What does a healthy child's throat look like, and how is it sick?
When the baby falls ill, the mother tries to inspect the child's throat before the doctor arrives, but nothing really can be made out. This is because there is no clear idea of how a throat should look healthy, and how sick. Redness of the larynx is not always a sign of a serious illness, and the absence of redness, which in most cases mothers try to see, is not always a sign of health. We need to understand everything in order.
Symptoms
Children often sore throatThere can be many reasons - from allergies to chemical burns, but most often children are affected by respiratory viruses. There may also be bacterial inflammations, injuries.
You need to see what happens to the baby’s neck when the baby begins to show certain symptoms or openly complain about them:
- pain when swallowing;
- labored breathing;
- runny nose;
- headache, chills;
- sudden fever, fever;
- enlarged submandibular lymph nodes;
- refusal to drink and eat.
How to conduct an inspection?
If a mother glanced down at the throat of a child who sluggishly made “aaaaa”, it should not be considered as a survey.
There are certain rules for inspecting the throat:
- The child should be placed at the window facing the sunny side. If there is no such window or there is not enough natural light, you can use a small flashlight.
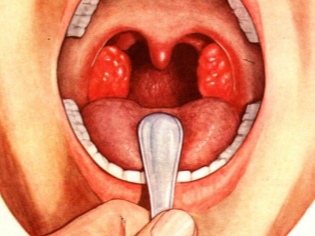
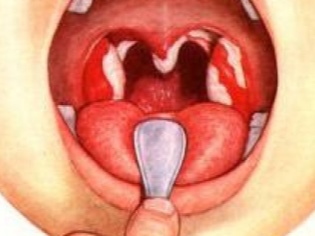
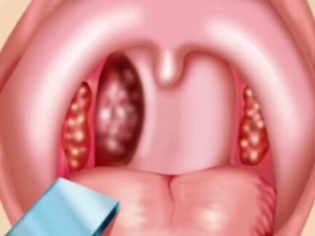
- It is clear that not every home has a medical spatula, but everybody has an ordinary tablespoon. With clean hands, washed with soap, take a clean spoon, pour over the handle with boiled water. After that, hands do not need to touch the handle.
- Using a spoon, gently push down on the center of the tongue. If you press on the tip, you can not see anything. If you put pressure on the root, then the child will definitely vomit, since this is the easiest and easiest way to induce a gag reflex.
- Tonsils are best seen., but to assess their condition, you need to ask the child to open his mouth as wide as possible so that the tongue is pressed against the lower lip.
- To assess the condition of the back wall of the larynxit makes sense to slightly press the tongue with a spatula or spoon.
- The child must breathe through the mouth, taking deep breaths.in which the language is reflexively omitted. So the area of the tonsils and lateral parts of the larynx is much easier to examine.
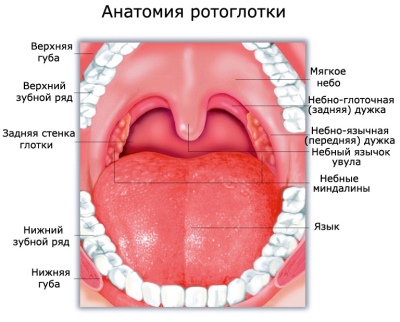
In order not to confuse the tonsil with the pharyngeal, it is necessary at least in general terms to imagine the structure of the throat.
Norm
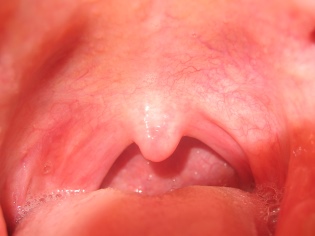
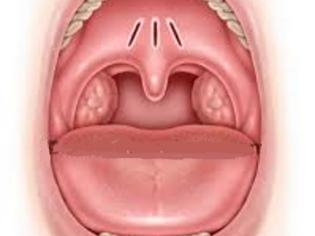
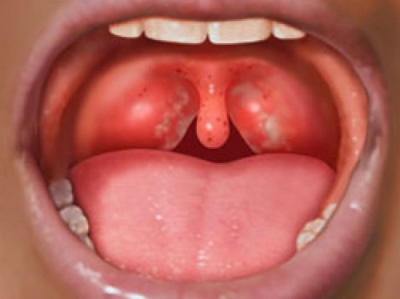
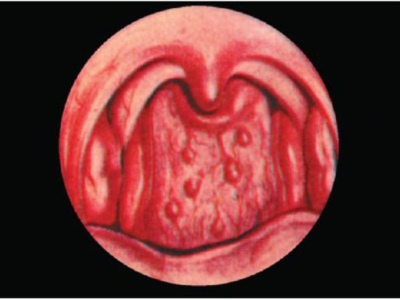
Normal healthy throat looks like this:
- In the oral cavity there are no visible changes, wounds, ulcers. The tongue is clear, with little or no physiological deposits.
