Childhood Obesity
Plump babes cause in many adults a real affection. However, overweight is not only a matter of aesthetic beauty. To maintain good health, weight should be maintained within the age norm. On the problems of childhood obesity will be discussed in our article.
When talking about obesity?
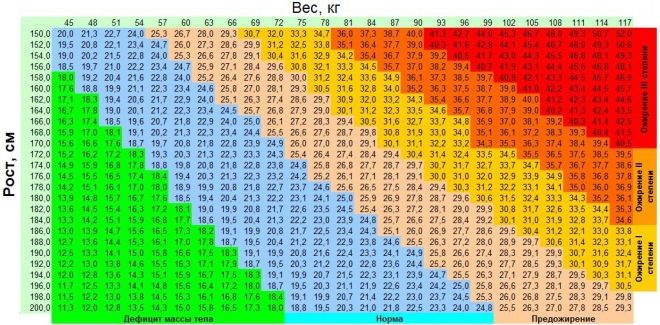
A pathological condition in which weight changes upward and exceeds normal age indicators by more than 15% is called obesity. Many specialists use a parameter such as body mass index to establish a diagnosis. This is the ratio of height in meters to double weight in kg. The body mass index is expressed in absolute numbers. Exceeding it above 30 indicates the presence of obesity in a child.
Obesity can develop at any age: both in newborns and adolescents. According to statistics, obesity is more common in girls under 8 years old than in boys. However, after puberty, this ratio changes. Often parents of newborn babies confuse obesity and large body sizes.
If at birth the mass of the child exceeds the norm, then this does not give grounds for the diagnosis of obesity.
Kids who are obese live in different countries. In economically developed countries there are more of them than in developing ones. This feature is largely due to excess nutrition, low physical exertion, as well as the abuse of fast food. In Asia, the number of overweight babies is several times lower than in Europe and America. This is due to the historical culture of nutrition and the absence in the menu of Asians an abundance of products containing saturated fats.
The incidence rates are increasing annually. This trend is rather unfavorable. Two out of ten kids in Russia are obese. In the countries of the former Soviet Union, an increase in the incidence rate is also increasing every year. Approximately 15% of babies living in Belarus and Ukraine are obese of varying degrees.
Rural areas have fewer children who are overweight. In many ways, this feature is due to greater physical exertion than in the city, as well as high-quality nutrition, which does not contain numerous chemical additives and preservatives. According to statistics, urban children have obesity in 10% of cases. For rural young residents, this figure is lower - about 6-7%.
The onset of the disease in childhood is extremely unfavorable. Many parents believe that excess weight only decorates the child and gives him a prettiness, however, they are mistaken. It is from an early age that babies begin to form eating habits. After all, you probably noticed that from the first months of life, the child has his own taste preferences. Some kids love porridge and chicken, and someone can not, without having to eat sweet fruit.
Small sweets can be identified from an early age. If at this time parents encourage each child to reach with a candy or a sweet calorie cookie, then the baby will develop an incorrect eating behavior. Over the course of his later life, he will be pathologically attracted to sweets and chocolate. Moreover, an adult already a person can not find any logical explanation for this.
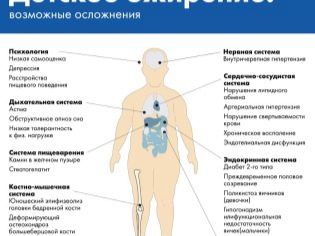
Children's endocrinologists deal with the treatment and diagnosis of various weight problems.The danger of obesity is that it can lead to permanent disruption in the work of many vital organs. Subsequently, babies have cardiovascular, neurological disorders, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as pronounced metabolic disorders. Late diagnosis of the disease and non-compliance diets contribute to the progression of the disease.
The reasons
The development of obesity in babies can lead to a variety of reasons. Most of the factors result from exposure from outside. Such action should be long and regular. This ultimately leads to the development of obesity.
The causative factors of overweight problems include:
- Excess nutrition. Daily excess of caloric intake of daily diet contributes to the saturation of the body with various nutrients. He begins to put all the excess in reserve. In the end, this leads to the fact that the child forms morbid obesity.
