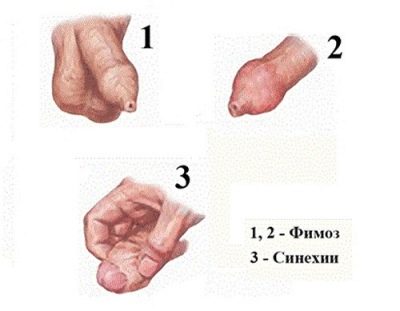
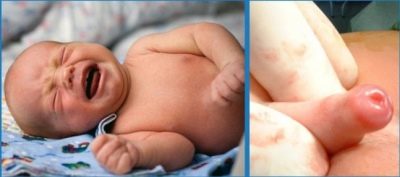
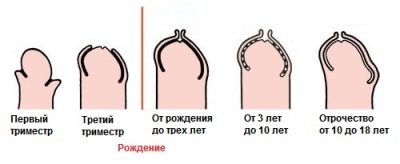
Sinechia in boys
Genital pathologies in boys are quite common. Future men have certain physiological features that are not diseases. This article will help parents figure out whether synechia are considered a norm or are pathological.
What it is?
The fusion between the head of the penis and the inner leaf of the foreskin, doctors call the term "Synechia". This condition occurs in every newborn male baby.
This feature in boys is due to nature. All babies under three years of age have physiological signs of synechia, i.e., this condition is not a pathological deviation, but refers to a variant of the norm. Over time, the child's synechia disappears completely, only in some cases, treatment is required to eliminate them.
Pronounced adhesions in the foreskin lead to difficulties in exposing the glans penis. The predominant localization of such "adhesions" - from the coronal sulcus of the penis to the urethral canal. Nature came up with these adhesions is not accidental. In toddlers, local immunity is still not functioning effectively. This can lead to the fact that the child "picks up" any infectious diseases. Adhesions prevent the entry of pathogens into the internal structures of the external genital organs.
Synechia is a completely physiological education in small boys. In no case should it terrify parents.
Compliance with the rules of personal hygiene, strengthening of local immunity and prevention will provide good control over the development of this condition.
If inflammation occurs, parents should always refer to a pediatric urologist. It is also worth doing if the child is three years old, and he still has pronounced fusion in the region of the foreskin and glans penis.
The reasons
According to statistics, adhesions on the external genitalia are completely by the age of 3 years. However, there are exceptions.
In the scientific literature there is information that signs of adhesions in the region of the foreskin are quite common in school and adolescence. A retrospective analysis shows that such children have never been seen by a urologist.
In the development of the disease it is necessary to allocate several groups of synechias. Some of them are considered physiological and are found in every newborn boy. Others - traumatic. Often they occur after injury to the intimate genital area. In this case, the obligatory consultation of the urologist and coordination of further treatment tactics is required. Some pronounced traumatic injuries that led to the appearance of synechiae require surgical treatment.
The intensity and number of synechiae can differ significantly. It is believed that various infectious diseases that occur in a child during fetal development in the womb can lead to an increase in adhesions. Microbes entering the systemic circulation of the baby through the nutrient vessels of the placenta rapidly reach the pelvic organs, contributing to the occurrence of the inflammatory process there. Ultimately, this disrupts organogenesis, which can be manifested by the appearance of multiple adhesions.
European scientists suggest that hereditary factors contribute to the development of multiple synechiae in a child. There is no scientific confirmation of this fact yet: this assumption remains as long as a theory, but it does take place.
The treatment of pathological adhesions of the foreskin and the glans penis is done by pediatric urologists or andrologists.
The mechanism of the natural separation of adhesions is simple. During growth, the child begins to produce a sufficient amount of smegma - a special secret of the sebaceous glands in combination with desquamated epithelial cells. The development of this biologically active substance contributes to the fact that the fusion between the foreskin and the head of the penis are eliminated independently. They are simply separated from each other by mechanical means.
The danger of the development of various pathological conditions lies in the amount of smegma released. If for some reason it begins to be produced in a significant amount, it can lead to its expressed stagnation. Such a biological secret is considered to be an excellent nutrient medium for the development and functioning of various pathogens.
Violations of the rules of personal hygiene, systemic infectious diseases against the background of low local immunity contribute to the ingestion of microbes under the foreskin, which leads to the development of numerous dangerous urological pathologies.
This situation leads to the development of complications in the child. The most frequent of them are balanoposthitis and balanitis. These conditions are usually quite uncomfortable and disrupt the well-being of the child.
