What to do if a child has a white plaque on the tonsils?
White throat, especially on the tonsils, always looks frightening, but because the fears of parents who find it in their offspring are well founded, because this can be a sign of quite serious pathologies. The fact that you can tell about the state of the baby white plaque on the tonsils and how to act if he appeared, you will learn from this article.
What does this mean?
White plaque on the tonsils and tongue of an infant can not speak about anything pathological and terrible. For babies who are on a dairy diet, eat exclusively breast milk or a mixture with a small proportion of complementary foods, a small white patina is normal. If there are no other symptoms of ill health, the child is alert, cheerful, eats well and sleeps, there is nothing to worry about.
It is much worse if such a bright patina on the tonsils appears in a child over a year old, who already eats not only dairy products. The plaque itself is not dangerous, it is always a symptom of the disease, so you need to carefully assess the condition of the toddler and understand what really bothers him.
Any plaque, including white, is a clear proof of the enhanced work of local immunity.
The nose and oropharynx - the entrance gate for all kinds of viruses and bacteria, as well as fungi. Naturally, they are the first to react to the penetration of a foreign microorganism. The nose is the production of abundant mucus, the task of which is to bind viruses, immobilize them, the larynx and pharynx - redness of the mucous membranes, violent inflammation, which is intended to create adverse conditions for reproduction for microbes and viruses.
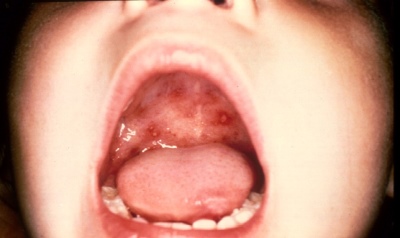
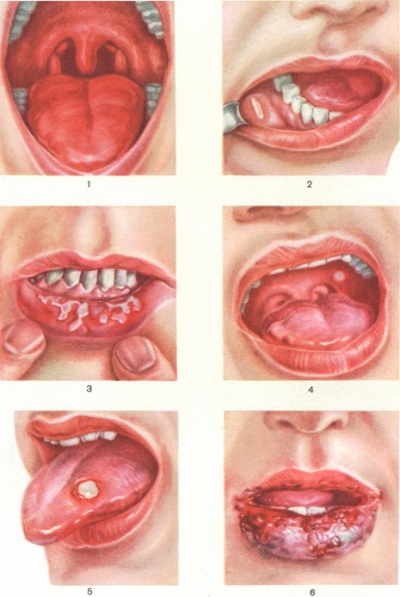
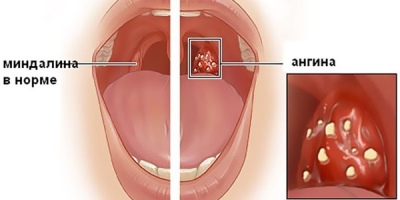
Tonsils (palatine, pharyngeal), which consist of lymphoid tissue, are an important link in the work of immunity, the same as the spleen consisting of lymphoid tissue. Understanding this, it is easy to imagine that they take a considerable blow when infected with something. White plaque on the tonsils is an accumulation of “fallen in the battle” immune cells-lymphocytes, discolored dead epithelium cells and virus particles or other pathogens “defeated by them”. According to the location, nature of the plaque, its density and shade, it is very likely to assume what kind of disease occurred in the child. However, for this, other symptoms should be assessed - fever, runny nose or lack thereof, the presence of inflammatory processes in the throat and other signs.
The reasons
Most often children are affected by viral infections. They are also leaders in the number of various symptoms, including white plaque on the tonsils. White dots, which gradually grow in volume and become similar to spots, may appear in some types of angina. At the same time, there is a pronounced swelling of the tonsil. Whitish bubbles are often a sign of stomatitis, they quickly move to other parts of the oropharynx - on the tongue, on the inner surface of the cheeks, gums, pharyngeal ring.
White bloom with virtually no temperature cause fungi. A fungal infection is considered to be a very dangerous condition, since it tends to spread quite quickly and sometimes affects the internal organs.
Below is a far from complete list of the most likely causes of white tonsillitis:
- Stomatitis. The mechanism of the onset of the disease to medicine is not yet very clear, in any case there is no single answer to the question of why lymphocytes suddenly begin to attack the peaceful and related mucous membranes of the oral cavity.There is an assumption that such a reaction is caused by viruses or microbes, but quite often laboratory tests do not show either one or the other. A white or slightly yellow patina on the glands (tonsils) is usually found at a very advanced stage of stomatitis. High temperature with stomatitis usually does not happen, if it is, it rests on subfebrile values - 37.0-37.50.
