Symptoms and treatment of colds in children. How to strengthen the immune system with frequent colds?
A cold in a child is a common and widespread phenomenon. Some babies suffer from colds up to 10 times a year. This problem is particularly relevant during the off-season, as well as during the cold season. What is really a cold, how to treat and what to do if a child is sick often, we will tell in this material.
What it is?
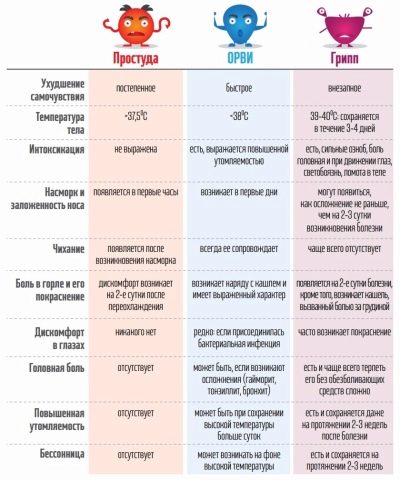
Such a disease as a cold, in the medical sense does not exist at all. What people call colds, from the medical point of view, may be ARVI, ARD, influenza, herpes virus, or the manifestation of an existing chronic respiratory disease. The famous pediatrician of the highest category, Dr. Yevgeny Komarovsky, claims that approximately 95% of all childhood diseases, called “colds” by mothers and grandmothers, are of viral origin.
Then why the people have approved the concept of "cold"? The answer to this question is quite simple: when a child is supercooled, gets under drafts, his immune protection decreases. We are surrounded by several hundreds of various viruses that are just waiting for the immune system to "fail" in order to penetrate the body and begin to destroy healthy, full-fledged cells, adjusting them for their own needs.
If the child froze for a walk, wet his feet, and the next day he started a runny nose, cough, fever, the parents immediately conclude - a cold. Indeed, thermal instability caused a decrease in local and general immunity, and viruses were able to start their destructive business.
Thus, speaking of colds in a child, one may suspect him of one of the acute respiratory viral infections - rhinovirus, adenoviral infections, respiratory syncytial virus, influenza virus, parainfluenza and about three hundred different ailments, differing only in the name of the causative virus and having only minor differences in the clinical picture.
Sometimes cough, runny nose, red eyes, which parents take for a cold, are symptoms of allergies. A rash on the lip, in the nose, on the chin, having characteristic watery blisters, which is also habitually called colds, is nothing but a manifestation of herpes virus infection - the virus herpes first type or herpes simplex.
All viruses, except for herpes, use the upper respiratory tract to enter the child's body. They affect the cells of the ciliated epithelium of the nose, nasopharynx, and larynx. And then, when the protective epithelium is crushed, penetrates the blood, causing the characteristic symptoms - intoxication, vomiting, fever, chills, muscle pain, headaches.
A herpetic virus replicates locally, but it has an amazing ability to stay in the body forever. If a herpes virus infection has occurred once, the pathogen will be in a dormant state in the body of its carrier for life, from time to time (for example, during hypothermia) letting it know about its characteristic rash and itching.
In allergies, respiratory manifestations with the common cold are usually not associated, unless, of course, the child is allergic to cold (this type of allergy is known to medicine, but it occurs infrequently).For the appearance of allergic rhinitis and cough, as well as allergic conjunctivitis, an aggressive allergen is needed. It is not always possible to track it, and therefore at the time of onset of symptoms the cause is not obvious.
The viruses themselves are not too dangerous for the child, they act at the cellular level and are active only until the immunity of the sick person is able to produce specific antibodies to the pathogen. It usually takes from 3 to 7 days, after which the child recovers. Complications of viral infections are dangerous.
The younger the child, the weaker his immunity. The common cold threatens the newborn to a lesser extent, since children are protected by passive immunity for up to six months, which they inherited from the mother’s blood even in utero. The baby also receives antibodies against common viruses with breast milk. But such immunity does not always work.
Most often, colds (we will call them as familiar to the reader) are found in children aged 6 months to 7-8 years. Then the immunity begins to grow stronger, "learns", accumulates information about viruses transferred by the child, has a supply of antibodies. Diseases as a result can be hidden and more easily.