The treatment of these urological diseases is done by pediatric urologists and andrologists. To eliminate the adverse symptoms of diseases, high doses of antibacterial drugs and anti-inflammatory drugs are commonly used.
Symptoms
Synechia can be seen in the child and independently. Usually they become noticeable during daily hygiene procedures. Connective tissue adhesions between the head of the penis and the foreskin, which look like dense cords, and are considered synechias. The number of such adhesions may be different for each child.
In some cases, the baby has the following characteristic symptoms:
- Swelling of the glans penis. It increases slightly in size, with severe edema may pulsate slightly.
- Redness of the glans penis. Usually this symptom occurs due to itching, which bothers the baby. Itching can be of varying intensity: from almost imperceptible to pronounced. Some babies begin to comb the intimate area, which leads to the appearance of characteristic marks on the skin of this area.
- Slight soreness during urination. This symptom is not common to all babies. Some children have a slight burning sensation. Going to the toilet to urinate can bring discomfort to the child. Toddlers and especially those who are not able to speak yet express it simply by crying.
- Soreness or difficulty exposing the head of the penis. The more adhesions the child has, the more pronounced this adverse symptom is. In some babies, when trying to bare the head, there is a real pain syndrome. If a similar situation arises, you should immediately contact your pediatric urologist.
How to treat at home?
Therapy of uncomplicated synechiae can be carried out independently. Such treatment can be more attributed to prophylactic. It comes down to the implementation and observance of all rules of personal hygiene. To accustom the baby to take care of yourself should be from an early age. The child must know the basic rules of hygiene that he will need in later life.
It is important to remember that young boys need to do daily scrubbing. With a pronounced formation of smegma - this can be done 2 times a day or more often (if necessary).In the future, the boys should be washed off once a day.
To prevent inflammatory diseases of the urinary organs during washing, you can use broths made from various medicinal plants. Perfect pharmacy chamomile and calendula. Many urologists recommend treating inflamed areas. miramistinom. It should be remembered that this drug has contraindications and must be appointed by the attending physician.
After washing, the skin should be gently soaked with a clean, ironed towel or sterile gauze, and then dried. Strongly rub the skin is not worth it. This may contribute to mechanical damage that will only aggravate the general condition.
Long wearing diapers for boys does not have a favorable effect. During hygiene procedures, the skin of the child "breathe", dried naturally and does not overheat.
If possible, try to teach your baby to the pot as soon as possible. This will help reduce the risk of developing adverse pathological conditions in the child in the future.
Treatment
Today, children's urologists and andrologists believe that there is no need for intensive treatment for boys under three years of age. Usually, the child is carried out only regular observation, which allows you to control the course and development of this state.
When you visit the medical commission in the clinic, the baby must be examined by a urologist. If, during such an examination, the doctor finds any complications or a pronounced deterioration in the course of the disease, he may prescribe a treatment to the child. However, such cases are quite rare.
With traumatic synechia, doctors recommend turning to holding chamomile or calendula baths. They help to reduce inflammation and improve the well-being of the child. Usually, 10-15 days is enough to achieve a positive effect. Baths can be carried out 2 times a day.
Sometimes doctors inject with a special needle into the area between the glans penis and the foreskin. hydrocortisone ointment. It effectively deals with inflammation and contributes to the rapid reduction of adhesions.
In some situations, doctors may resort to the appointment of special ointments that have absorbing effect, for example, «Contractubex». Such funds are applied to the affected areas and help reduce adhesions. The choice of the duration of such treatment and the frequency of use of the drug remains for the treating urologist, since it requires a preliminary assessment of the overall condition of the baby and the identification of its associated diseases.
In children older than three years with pronounced adhesions in the foreskin, which cause adverse symptoms in a baby, can be performed surgery. Indications for surgery sets the pediatric urologist. In this case, all adhesions are surgically intersected, which leads to the release of the glans penis and a significant improvement in well-being. Usually such operations are carried out already in children in adolescence.
After the surgical treatment, the child is prescribed anti-inflammatory ointments, which are applied topically. They help eliminate the residual symptoms of inflammation and promote healing of damaged tissues. Typically, these ointments are written out for 2-3 weeks, followed by cancellation.
After treatment, the child does not have any residual signs of synechiae and adverse symptoms. In the future, the child should regularly visit the urologist at least once a year.
See the next video on what synechia and intimate hygiene rules are for boys.