- Tonsils are not enlarged, symmetrical, have a pale pink shade. Plaque, vesicles, ulcers, enlarged tubercles with pronounced boundaries and seals on them are not visible.
- The palate and palatine arches are pink. - sometimes more, and sometimes less saturated, but uniform. There is no plaque, ulcers, no stains.
- The lateral parts of the larynx are normally not swollen, pink.
- The back of the larynx, rich in blood vessels, may be redderthan the other parts of the throat, but it is only the state of the vessels that should be assessed - whether they are enlarged, whether there are pronounced hillocks, ulcers and plaque.
What does pathology look like?
The visual signs of a sore throat are much more diverse and point to very definite diseases. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a qualified doctor, who will be based not only on examination of the throat, but also on the total value of other symptoms, as well as the results of laboratory tests.
However, knowledge of the distinctive features of throat pathologies has not been disturbed by any parent yet. This is useful at least in order to know when urgently to call an ambulance, and in what cases to go to an appointment at the clinic or to call a doctor at home.
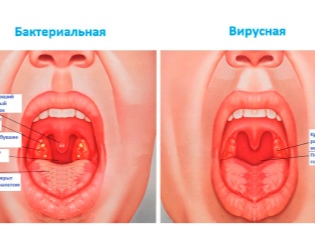
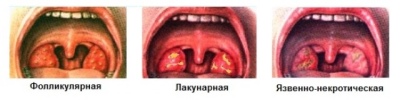
In the early stages sore throats tonsils become bright red, after a few hours they become covered white bloom. There may appear ulcers, some purulent or necrotic areas. The lumen of the larynx may be narrowed. With such inflamed tonsils, nearby lymph nodes may increase.
Sore throat is always accompanied by high fever, severe intoxication. After an acute period, a follicular tonsillitis can begin, which is well distinguished during the examination due to a bright sign - a loose purulent coating on the tonsils.
How to recognize a sore throat, see the next video.
- Necrotic angina characterized by dead gray areas of lymphoid tissue on the tonsils, sometimes the process extends to the palatine arches, and the tongue.
- Fungal sore throatAs a rule, it is accompanied by redness and inflammation of the tonsils, the appearance of visual friability, as well as yellowish-green deposits. Fungi in the throat are most often related to the genus Candida.
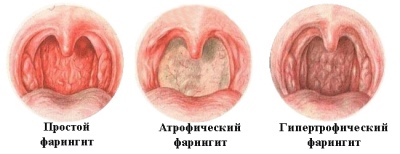
- Pharyngitis - a common childhood disease, which quite often begins to develop with a viral disease, with allergies, with some fungal infections (less often), as well as with bacterial infection. In almost all types of pharyngitis, the mucous membrane of the larynx is affected.
- With the simplest form (catarrhal pharyngitis) there is a slight reddening, as well as a slight swelling in the larynx, which does not affect either the amygdala or the sky.
- With a visible increase in the pharyngeal tonsils, pronounced redness and swelling of the larynx itself, we can talk about the possible hypertrophic pharyngitis.
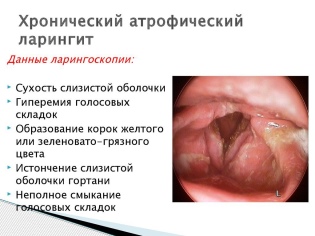
- Atrophic pharyngitis associated with atrophy of the mucous membrane, throat "lacquer", a bright sign - the vessels on the back of the pharynx. They become larger, visually they become smaller.
- Granular pharyngitis it is easiest to identify: the back wall of the larynx is covered with granules resembling growths in the throat. Slime clots may occur.
- May occur candidiasis. This disease is also called throat thrush, for a characteristic fungal plaque. Body temperature during white patches in the larynx rarely rises, complaints of difficulty in swallowing and pain may or may not be. The most important visual symptom is a white, cheesy patina on the larynx and palate, sometimes on the tonsils. These parts of the larynx may be slightly enlarged, inflamed.
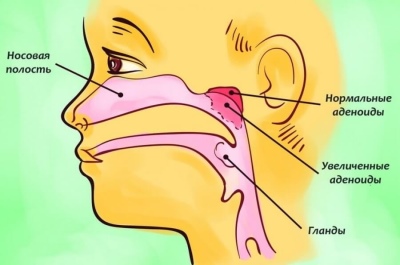
- Adenoids - This is often a childhood disease. It is accompanied by difficulty in nasal breathing, night snoring, and sometimes - a decrease in hearing. At home, to see the state of the adenoids because of their anatomical location is impossible. After all, adenoids in the throat are located in the arch of the nasopharynx. Only a doctor is able to see them, estimate the size, degree of swelling, the stage of the disease - using a special mirror with which he can look behind the soft palate.