Respiratory diseases are most difficult for children aged from 6 months to 1 year and from 1 year to 3 years. They have the highest percentage of deaths from influenza and complications from all other acute respiratory viral infections. At 2-3 years old, the kid suffers more often than one-year-old crumbs, since he already attends kindergarten and is in contact with a large children's team.
Infection occurs through airborne droplets and contact routes; all respiratory viruses and herpesvirus are highly contagious, and therefore easily cause epidemics and even a pandemic.
Allergic manifestations, similar to a cold disease in the clinical picture, are not infectious and are not transmitted to other children, even through close contact, the exchange of toys, dishes, and things.
The reasons
In the common sense of the common cold, there is only one reason - hypothermia. If you look at the question more broadly, it becomes clear that the real reason lies in the reduction of immunity, because a strong immunity may well withstand viruses, and in childhood the immunity is weak and not “trained”.
Premature babies are most susceptible to colds, as well as toddlers who have diseases and abnormalities of the respiratory organs, kidneys, and cardiovascular system since birth. The risk group includes children with severe impairments of the immune system (HIV, AIDS, a number of rare genetic syndromes with congenital immunodeficiency).
Children under 3 years old, even healthy ones, all without exception are at risk because of the age-related weakness of immunity. The virus is more likely to cause the disease, if the child has a weight deficit, he does not feed fully and in a balanced way, suffers from a vitamin deficiency, leads an inactive, mostly sedentary lifestyle.
The chances of getting sick from a child are higher if there are infected people in his family. Although if a nursing mother gets sick, then the child most likely will not have the disease, because with breast milk she will give him antibodies to a specific virus developed in her body.
For children who have already grown out of infancy, contact with the diseased is dangerous. It is important to not be able to infect a child if mom or dad is sick. Children are most susceptible to colds if their immunity is weakened by a recent illness performed by an operation.
Immunity falls during periods of severe psychological distress and severe stress, which is why children so often start to get sick when the familiar world collapses for them - parents get divorced, they are sent to kindergarten, school starts, parents leave for a long time or the whole family moves to a new place residence.
Frequent diseases are sometimes caused by improper care, or rather, gross errors on the part of parents. In families where “greenhouse” conditions are created for children from birth, they coddle the child, try to protect it from the sun and wind, from any drafts, coddle and overfeed, they get sick more often. Attempts by parents to protect a child from diseases with frequent medication for any reason also adversely affect the state of children's immunity.
In the families of nomadic peoples, where there are many children and all summer and autumn, until snow appears, they run barefoot along the street, bathe in small rivers, where they are not forced to eat soup or cutlet, where the child gets food not when it is lunch time, and then, when he wants and asks for food, ARVI, flu and other colds are rare.
The mucous membranes of a child with normal immunity are a reliable barrier against viruses. If something is wrong with the child’s condition or the external conditions do not contribute to the health of the mucous membranes, then infection occurs.
We dealt with internal factors, but external ones need clarification. To resist viruses, mucous membranes must be sufficiently well moistened.
If in the room where the child lives, always keep the vents closed and the heaters turned on (so that the child does not catch a cold or freeze!), The probability of falling ill increases tenfold as the drier air dries out the mucous membranes, this barrier becomes thinner.
Signs of
Usually, the common cold becomes noticeable with the first signs of malaise. But the disease begins earlier, from the very moment of infection, just during the incubation period the child may not feel anything unusual. The duration of the incubation period can be different - from several hours to several days, and here the main role is played by a specific pathogen and the age of the patient. The younger the child, the shorter the incubation period. On average, the invisible period for most colds lasts about 1-2 days.
Attentive parents at this stage may notice some oddities in the child’s behavior. So, the baby can often scratch the nose or rub the ears. This is due to a feeling of dryness and itching in the nose, which may be slightly pronounced after infection. Often, in the incubation period, children become more lethargic, scattered, they get tired more quickly, sleep longer. In the absence of other signs of illness, few parents may suspect the onset of the disease.
At the end of the incubation period, the virus enters the bloodstream and noticeable, obvious signs of illness begin. As a rule, a viral infection starts with a rise in temperature.