- Excessive consumption of sweets. Such fast carbohydrates are very dangerous. Once in the body, they begin to be absorbed in the oral cavity. Glucose (ordinary sugar) contained in such sweets rapidly leads to hyperglycemia (increase in blood sugar levels). In order to normalize blood sugar levels, the body secretes a huge amount of insulin and hyperinsulinemia occurs. This condition is fraught with the fact that all excess sweets are deposited in special fat depots - adipocytes, which contributes to the development of obesity.
- Lack of exercise. To burn excess calories from food requires active movement. Kids who eat a lot of high-calorie or sweet foods, but do not attend the sports section and spend most of their time at home with a tablet or phone, are at risk for the possible development of obesity. The balance between the incoming calories and their utilization and maintains a normal weight at any age.
- Heredity. Scientists have found that 85% of parents who have problems with excess weight, kids grow, who also have difficulties with being overweight. For a long time, experts believed that there is an “obesity gene”. However, to date there is no scientific evidence. Most likely, in the families where family members developed obesity, the wrong eating habits were formed. High-calorie food in this case leads to weight problems in both adults and toddlers.
- Chronic diseases. Various pathologies of the pituitary gland, adrenal glands, thyroid gland lead to pronounced disorders in metabolism. Usually such diseases are accompanied by multiple adverse symptoms. Being overweight is only one of their clinical manifestations. To eliminate obesity in this case, treatment of the underlying disease is indispensable.
- Big weight at birth. If a newborn baby has a body weight of more than 4 kg, then this is a significant risk factor in his later life for the formation of overweight. In this case, obesity is not caused by a large birth weight, but further overfeeding of the child. Low physical exertion only aggravates the development of the disease.
- Strong emotional stress. More and more scientists are saying that various “jams” lead to the development of weight disorders. Most often this condition occurs in adolescents. Excessive loads at school, the first unrequited love, the lack of friends causes the child to have a strong desire to "relieve" stress with the help of a chocolate or candy. In children aged 5-7 years, the development of this type of obesity often results in a painful divorce of parents or moving to a new place of residence.
In some cases, the combined effect of several factors leads to the disease.Eating disorders with reduced physical exertion always has the most important effect on the fact that the baby has extra pounds.
The intervention of the parents in this case should be as delicate as possible. It is necessary to show the child that you are on his side and are trying to help, because you love and care about him a lot.
Classification
There are several clinical forms of the disease. This has influenced the creation of several classifications, in which the main variants of obesity are highlighted, taking into account certain features. These nosological groups are necessary for doctors to establish a diagnosis and choose the right treatment tactics.
All normal weight indicators by age are usually collected in a special centile table. Using this document, you can determine the approximate rate of body weight for a child of different gender and age. All pediatricians use these tables to determine if a particular baby is showing signs of obesity. Norm is a match for a centile of 25, 50, and 75. If the child has a weight corresponding to centiles 90.97 and above, this indicates that the baby has obesity.
Doctors distinguish several clinical forms of the disease:
- Primary. May be exogenous constitutional and alimentary. In case of eating disorders and nutritional problems, they talk about alimentary (alimentary) obesity. If the baby has some features of the constitution and hereditary characteristics, then this is an exogenous constitutional option. Obesity is treated in this case with the help of prescribing therapeutic nutrition and with the obligatory selection of optimal loads.
- Secondary. Also called symptomatic. This type of obesity is characteristic of many chronic diseases that cause pronounced metabolic disorders. In girls, this condition occurs in various diseases of the ovaries, and in boys, mainly in the pathology of the thyroid gland. Treatment of overweight in these situations is impossible without eliminating the causes of the underlying disease. The correct tactics of treatment necessarily include the complex treatment of all chronic diseases that are the main cause of obesity.
Children's endocrinologists distinguish several dangerous periods during the development of a child, when the chance of obesity in a baby is as high as possible. These include the age of 3 years, 5-7 years, as well as puberty (12-16 years). At this time, parents should monitor the appearance of their child as closely as possible. If the baby has signs of excess weight, you should definitely consult with your pediatrician about this problem.
