Symptoms and treatment of tetanus in children
One of the most dangerous consequences of infection of wounds and abrasions is tetanus. Both his parents and doctors are rightly afraid of him. And all because even with the current level of development of medicine for tetanus, no one is insured. About how a child can get this disease and how to treat it, we will tell in this article.
What it is?
Tetanus is a severe infectious disease, occurring exclusively in the acute form, which is expressed by convulsions, muscular tension and damage to the central nervous system. Only one substance can cause such a condition - tetanus exotoxin, which produces tetanus bacillus. It is one of the most powerful bacterial poisons known to science today. Only Botox is more dangerous than him. Once in the child’s body through wounds, the abrasion bacterium begins to produce this exotoxin in large quantities.
The wand is opportunistic. As long as there are no suitable conditions for it, it does not pose any danger. Normally, the bacterium is found in the intestines of every person and many animals, and it enters the environment with feces. In large quantities, the tetanus microbe is found in the soil in rural areas, where the level of pollution by fecal masses for objective reasons is much higher. In the ground, in water, on various objects, the wand can exist only in the form of spores, but in this form, neither sunlight nor air can kill it. In the earth, for example, it can live almost a century, and in salty sea water - more than half a year.
The tetanus bacterium becomes active and dangerous when released into the environment where there is no oxygen and the temperature is above 37 degrees. Ideal habitat - deep wounds, cuts, abrasions. The toxin, which secretes a microbe, paralyzes the motor cells of the central nervous system.
The disease has been known since ancient times. The great doctor Hippocrates died of a tetanus own son. The study of the disease began in the XIX century, then the anti-tetanus serum was created, and in the early twentieth century it was possible to obtain toxoid, which is used for prevention.
The hotter the climate in the region and the higher the humidity, the more cases of tetanus are recorded there. Unfortunately, the vast majority of cases occur in newborns - about 75-80%. They are infected with a stick through the umbilical wound. In second place - children under 14 years old, mostly boys, because they are more often injured. More often than others, children living in rural areas suffer from tetanus. At risk - babies from 3 to 7 years, because they are the most inquisitive, active, often injured, fall, damage the integrity of the skin.
Mortality and projections
Mortality from tetanus is high. Even with the current level of development of medicine, it is about 25%. And science cannot do anything about it because of the aggressiveness of the bacterium - exotoxin rather quickly causes heart paralysis, respiratory arrest, severe rapidly developing pneumonia, and sepsis.
Mortality among unvaccinated children reaches 80%. In newborns, mortality is even higher - up to 95-97%.
Projections for the future after suffering tetanus depend on the pathological changes caused by the toxin in the body. The most "innocuous" consequences are bronchitis, sprains and bone fractures that can occur during the acute period.The most difficult with dubious predictions are pulmonary edema, muscle and tendon ruptures, muscle tears from bones, vein thrombosis. Late complications - spinal deformity, paralysis of the facial nerves.
After an illness, a child can begin to attend school or kindergarten only after 2 months, it is exactly how long it takes for the body to recover after tetanus. Registered with a neurologist, he will stand at least 2 years if there are no significant complications.
Causes and mechanism of occurrence
Tetanus bacillus is widespread, so you can get it anywhere. It does not depend on hygiene, nor on the state of immunity. If a microbe has penetrated into a wound, especially into a deep wound, then it quickly enough starts producing a toxin. The poison spreads through the body through the bloodstream and affects the spinal and medulla, but not completely, but selectively only intercalated neurons of the reflex arcs.
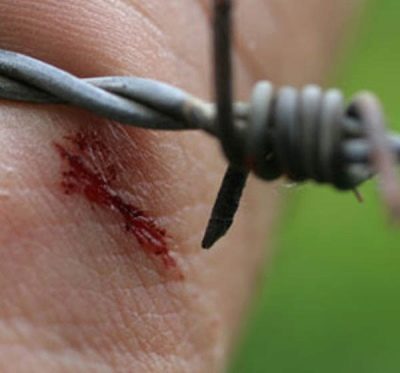
The most dangerous are deep and lacerated wounds that could not be treated in time. A child can get such wounds on the legs and arms when falling, after a cut, during an open fracture. The incubation period is about 8 days for babies and up to 25 days for older children. The farther the wound from the brain and spinal cord, the longer the incubation and the easier the flow. In newborns, the incubation period can last from several hours to 14 days.