The highest temperature is observed with the flu (up to 40.0 degrees), with adenoviral and rhinovirus infections, the thermometer can show from 37.5 to 39 degrees. Muscle pains, chills, aching joints, pain and pressure sensation in the eyeballs, photophobia are added to the heat.
Parents can pay attention to the fact that the children have watery eyes, the child may complain that he has pain in his legs, arms, back. The temperature can be kept from 2-3 to 5-6 days. The duration of the febrile period depends on the specific virus. With the flu, it lasts about 4-5 days, with adenovirus infection - up to 6-7 days. It is most difficult for parents of babies, for whom it is important to distinguish such heat from temperature, sometimes observed during teething.
In viral infections, the temperature is always high and persistent, whereas during dentition it is easy to reduce it with the help of antipyretic agents.
High fever can cause symptoms of intoxication - the child will develop vomiting and diarrhea, abdominal pain. In this case, it is important to exclude an intestinal infection, and without a doctor you cannot cope with this task.In small children, if the virus enters the bloodstream, a small rash may appear, associated with impaired vascular permeability and integrity. From the nose in babies can go to the blood.
Obligatory for the majority of colds symptoms - runny nose, cough. A runny nose with flu is characterized by the absence of nasal discharge, but for most other acute respiratory viral infections, it is usually accompanied by rhinorrhea (leakage of clear, liquid nasal mucus). A cough with a viral infection is always always dry and frequent at first, it gradually becomes wet - with the sputum, the body begins to get rid of the ciliated epithelium particles and dead viruses by the time of recovery.
Shortness of breath with a cold most often develops in young children. It is considered a rather dangerous symptom.
In a mild course, all the symptoms, although acute and rapid, are somewhat erased. In severe infections, the symptoms are more pronounced. And with the most severe toxic form of a cold, convulsions, loss of consciousness, and delirium can be observed.
Complications
As already mentioned, colds are dangerous precisely because of their complications. What could threaten the child and how to protect him from this? First of all, it should be understood that complications can develop both during the disease and after it.
In the first case, the most common threats are the development of febrile seizures on the background of high temperature, dehydration on the background of intoxication, vomiting and diarrhea, as well as hemorrhagic syndrome associated with the violation of the integrity of blood vessels by the virus. Due to the high heat, there may be irregularities in the work of the central nervous system.
After the illness suffered, other complications may appear. Most often, respiratory symptoms acquire a protracted and even chronic course. So, often due to a viral illness, the child develops bronchitis. A dangerous consequence can be pneumonia. Unpleasant and difficult to treat bacterial rhinitis, tonsillitistracheitis.
It often happens that after suffering flu or ARVI the child became hard to hear. Be sure to visit a doctor, because hearing loss can be a sign of otitis, which is successfully treated, and a sign of neuritis of the auditory nerve, in which the changes are almost irreversible. Complications on the ears - one of the most frequent. Pus in the eyes can talk about the development of bacterial conjunctivitis, pain in the legs and joints can be a sign of polyarthritis.
The probability of complications is higher, the younger the child. Negative effects can also occur if the primary disease is not properly treated.
According to expert estimates, the likelihood of complications from a viral infectious disease is on average about 15%. In infants, it is about three times higher.
Treatment
Properly treating colds is to maintain immunity, to create conditions for the child in which its natural defense mechanisms can mobilize as soon as possible and give a decent immune response to the invasion of the virus. The sooner parents pay attention to the “harbingers” of an impending disease, the more chances there are to minimize its consequences.
At the earliest stage, abundant irrigation of the nasal mucosa, gargling, steam inhalation and plenty of warm drinking will help the child. Anything that can moisten the mucous membranes and increase their resistance to the action of the virus will benefit. The disease manifests itself, but in mild form and the child quickly recovers.
If the symptoms have already appeared, treatment will also be aimed at supporting immunity, but in addition the child will need symptomatic treatment. First of all, at the first signs of a cold, you need to measure the temperature, and if it is high, put the baby in bed and call a doctor. A pediatrician is necessary for all babies up to 3 years old, even if the symptoms are not very pronounced, as well as for all older children with severe symptoms.
It is not necessary to call the clinic, but immediately to an ambulance if the fever of a baby under 3 years old does not subside after the use of antipyretic drugs, if vomiting has opened and diarrhea has appeared, the first signs of dehydration have appeared. Loss of consciousness, confusion of speech, delirium, convulsions are also a reason for calling an ambulance.