There is also a classification according to the degree of overweight. She was offered by A. A. Gaivoronskaya. With this classification, obesity can be divided into several categories, depending on the quantitative excess of weight over normal levels.
According to this division, there are several degrees of the disease:
- Obesity 1 degree. In this case, the weight exceeds 15-24% of the age indicators of the norm.
- Obesity 2 degrees. Excess body weight over normal rates is 25-49%.
- Obesity grade 3. Excess body weight over normal rates is 50-99%.
- Obesity 4 degrees. Excess body weight over the norm is over 100%.
Appearance
Excess weight significantly changes the appearance of the child. Excess fat accumulates in the subcutaneous fat. Normally, its interlayer is moderately expressed. In obesity, fatty cells (adipocytes) increase in size and volume, which leads to an increase in the thickness of the subcutaneous fat. Its largest accumulation is localized in the abdomen, on the outer surface of the arms and legs, in the buttocks and thighs.
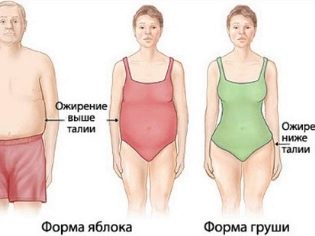
During puberty, there are specific differences in the distribution of subcutaneous fat. Thus, in girls, the greatest accumulation of excess kilograms is deposited mainly on the hips and buttocks, that is, in the lower half of the body. This type of obesity is also called "pear shaped"As the volumes of the predominantly lower half of the body increase.
Male obesity is also called obesity type "apples". In this case, the accumulation of extra pounds occurs mainly in the abdomen. This type of disease contributes to the fact that the waist disappears, and the configuration of the child’s body becomes excessively round. Toddlers look evenly plump, and in some cases even overly full.
Grade 2-3 obesity is accompanied by an increase in the thickness of the subcutaneous fat layer in the face and neck. This leads to a change in the appearance of the baby. He has not only cute plump cheeks, but also a shortened-looking neck. With 4 degrees of obesity, the eye slits somewhat narrow. The appearance of the child becomes sick and causes no longer emotion, but compassion.
Main symptoms
Obesity causes not only a change in the appearance of the child, but also leads to the appearance of various adverse symptoms. So, sick kids have blood jumps pressure, pulse accelerates, resistance to physical stress decreases, headache appears, shortness of breath develops. With prolonged obesity to adolescence, a child may develop metabolic syndrome. This is a dangerous condition caused by persistent hyperinsulinemia. It is dangerous in that it can lead to various cardiovascular diseases and diabetes.
With the development of obesity at school age, there are multiple adverse symptoms. So, it becomes more difficult for children to concentrate on learning new educational material, they quickly tire, they have daytime sleepiness, slowness. For a teenager, public opinion is very important.
Often, obese children have significant communication problems and have little new friends. This leads to the fact that the teenager feels useless and closed to communication, including with his parents and people close to him.
If obesity is secondary, then, in addition to being overweight, the child has other, more dangerous symptoms. Thus, the following clinical signs appear in adolescent girls with abnormalities in the ovaries: hair grows excessively, acne appears, severe hair loss occurs, the menstrual cycle is disturbed, the skin becomes excessively oily and prone to any pustular inflammation. In adolescent boys with secondary obesity, which developed on the background of pathologies of the pituitary or reproductive system, disorders such as gynecomastia (breast enlargement), cryptorchidism, hypoplasia of the external genitalia, and others appear.
Severe obesity leads to impaired breathing. Excessive subcutaneous fatty tissue in the abdomen and chest leads to the fact that the diaphragm is significantly tightened. This condition causes the appearance of a child. apnea. This pathological condition occurs during sleep. It is characterized by pauses in breathing, which contributes to the development of oxygen starvation of vital organs.