- Cysts on the tonsils. These benign neoplasms usually appear on the tonsils due to a violation of the drainage functions of the lymphoid tissue. Cysts are single and multiple. See them easily. The child complains of tickling, feeling something stranger in the throat when swallowing, his voice can become nasal, nasal breathing is disturbed. White plaque is localized exclusively in the area of formation of the cyst, then it does not spread. There may be no temperature at all.
- Pharyngomycosis. This disease is caused by fungi that infect the throat. At first, you can suspect the usual pharyngitis and this illusion is quite dangerous. In case of pharyngomycosis, colonies of fungi multiply rapidly and, in the absence of specific antifungal treatment, can affect the internal organs. A white patina appears both in the throat and on the tonsils, it is focal. If Candida fungi are the cause of the disease, the plaque will be milky white. If mold fungi, then a little yellowish. The process can proceed without temperature.
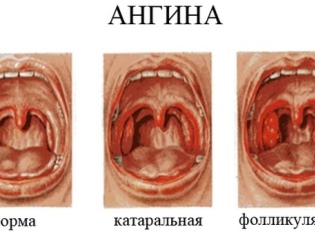
- Angina. All types of this disease are characterized by changes in the tonsils. They become swollen, inflamed, with some forms of sore throat on a bright red, contrasting amygdala appear white plaques, pustules. In the case of the Simonovsky-Pauta-Vincent's bacterial sore throat, the plaque on the tonsil looks like a stretched thin film of a white dirty serous color. Almost always, the disease is characterized by acute, high fever, severe pain in the throat. Any form of angina with improper treatment can give such a visual symptom as the appearance of ulcers, pimples, white spots, traffic jams on the tonsils.
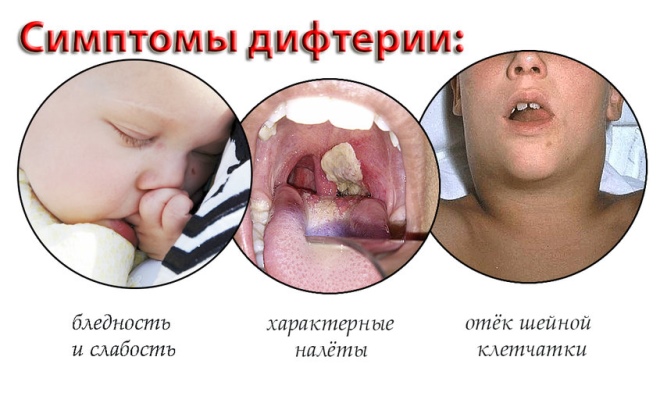
- Diphtheria. In the case of this dangerous infectious disease, the affected tonsils and throat swell dramatically, with the risk of respiratory failure in children. White bloom has the appearance of a film, with the removal of which bleeding wounds appear. Not long ago, diphtheria was considered deadly. Now all children in certain age categories receive mandatory vaccinations against diphtheria (DPT). Therefore, the probability of getting it is not as great as it seems. But to eliminate the danger is not worth it.
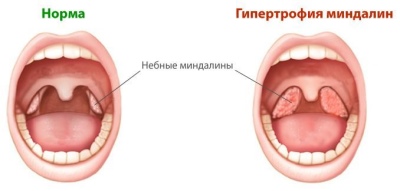
- Adenoids. Most often, this diagnosis is given to children aged 2 to 7 years. The child has nasal breathing, sometimes completely. It is associated with hyperplasia of the pharyngeal tonsil. Only a pediatric ENT is capable of seeing plaque and bumps on the pharyngeal tonsil, since its anatomical location is such that it is impossible to look into the nasopharynx vault without a special mirror. Plaque with adenitis appears when the disease is exacerbated, proceeds against the background of a concomitant catarrhal or viral malady.
Diagnostics
Even very caring and worried parents drop into the child's throat not every day, and therefore you must be attentive to the behavior of the baby and his complaints. Raid - Obviously not the first sign of the onset of the disease. If the baby is coughing, he has a sore throat, has pain when swallowing, chews his pain, does not breathe in his nose, it is necessary to take temperature and inspect the throat.
To do this, use a small flashlight and a spoon with a flat handle. You need to put the child at the window. It is not necessary to push the spoon strongly on the tongue, especially on its root - this provokes reflex vomiting. It is enough to slightly pinch the tip of the tongue to the lower teeth.
Estimate the color of the oropharynx, in a healthy child it is pink and monophonic.