Let's say right away that medicines that can quickly cure a viral infection have not yet been invented. The best drugs targeted antiviral effects are used in the hospital and mainly in injections, and everything that is advertised on TV has almost no relation to the treatment of viral infection. Antiviral drugs do not have proven clinical effectiveness.
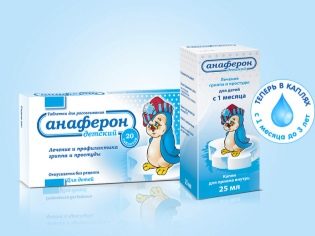
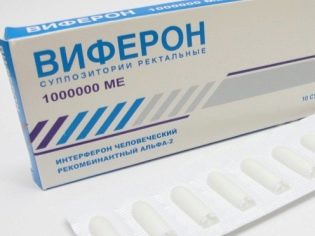
The called doctor, of course, will give the appointment. Usually recommended are means such as “Anaferon for children” in tablets, “Immunal"(Drops),"Oscillococcinum"(Dragee)," Viferon "(candles). These drugs are homeopathy. With respect to them, not only the antiviral effect, but also the effect in general, has not been proven. The doctor was not mistaken, he just knows that these funds can not harm the child, and only his own immunity can cure him. Therefore, parents can, with a clear conscience, reject such drugs and concentrate on organizing the proper care of a sick baby.
It is preferable to treat children under one year in the hospital due to the high risk of complications. The remaining children, if the disease is mild, can be treated at home. To mobilize immunity, a small patient should be in a well-ventilated room. The air temperature in the room should not exceed 21 degrees Celsius. Humidity in the room should be at least 50-70%.
If there is no special device - a humidifier, you can simply hang wet towels over the radiators and make sure that they do not dry out, wetting them in a timely manner. In this microclimate, recovery will go much faster, because the mucous membranes will not dry out.
The second prerequisite - plenty of drink. It should not be hot or cold. Give your child drinks at room temperature, so the liquid will be absorbed faster by the body. Carbonated drinks, juices, milk are not suitable for drinking. But the perfect rosehip decoction, tea with chamomile, homemade cranberry juice and dried fruit compote. If the baby cannot or does not want to drink, it is impossible to drink it due to age, it is better to immediately contact the “ambulance”. Especially if the child has vomiting and diarrhea.
With a strong intoxication, the baby should be given not just to drink, but to drink special solutions that will help to compensate for the loss of water and mineral salts in the body. Powder "Smekty", "Rehydron»Humana Electrolyte is easy to dilute and apply. If it is not possible to feed the child with such a solution, it should be taken as soon as possible to the hospital, where saline, vitamins and necessary supplements to compensate for the mineral metabolism will be administered intravenously.
Temperature for colds is important. It contributes to the development of interferon, enhancing the immune response. Therefore, without the urgent need to fight the heat is not worth it. Only if the temperature has exceeded 38.0 degrees, should antipyretic agents be given to the child.
Acetylsalicylic acid based preparations should be avoided, they are not suitable for children. It is best to give paracetamol or any drug based on it ("Nurofen" - syrup or "Cefecone D"- candles). Anti-inflammatory nonsteroidal drugs, such as "Ibuprofen" in age dosage, can also help.
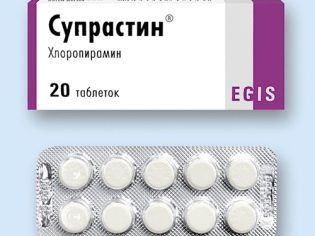
When nasal congestion can be applied vasoconstrictor drops ("Nazol baby", "Nazivin Sensitive", "Nazivin"), but not more than five days in a row.Such remedies facilitate nasal breathing, preserve the effect for a rather long time, but cause a rapid drug addiction. A sore throat can be rinsed with saline or furatsilina. With a strong intoxication, the child can be given antihistamines, such as "Suprastin", they reduce the sensitization of the body.
Muscle pain will help reduce any warming ointment, the use of which is not contraindicated in this age. Remove manifestations of herpes infection on the lip or in the nose can be local application "Acyclovir"- a drug designed specifically to combat viruses herpes. For dry cough, mucolytic drugs are prescribed in syrup.