Symptoms
Before the onset of the disease, the first signs of future tetanus sometimes appear. Muscles in the area of injury may begin to tremble, spontaneously strain. There is a headache, the child begins to yawn, the throat can ache, sleep and appetite are disturbed.
The first phase of the disease lasts up to two days. It all starts with pulling pains in the area of injury. The cut itself, by the way, can already heal, heal. After a few hours - a maximum, a day, the child manifests the so-called trisism - tension and cramps of the masticatory muscles. It becomes difficult for the child to close the mouth. In some cases, it can not be opened, because the cramp tightens the jaws in a closed state.
How difficult the main phase of the disease will be depends on whether the child has tetanus vaccinations or not, and how quickly the parents went to the doctor and the baby was able to receive emergency help. Average, the height lasts 10-12 days, in some cases up to three weeks.
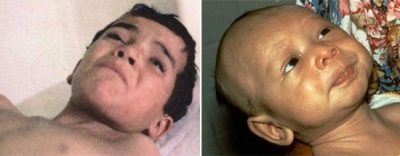
A so-called sardonic smile appears on the face of a child due to muscle contraction - the mouth is stretched, eyebrows are raised, as when laughing and crying. Such a mimic "mask" expresses great suffering. Then a spastic picture of the muscles of the back and arms and legs develops.
Swallowing is difficult due to the fact that the spasm reduces the muscles of the larynx, the occipital tone is increased. The shoulders, back, abdomen become stiff, tense. In severe cases, the whole body is reduced to a painful spasm, the ability to move is retained only in the hands and feet. Convulsive seizures last from a few seconds to a few minutes. Severe tetanus is accompanied by almost continuous spasm.
The attack can begin spontaneously, and can be triggered by a harsh light, the voice of a person, an unexpected sound. In response to such an external irritant, the baby’s face turns blue, “inflates”, eyes look bulging, sweating increases. The poses that a child can take in a fit are varied. Most often, he arches arched, leaning on the bed only heels and the back of his head. Children usually do not lose consciousness. In the process of recovery, convulsions gradually subside, seizures become more rare, shorter, until they stop altogether. It is during this recovery period that various complications can develop.
Tetanus is less dangerous for a vaccinated child; in the case of infection, it develops only a local form of the disease, in which convulsions and spasms do not affect the whole body, but are only observed in the affected limb or another part of the body. Often, such a tetanus still becomes common. In infants and newborns the disease is of a general nature.
Always acute stage is accompanied by sleep disturbance up to complete insomnia, as well as high temperature.
Severity of the disease
In mild form, all the above symptoms are moderately expressed, the temperature is at 37.0-37.9 degrees. The incubation period has a long period (about 3 weeks), seizures are mild.
Medium severity is characterized by convulsive seizures, which are repeated several times a day. The incubation period (after injury or injury) is approximately two weeks. Body temperature - from 38.0 degrees. Symptoms develop quickly, in 3-4 days.
Severe tetanus characterized by intense and frequent seizures, palpitations, heavy sweating and drooling. The temperature is very high (from 38.5 to 40.0 degrees), the incubation period was about 7-10 days. Muscles are in an increased tone even in intervals between attacks of spasms. The seizures themselves are repeated more than 10 times a day.
Very severe tetanus - this is a critical condition in which the convulsions are constant, almost without interruption, the temperature is at elevations of 40.0 degrees and higher, breathing is increased, the child sweats heavily. In attacks, the skin turns blue, the baby is experiencing respiratory failure. The incubation period from the moment of injury to the development of the first signs does not exceed 7 days, all the symptoms develop in a matter of hours, and sometimes with lightning speed.
Diagnostics
When high fever and convulsive syndrome, characteristic contractions of the facial muscles, with difficulty swallowing in infants, parents should immediately call an ambulance. Doctors evaluate the type and strength of the spasms, measure the temperature of the child and take him to the hospital. Sometimes, diagnostics require the taking of cerebrospinal fluid for analysis to distinguish tetanus convulsions from convulsive syndrome that accompanies meningitis and some craniocerebral injuries.
