Symptoms and treatment of poliomyelitis in children
Poliomyelitis was stopped by the universal efforts of the governments of many countries of the world. But it is not yet possible to completely eliminate the disease from their list of existing serious diseases. In this article we will talk about what constitutes this dangerous disease, how to recognize it and how to treat it.
What it is?
Polio is a viral inflammation of the cells of the gray matter of the spinal cord. Ailment is most often childish and very contagious. Spinal cells are affected by poliovirus, which leads to their paralysis. As a result, the nervous system ceases to function normally.
Usually there are no visible symptoms in polio, only when the virus enters the central nervous system, it causes paralysis and paresis.
They began to study the disease in the 19th century, and in the middle of the 20th century, polio acquired the scale of a national disaster in many countries, including European ones. The polio vaccine was developed independently by American and Soviet scientists. In recent years, countries have announced that they are free from polio. Outbreaks of illness are occasionally observed only in three states - Nigeria, Afghanistan and Pakistan.
In 2015, two cases were recorded in Ukraine. Doctors have every reason to believe that in this country polio can spread because only half of Ukrainian children received vaccine from the disease, according to statistics. In Russia, the situation is under control, but it tends to worsen. First of all, it is connected with the influx of migrants, including from neighboring Ukraine.
Causes
The cause of polio is a picornovirus from the enterovirus family. The virus is quite stable, for example, in an aquatic environment, it can live up to 100 days without losing its properties, and in human feces up to six months. The virus is not afraid of low temperatures, and also perfectly reflects the attacks of gastric juice, passing through the human food paths. Destroy the virus can boiling water, sunlight, chlorine.
A child may be infected by a sick person or carrier who has no visible symptoms.
Through the mouth, the virus is released into the environment for several days, and with feces - for weeks and even months. Thus, there are two possible ways of infection - airborne and alimentary (through dirty hands, with contaminated food). The ubiquitous flies make a significant contribution to the spread of this virus.
After penetration into the child's body, the poliovirus begins to multiply in the lymphoid tissue of the tonsils, in the intestines and lymph nodes. It gradually enters the bloodstream, and from there into the spinal cord and central nervous system.
The incubation period ranges from 3 days to one month, most often from 9 to 11 days. At the end of the period, the first signs of the disease may or may not appear, and then it will be possible to recognize poliomyelitis only according to the results of laboratory tests.
Most cases of polio are recorded in summer and autumn. At risk - children from six months to seven years. In the first few months of life, polio does not threaten a child at all, since maternal innate immunity reliably protects the baby from this type of enterovirus.
After an illness, a persistent lifelong immunity is produced to the polyvirus.
Symptoms and signs of forms
In most children, polio does not appear even after the end of the incubation period. Symptoms will depend on the form of the disease and the immunity of the child.
Inapparatory
No symptoms. Paralysis does not develop. Detected only in blood tests. Markers are antibodies to poliovirus.
Visceral
The most common form. At the end of the incubation period at the very beginning of the disease, there may be symptoms of the most common viral infection - sore throat, headache, fever, and sometimes diarrhea and nausea.
The disease recedes in about a week. Paralysis does not develop.
Non-paralytic
When it shows all the symptoms of viral infection (sore throat, fever, abdominal pain), but more pronounced than in the visceral form.
There is tension in the occipital muscles, neurological manifestations. The disease is accompanied by a severe headache, but does not cause paralysis.
The child recovers in 3-4 weeks.
Paralytic
This is the rarest and most dangerous form of the disease. When it all begins, as usual ORVI, but the symptoms are rapidly progressing, the child's condition rapidly deteriorates until the occurrence of delusions, episodes of loss of consciousness, seizures.
If the child holds his fingers along the spine, he will experience severe pain. If you ask the child to touch the lips of their own knees, it will not work. Sits a baby with such a form of the disease with the trunk tilted forward and with an emphasis on both hands, in the so-called tripod pose. This form can cause paralysis. Typically, paralysis occurs with the death of one-fourth of the nerve cells.