During treatment, it is often recommended to give the child "Gluconate calcium, Vitamins. For parents who love to treat children with several drugs at once, the following information will be useful:
- if you give the child two drugs at the same time, there is a 10% chance that they will interact negatively with each other;
- if you treat a child with three drugs at once, the likelihood of side effects and allergic reactions increases up to 50%;
- If you give your baby five medications in a single course of treatment, the likelihood that they will enter into an inadequate reaction increases to 90%.
With proper treatment, the child will recover in 3-5 days without complications and negative consequences. Self-medication can end very sadly — at home, the unprofessional gaze of a mother or grandmother makes it very difficult to consider the symptoms of incipient complications.
How can you not treat a virus?
As already mentioned, improper treatment increases the chances of developing complications, and therefore parents should be aware of The most common mistakes that tend to make moms and dads, if the child suddenly fell ill with colds:
- Do not inhale at high temperatures.
- You can not rub the child badger fat, fat, if he has a high body temperature.
- Attempts to rub the child with vodka or vinegar can lead to critical narrowing of the vessels.
- It is impossible to treat a child with a cold with antibiotics if he does not have bacterial complications. The use of antibacterial drugs increases the likelihood of severe complications, and antibiotic viruses are completely insensitive.
- You can not wrap the child in the heat, it should be stripped to the pants and T-shirts, cover it with only a thin sheet.
- It is strictly forbidden to prescribe independently any child any drugs, to give funds from the field of alternative medicine, without consulting a doctor.
- You can not put ice on the temples of a child with a high temperature - this is fraught with spasm of the vessels of the head.
- Do not force the child to eat at any cost. A hungry body is easier to cope with the disease, because energy is not spent on the digestion of food. It is because sick children refuse to eat. Feed need on demand. But water is a must.
- During a cold, you cannot feed the child sweets and sweets - such products obviously will not do him good.
Folk remedies
Traditional methods of treating colds are known to many, but not all of them are equally useful. Inhalation of vapors of boiled potatoes in their uniforms often causes burns to the mucous membranes of the respiratory organs, and the instillation of onion juice into the nose can cause dying of the membranes. Therefore, in treating children, one should not blindly trust all means that are positioned as effective for colds and flu.
For children from 6 years old, in the absence of allergy, essential oils can be used in small quantities - fir, pine, eucalyptus. They are added drop by drop into the inhaler and inhaled vapors if the baby does not have temperature and complications. With heat and bronchitis, such a “treatment” only hurts.
With herbs, you should be careful, referring to the instructions on the use of herbal remedies, because they are quite allergenic. The use of honey and bee products in the treatment of colds in a child requires special care; for children under 3 years old, such recipes are not recommended at all. Propolis tincture for kids older than 3 years should be necessarily water-based, and not alcohol. Honey to prepare a warm drink should be of high quality. But the main thing - the child should not be allergic to all these products.
Acupressure well helps to relieve headaches, and chest massage at the stage of recovery, the so-called drainage massage, will help the earliest sputum discharge from the bronchi.
There are also recipes that do not withstand any criticism - for example, advice to bury a baby in the nose with a cold of breast milk. Milk is a good breeding ground for bacteria, and viral rhinitis very quickly runs the risk of severe bacterial rhinitis, which will require serious antibiotic treatment. Mustard, generously poured by grandmother's hand in the socks of his beloved grandson, can cause only the strongest allergies, but does not bring recovery in any way.
Prevention
Precautions and common sense will help protect your child from a wide variety of colds. The child should not supercool. But when choosing winter clothes and shoes for him, remember that overheating is no less terrible than hypothermia. If the baby is sweating during the whole walk, he is more susceptible to decreased immunity and the occurrence of viral and allergic diseases. The child should not walk in wet shoes. If the legs are soaked, be sure to change it into a dry pair. In winter, you also need to make sure that your child’s hands and face do not get cold on the street.
If the baby walks barefoot around the house, there is nothing wrong with that. Many parents believe that walking with bare feet contributes to hypothermia. In fact, the vessels of the lower extremities may, without negative consequences for the body, narrow and not release internal heat. You cannot catch a cold from such a walk. But if the baby is sitting on the cold booty, then hypothermia is very, very likely.
