forums as we would like. Most often, women describe several unsuccessful attempts to become pregnant by this method, after which they nevertheless agreed to an IVF protocol, the effectiveness of which is usually somewhat higher.
Women’s insemination forums often include men who offer sperm donation services at home for subsequent home administration of biomaterial using a special pharmacy kit. In this case, for their services, men take from 5 to 20 thousand rubles.
Women who still managed to become pregnant after intrauterine insemination, claim that it is a very convenient and painless way. Most made two sperm injections - the day before ovulation and the day of ovulation. Personal stories prove that chances are higher for women who have been stimulated by ovulation, although it also increases the chances for twins, because more than one egg matures.
About what insemination is, see the next video.