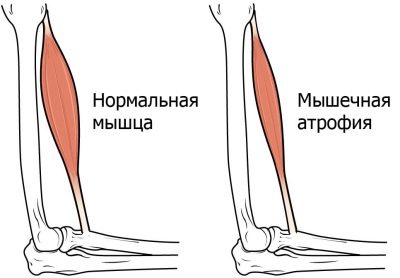
Full paralysis is quite rare, it occurs only in 1% of cases. But here are partial paresis of individual muscles are more common. Paralytic manifestations do not occur immediately, but as the temperature decreases, closer to recovery. The most frequently atrophy muscles of the legs, less often the respiratory system or torso.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of poliomyelitis are very similar to the clinical manifestations of many diseases caused by enteroviruses and herpes viruses. That is why when symptoms of ARVI appear, it is important to call a doctor in order not to lose time and to detect the disease, if any. Laboratory diagnostic methods will help in this.
Blood, a swab from the nasopharynx and a sample of feces will be sent to the laboratory. It is in them that a virus can be detected.
First of all, the doctor will need to distinguish polio from similar traumatic neuritis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, transverse myelitis. Poliomyelitis is characterized by a high temperature at the onset of the disease, descending paralysis, decreased tendon reflexes.
If you suspect that a child has polio, they are necessarily hospitalized in an infectious disease hospital.
Consequences and complications
The dead cells of the spinal cord are gradually replaced and scarred, therefore the functions of that part of the body for which they were responsible are partially lost. The spinal form of paralysis, in which the thoracic, cervical and lumbar regions are affected, is threatened with flaccid paralysis of the limbs.
With bulbar poliomyelitis, cranial nerves are affected, so complications will be located higher - basically, the process of swallowing and the reproduction of sounds by the vocal apparatus is disturbed. The most dangerous is considered respiratory muscle paralysis, it can lead to death.
Both the facial nerves and the brain can be affected if the virus reaches the central nervous system. The latter is fraught with the development of life-long persistent paralysis.
Prognosis for non-paralytic polio is favorable.
When paralytic pathology in varying degrees, remain with the child for life.However, a competent and responsible approach to rehabilitation makes it possible to avoid disability in case of non-severe lesions and to restore motor functions in full or almost complete.
Treatment
Despite the fact that mankind has worked hard to create a vaccine against polio, there is no cure for this disease. The virus is completely insensitive to antibiotics, and antiviral drugs are not able to slow down its progress.
The only protector of the child at this moment is his own immunity. Only he is able to produce antibodies that can kill the virus before it hits the brain and kills a large number of spinal cord cells.
All therapy is reduced to the fact that the child is symptomatic care. When the temperature rises, they give antipyretic agents, with muscle pain they give painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs.
The occurrence of paralysis is closely monitored by doctors in the hospital, when neurological disorders and convulsions appear, muscle relaxants are prescribed to the child - muscle-relaxing drugs, anticonvulsant treatment regimen.
If the respiratory function is damaged, resuscitation assistance is provided by connecting the child to the ventilator.
In the process of treatment, the child is shown abundant warm drink, bed rest and complete rest.
Greater attention is given to the recovery period. It will be there that will decide whether paralysis will remain or pass, whether the child will receive a disability or not. Rehabilitation after poliomyelitis begins with a restriction of physical activity and physical activity of the child. Strain muscles can not be to limit the paralyzed zones.
Then gradually increase the load. The child is prescribed:
therapeutic gymnastics (exercise therapy);
hydrotherapy;
electrical stimulation of paralyzed or atrophied muscles;
massotherapy.
All these measures are needed exclusively in the complex, and the rehabilitation period promises to be slow. The task of this stage is not even to restore the functions of dead brain cells, but to stimulate compensatory mechanisms — healthy cells should take on some of the functions of dead brothers. If this is achieved, then forecasts are more favorable.
During this period, hormonal preparations, enzymes, vitamins, calcium and magnesium preparations can be prescribed, since these substances provide faster contact when conducting nerve impulses between the brain, nerve cells and muscles.
Can adults get sick?
Despite the fact that polio is already routinely considered a childhood disease, adults can also become infected with this ailment. They have a harder illness, and the consequences are always more pronounced and dangerous than in children. In adults, death is also more likely.
Vaccination against polio for adults is recommended to be done once every 5-10 years, and each time before visiting countries where polio has not been defeated. Recall, this is Afghanistan, Pakistan and Nigeria.