In the season of increased incidence you should not take a child to a place where there is a large crowd of people, if there is an opportunity, it is better to refuse to travel in public transport.
There is vaccination for influenza, and it should not be neglected. Vaccination will not only reduce the chances of contracting this dangerous infectious disease, but will also allow the disease to proceed more easily if the infection does happen.
There is no vaccination against other infections, but there is protection - a strong and healthy immunity. Parents should strengthen it, preferably from the very birth of the crumbs.
How to increase the body's immune power?
The process of working to strengthen the immune system should be systematic and lengthy. After the appearance of the baby in the family, parents need to decide how exactly they intend to strengthen the health of the crumbs. Hardening can be practiced from 1 month. It should be gradual, phased in order not to catch a cold. Usually used douche after normal bathing with water, the temperature of which is slightly lower. First one degree, then two degrees, and so on. Dr. Komarovsky recommends gradually bringing the water temperature for evening bathing to 25 degrees Celsius.
When the child grows up, he does not need to be protected from walking barefoot on the grass, sand, pebbles, on the floor in his own apartment. Useful for immunity bathing in open water and pools. Not only water, but also solar and air baths make it possible to make children's immunity stronger and more durable.
You should not abandon the prophylactic vaccinations put by age - they allow the baby to form protection against the most dangerous viruses and bacteria. Annually vaccinate a child against the flu, and in the summer, if you are going to go to the sea, from a rotavirus infection. Refusal of vaccinations does not make the child stronger, this is one of the common misconceptions regarding vaccination.
In infancy, it is not necessary to abandon breastfeeding early - the child gets many antibodies from the mother's milk. Artificial milk formula, even the most expensive and useful, will not be able to give him such protection. When a son or daughter grows up, it is important to instill in the child a good habit of eating properly and balanced as early as possible. In the diet of the offspring, there should be enough meat and fish, dairy products, butter, and, of course, fresh vegetables and fruits. Babies who are "pampered" with pizza and burgers rarely grow up healthy and strong.
It is worth taking care that the child from an early age was an activity that he likes, preferably active in the open air. Computers and tablets are not the best assistants in strengthening immunity.
When choosing a sport for a child, you need to understand that a chess club, boxing, and karate are sports in which training usually takes place indoors. But skiing, cycling, swimming, figure skating, hockey and football, equestrian sport - what you need for a child, whose immunity needs to be hardened.
If a child has no inclination for sports and he demonstrates a natural inclination for drawing or playing music, you can have a good family tradition - in the evenings you can all walk together in a park or a public garden, on the weekends you can go nature, play badminton and volleyball, swim and sunbathe.
If the question of improving the immune defense has never faced the parents and the child has grown up often ill, there is no need to despair. Starting hardening, gymnastics, walks and sports is not late at any age. However, a more reverent attitude to lifestyle correction will be required. Before starting hardening and choosing a section for a child, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
By the way, the pediatrician can prompt and some effective means - food supplements that activate the immune system. Such supplements include echinacea and wild rosehip syrup.
To strengthen the immune system with frequent colds, help the correct approach to the period of recovery of the child. Parents just need to break the vicious circle of permanent diseases. To do this, after another cold infection you should not take the child to kindergarten or school immediately after recovery. Give him time to recover, walk more outdoors, even in winter, play active games outside.
You should not rely on medicines, which are positioned by manufacturers as a means for the prevention of diseases in the cold period. Usually they are homeopathic and absolutely have no effect on immunity.
For an often ill child it is important to observe the daily regimen, it is enough to sleep at night (at least 9 hours), to alternate activities more often - after the kid has painted a little, it is necessary to take a walk, and then you can plan a quiet reading or game. It should protect the baby from situations in which he will experience strong experiences. Follow the psychological climate in the family, be interested in the affairs of the baby in kindergarten or school. Teach him calmly to experience troubles and blows of fate, and then his immune defense will be stronger and more reliable.
Frequent illness at an early age is no reason to believe that it will always be so. In 90% of cases, respiratory problems and susceptibility to viruses "outgrow", and by adolescence the child begins to get sick less often.
To learn how to treat a cold in a child correctly, see the next video.