Treatment
Tetanus is never treated at home. The child should immediately be hospitalized in an infectious disease hospital, where he will receive emergency help and will be closely monitored for each subsequent phase of the illness.
Therapy includes several important points:
- The wound, even if it has already been healed, requires urgent opening and processing, to ensure the access of oxygen inside the wound so that the pathogen can die.
For the disposal of toxin, which has a destructive effect on the central nervous system of the child, tetanus toxoid serum is administered.
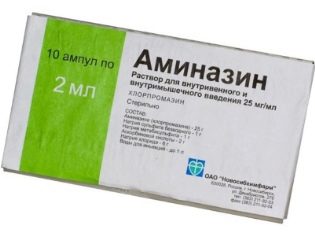
The child is administered drugs that relax all muscle groups, relaxants Aminazin, Seduxen and others.
The ill is placed in a separate shaded box with noise insulation to avoid external influences and provocation of convulsive syndrome.
If the exotoxin has already struck important organs and systems, conduct resuscitation actions - artificially maintain ventilation of the lungs, monitor the work of the heart.
According to the situation, they solve the issue of nutrition. Because of a strong spasm, it is difficult for a child to eat, sometimes it is extremely difficult to feed a baby even through a tube or intravenously. Depending on the frequency of attacks, the nature of spasms, choose the best option for feeding liquid food. Usually, a probe is inserted after preliminary injection of muscle relaxant drugs.
If there are complications, treat each separately. In the hospital, the child can spend from 30 to 90 days.
Prevention
Expectant mothers should not even consider the option of home birth. Whatever beliefs held by a woman and her family members, the health of the child is more important.It is during home deliveries that take place in the absence of sterility using untreated and unsterilized cutting tools, the highest probability of infection of the newborn with tetanus bacillus.
All the injuries and injuries that a child receives in the process of active knowledge of this world, must be properly processed promptly. For this purpose, antiseptics are used, all foreign objects, soil particles are removed from the wound. It is not always worth trying to do it yourself, it is better to consult a doctor and conduct a primary surgical treatment of the wound. This is quite enough to prevent the development of a tetanus wand spore. However, even the timely treatment of the wound does not always protect the child from the development of the disease.
During the walk, you should carefully monitor that the child does not approach stray animals, especially dogs. Their bites are often accompanied by infection with tetanus bacteria.
The most effective prevention is vaccination. The vaccination is included in the schedule of the National Preventive Vaccination Calendar and is considered planned. This is the same DTP - vaccine, which, in addition to the pertussis and diphtheria component, includes tetanus toxoid. Children after 4 years of age are vaccinated without the pertussis component of the ADS vaccine.
Adults do revaccination preferably once every 10 years. Children are given the first vaccination at 3 months, then at 4.5 months and half a year. Revaccination is prescribed for one and a half years, provided that the child was vaccinated in accordance with the schedule at exactly 3 months. If for some reason vaccines were given later, then 12 months are counted to determine the timing of revaccination from the third vaccination. The following revaccinations are performed for children at the age of 7 and at the age of 14.
Parents who are categorically opposed to vaccinations in general and DTP in particular should be especially vigilant, because unvaccinated children have a higher risk of becoming infected with tetanus, and the severity of the disease is always greater than in children who have been vaccinated.
Sometimes there is a need for emergency prevention. Her conduct and vaccinated and unvaccinated children in the following situations:
injuries to the integrity of the skin (cuts, lacerations, deep splinters, severe abrasions);
second, third and fourth degree burns - thermal, chemical and others;
penetrating wounds of the gastrointestinal tract;
long carbuncles, severe furunculosis, gangrene;
animal bites.
In all these situations, the child is given a dose of tetanus toxoid in order to avoid the development of a serious infectious disease.
The main prevention of tetanus - meeting the timing of vaccination, which must be reported by the pediatrician at each subsequent visit to the doctor's office.
But wounds and deep injuries should not be smeared with iodine at home, it is better to deliver the child to any emergency room, where he will not only be treated correctly for the lesion, but must be given emergency prevention by injecting a tetanus toxoid.
About what dangerous tetanus, see the following video.