Prevention
Nonspecific disease prevention includes standard hygiene requirements - the child must wash his hands after returning from a walk and before eating, adults must fight flies, as they are carriers of the poliovirus.
Children with suspicion of this disease are isolated in special hospitals, and in kindergarten or school that they attend, quarantine is declared for 21 days. During these three weeks, medical workers closely monitor the slightest changes in the state of health and condition of the other children, taking temperature daily, inspect the tonsils.
Vaccination and effects of vaccinations
The most effective prevention of this disease - vaccinations. Today, two types of vaccines are used in Russia: one contains live, but severely weakened, polioviruses, the other contains completely inactivated viruses killed by formalin.
Polio vaccination It is included in the list of mandatory on the territory of the Russian Federation, it is included in the National Calendar of preventive vaccinations and is free of charge.
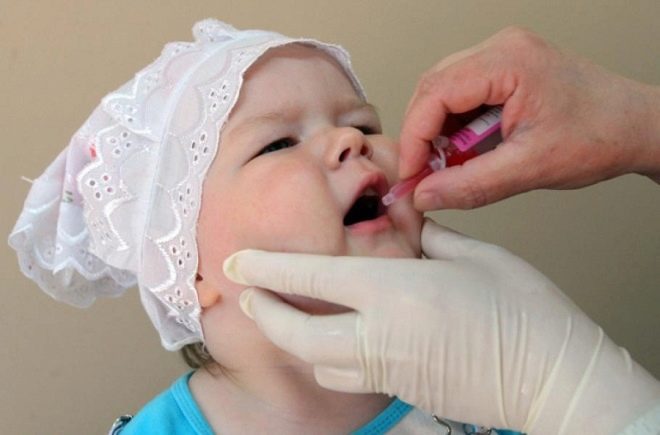
The first wave of vaccination begins at a very early age. Vaccine in the form of drops for oral administration is given to a child at 3 months, at 4.5 months and at 5 months. Then the drops will give the child in one and a half years, at the age of 6 and at the age of 14.
Very often, pediatricians combine polio vaccination with DPT vaccination (vs whooping cough, diphtheria and tetanus), however, provided that the child at this point is older than 2 years.
Vaccination can be not only in the form of drops, but also in the form of a solution for injection, but such vaccines are made only abroad (in France, Belgium) and are purchased by the Russian Ministry of Health annually.
Multicomponent vaccines, which immediately combine components against whooping cough, tetanus, diphtheria and polio, are also manufactured by foreign pharmaceutical companies.
Domestic vaccines are offered free of charge at the children's clinic. If parents have a desire to instill a baby with an imported drug, then they will have to pay for it.
It is not recommended to feed the child abundantly before the vaccination, it is important that on the eve of the visit to the clinic he should empty the intestines. At the time of vaccination, the baby must be healthy, it should not have fever and other symptoms of possible diseases.
After vaccination, the child does not feed or drink for an hour.
Vaccination is not dangerous for children's health, although it can sometimes cause certain unpleasant consequences, in particular, diarrhea. It is temporary and does not pose a danger to the child.
In one case per million, the administration of a live vaccine causes polio disease. If the vaccinated child is sick, then the probability of paralysis is estimated at only 1%.
Sometimes a child may react to the vaccination with a small allergic reaction of the type of urticaria. The vaccine does not usually raise the temperature.
After vaccination, you can walk and swim, and lead the most ordinary way of life. That's just with the introduction of new products in the diet of the child after vaccination is better to abstain at least for a week.
Contraindications for vaccination
Children are released from vaccination, who reacted to the previous vaccine with violent manifestations from the nervous system, who had neurological disorders after vaccination. Children with HIV infection and other causes of immunodeficiency, also do not get vaccinated.
If a child is sick or has had a viral infection for a long time, the vaccine is temporarily delayed. At the same time, other diseases not caused by viruses are not grounds for cancellation of the next vaccination.
You should not refuse this vaccination, as poliomyelitis is a dangerous disease that can make a child disabled, despite the level of development of modern medicine, its capabilities and the timely provision of skilled care.
For more information about polio, see the following program by Dr. Komarovsky.