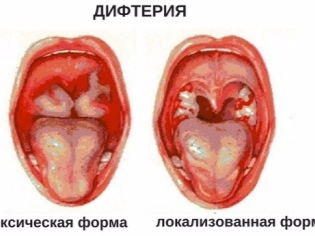
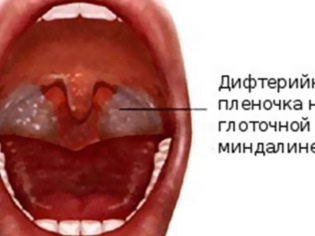
- Diphtheria. This is an infectious disease in which the oropharynx is most often affected. In diphtheria, the child will have enlarged tonsils, an inflamed swollen throat. A characteristic visual sign of the disease is a film deposit in the larynx and tonsils. The overlap can be extensive, and can be islets, it is hardly removed with a spatula, and then red bleeding spots remain. Usually the film has a grayish color.In diphtheria, swelling of the neck can develop, the lymph nodes often become inflamed, and the temperature rises to 38.0-39.0 degrees.
- Laryngitis is accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the larynx. On examination, severe redness and swelling of the throat are recorded. Then redness extends to the mucous membrane of the epiglottis.
The vessels of the posterior wall of the larynx are greatly enlarged, blood may leak from them, this is expressed by the appearance of red spots. Red dots are characteristic, incidentally, and complicated flu. With laryngitis, the child usually has hoarseness, a dry, barking cough that becomes stronger at night.
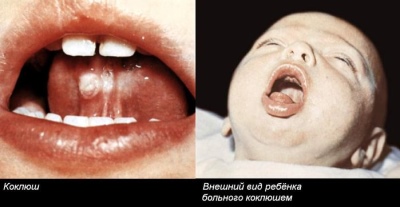
- Whooping cough - contagious bacterial disease, which is accompanied by strong coughing attacks. Sometimes accompanied by inflammation of the larynx, which is mechanical in nature. With constant strong attacks of suffocative cough, the mucous throat is irritated. However, visual examination of the larynx alone cannot be the basis for a diagnosis.
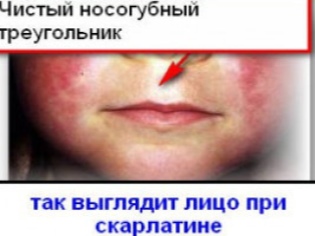
- Scarlet fever very easy to recognize, just by examining the throat of the baby. The most striking feature is the so-called scarlet-tongue tongue: in the first days - with a white patina and with barely visible bubbles, and then - of a rich bright raspberry-scarlet color, with a pronounced granular structure. The tonsils are inflamed, often covered with a rash, similar to pimples.
With a severe course of this contagious disease, small sores can be observed on the throat. Scarlet fever will help recognize its other characteristic symptoms - reddening of the skin, the appearance of a rash (with the exception of the nasolabial triangle).
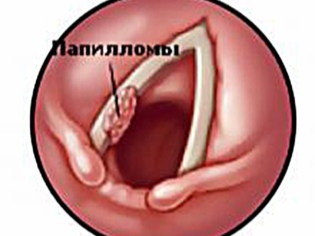
- Laryngeal papillomatosis. This is a benign tumor that can be easily seen on one of the parts of the larynx, if it has a place to be. Papilloma is rarely single, usually with a disease in the larynx there are several such formations. Quite often, they capture areas of the soft palate, tonsils, they can even appear on the lips. Polyps of the larynx also appear almost the same, but they have a smaller area of distribution and are usually more localized.
When should I call an ambulance immediately?
In all cases when parents suspect a child of the throat, be sure to consult a doctor. After inspecting and finding a problem, in no case do you need to start self-medicating. The fact is that the symptoms of many of the diseases described above are similar, and mother, who not every day sees the sore throat in different people, may well confuse the relatively safe laryngitis and whooping cough, which is very dangerous for children under 2 years of age.
Sores in the throat can also be misleading, as well as plaque in a language that is characteristic of many infectious diseases.
Therefore, only a doctor can make the right conclusion; in his arsenal there is not only special equipment for visual examination of the throat, but also a laboratory. He will quickly be able to answer the question of which pathogen and how long he has settled in the larynx, which antibiotics or antifungal drugs he is sensitive to.
There are symptoms that should make a sensible mother immediately call an ambulance:
- On examination, a narrowing of the larynx is noticeable, and at the same time the child has difficulty breathing. This may indicate a laryngeal stenosis. The condition is deadly, especially for young children.
- On examination, the mother noticed ulcers, ulcers in the throat (on any part of it), and at the same time the child has a high temperature (above 38.5-39.0 degrees).
- During the home examination, the mother saw bleeding vessels in the posterior wall of the larynx, and the child had strong fever and intoxication (with or without vomiting).