Excess kilograms exert strong pressure on the musculoskeletal system. The baby becomes much harder to walk and move. In the later stages of the disease, the child cannot even perform the usual active movements. While walking, the baby feels soreness in the joints and muscle weakness. This leads to the fact that the child walks less on the street and is more at home.
Complications and consequences
The long course of the disease has negative long-term effects. In children with obesity, the likelihood of developing cardiovascular, neurological and orthopedic diseases increases many times over.Persistent violations in the reproductive sphere lead to the fact that in adulthood, they can not conceive a child and have significant difficulties with carrying.
Pathological fractures are also most common in people who are obese. In this case, the fragility of the bones due to significant pressure on the organs of the musculoskeletal system overweight. According to statistics, obese boys in childhood often have various anatomical disorders in their feet. This can lead to the development of flat feet and valgus deformities.
Disturbed eating behavior leads to the fact that the child appears numerous chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. Most often it is: chronic gastritis and pancreatitis, cholelithiasis with the development of calculous cholecystitis, enterocolitis and irritable bowel syndrome.
Often these pathologies in children go from acute to chronic. This leads to the fact that the child is prescribed medications for continuous use throughout his life.
Diagnostics
Often parents do not pay attention to the presence of obesity in the baby. Especially if the child is of preschool age. They think it's cute. Many fathers and mothers believe that all symptoms will pass on their own by adolescence. In some cases, this does happen. However, they provide the child a "bearish" service.
Childhood is a very important period of life. It was at this time that the baby formed all the basic habits and behaviors that he would later transfer to adulthood. Nutritional behavior is also formed in childhood. All taste preferences remain then throughout life.
If the baby gets used to eating fast food or too fat and fried food, then later he fixed this behavior as a persistent eating habit. As an adult, it will be extremely difficult for him to refuse such products. In order to avoid this - you should carefully monitor the diet from an early age.
If there are signs of obesity, it is necessary to take the baby to consult a doctor. The specialist will be able to identify the cause of the disease, prescribe a complex of examinations to detect secondary obesity, and will also recommend to parents what course of therapy is required.
Obesity is a disease that needs to be carefully monitored and therapy administered.
Treatment
According to the clinical recommendations, the treatment of obesity is carried out taking into account the severity of overweight. An integral part of the treatment is the appointment diets. If a child has risk factors that trigger the development of obesity, then diet should be followed throughout life.
Medical nutrition should be low-calorie. Fatty foods, especially those with saturated fats, are completely excluded from the baby’s diet. In the diet of an obese baby, there must necessarily be a sufficient amount of coarse fiber. It is mainly present in fresh vegetables and fruits. Industrial sweets (cakes, pastries, sweets, chocolate, etc.) are completely excluded.
In addition to therapeutic low-calorie nutrition, optimally chosen physical activity is required. If the severity of overweight is low, visiting sports sections will do. With a significant excess of extra kilograms, playing sports without the control of doctors is very dangerous. In this case, physical therapy exercises are well suited.
The intensity and complex of physical exercises is coordinated with a sports medicine doctor or a professional instructor with a specialized education. Excessively active training in obese babies is not permissible, since they can cause the child various complications from the musculoskeletal system.Exercise should be at a quiet pace and with a certain frequency of repetitions.
Various physiotherapy methods can also help in the fight against obesity. Cavitation, ultrasound therapy, therapeutic massage eliminate extra centimeters. It is important to remember that only physiotherapy alone can never completely eliminate obesity. For the treatment of obesity, a systematic approach is needed, which includes the compulsory proper nutrition or therapeutic diet, as well as the selection of optimal physical exertion.
To eliminate the symptoms of secondary obesity, treatment of the underlying disease is required. In this case, extended diagnostics may be required. Usually, children's endocrinologists with the active participation of gynecologists, nephrologists and other specialists in need are involved in the treatment of secondary obesity. Prevention of obesity plays a very important role in preventing overweight in babies.
Rational nutrition, active physical exertion and good psycho-emotional attitude contribute to excellent health and maintaining a normal weight throughout life.
Should the weight and height of the child meet the standards? Dr. Komarovsky answers these and other questions related to the problems of overweight in children.