It is difficult to assess the condition of the tonsils by eye, since there is no uniform size - in some children they are larger due to the congenital characteristics of the organism, in others it is smaller. But the inflammation on the tonsils and the white plaque accompanying it is not difficult to see. Normally, no films, ulcers and plaques on the tonsils should be. Be sure to evaluate whether plaque spreads in the form of small dots or tape to adjacent tongues, cheeks, and throat.
Examine and evaluate the degree of lymph nodes under the jaw, in the back of the head, and undress the child and carefully examine the skin for rashes, obscure formations, acne, which appeared suddenly. After that, parents should definitely call a doctor.
It is not necessary to take a child to an appointment at the clinic, some of the diseases that appear as a white patina are very contagious.
A doctor who attentively listens to everything that the parents saw during an independent examination will have to find out not only what ailment “happened” to the child, but also which particular pathogen is to blame. This is important for the choice of treatment tactics. Therefore, the baby must take swabs from the throat and tonsils. This allows you to accurately determine the bacteria or fungi settled in the oropharynx, and provide the necessary assistance. In addition, there is always a blood test, urine and feces.
Treatment
If bacteria cause the disease, the child may need antibiotics. Most often, treatment begins with antimicrobial agents of the penicillin group ("Ampicillin"," Augmentin "). If after three days there is no change in the child’s condition, the doctor may change the drug for a drug from another antimicrobial group, for example, a macrolide or a cephalosporin antibiotic. Treatment should be a course, at least 5 days. If the baby has become better, and the plaque began to disappear, before the end of the course of taking the drug, then it is impossible to interrupt the treatment.
If the doctor determines that the plaque has caused a viral infection, it may advise antiviral agents. Although their effectiveness today is not clinically proven. The most effective treatment will be associated with the local treatment of the tonsils. To do this, use the balm "Viniline", Antiseptic"Miramistin, Rinsing with furatsilina solution.
Fungal diseases in children are treated in a complex - using local treatment and antifungal drugs inside. The drug is chosen depending on the type of fungus, which is found in the analyzes. Fungal infection can be completely cured and minimized only as a result of early treatment, rapid diagnosis and a rather long course of medication - from 14 days. Then, after a short break, the course is usually repeated.
If it's a matter of enlarged pharyngeal amygdala, then the doctor will definitely put the stage and degree of adenitis. The first degree does not require surgical intervention, grade 2 adenoids are a very individual situation. If breathing is not completely disturbed, the doctor will definitely take the opportunity and advise to treat them at home. When adenoids 3 degrees are usually removed. But since this is an important immune organ, any chance of preserving them is important both for the doctor and for the child. The enlarged amygdala can be cut with a laser. This is the most benign type of intervention.
Regardless of the reason that caused the appearance of white bloom, the child may be assigned general strengthening and therapeutic physiotherapy at the stage of recovery. This warming, inhalation with non-bacterial and non-fungal diseases. Effectively showed itself and the method of treatment of enlarged and inflamed tonsils ultrasound.
The fact is that ultrasound has a surprisingly strong effect on lymphoid tissue. He helps her recover, oxygenates, helps to become more susceptible to drugs.Before and after exposure to the sensor, the tonsils are washed first with an antiseptic, and then with a prescribed drug solution prescribed by a doctor.
This method is not suitable for children in whom the disease is acute infectious, but after recovery, it will help to quickly rehabilitate and restore the ability of the tonsils to maintain local immunity.
Useful tips
- Problems with the tonsils and other organs of the respiratory system will be much less, if the baby breathes sufficiently moisturized air. It is desirable that she in the apartment was not lower than 50%, but not higher than 70%. Create such conditions will allow a special device for domestic use - a humidifier.
- Treatment of tonsils should not be carried out independently, without the advice of a doctor. Folk methods can harm a child.
So, with white bloom it is impossible to inhale with steam and apply warming compresses to the throat, because for bacteria and fungi the heat and moisture from the steam is the optimal environment for more rapid reproduction.
- When detecting white plaque on the tonsils, do not try to remove it yourself. with the help of improvised means. This can injure a child, cause bleeding, infection with additional microbes, and in the case of a fungal plaque - will lead to a more rapid spread of colonies that can cause serious complications, such as fungal sepsis.
- Immediately after the child's temperature drops, you can begin to walk in the fresh air. For the respiratory organs and for the process of restoration of the lymphoid tissue after infection, it is very important that the child lead an active lifestyle. In addition, walks help the immune system to recover and get stronger faster.
For more information on what to do if you find a white patina on the tonsils of a child, see the following video.