Phimosis in boys
Boys and girls from birth have certain physiological features and differences. Diseases of the sexual sphere always bring parents into real confusion. Phimosis is one of such diseases.
What it is?
In boys, phimosis is a pathological condition in which it is impossible to open the head of the penis due to the narrowing of the orifice of the foreskin. Usually this pathology is manifested by an increase in the size of the foreskin and some urinary disorders. The incidence of phimosis in boys is quite high.
It is important to note that it decreases with age. So, in children 7-9 years the incidence of phimosis does not exceed 10%. In adolescents, it is less than 2%.
A newborn boy has its own physiological features that distinguish it from an adult male. Normally, all babies born between the glans penis and the inner shell of the foreskin there is a message. These structural components are interconnected. This feature nature has provided no coincidence. This helps to prevent infection on the delicate tissue of the external genitalia, and therefore reduces the risk of secondary infection.
As the child grows up, various physiological changes occur in his body. Every second boy by the age of 1 year opens the head of the penis. By 2-3 years, this value is already 90%. In some cases, deviations do develop. They lead to the development of various diseases in babies, including phimosis.
Typically, the reproductive system of boys is formed up to 6 years. If a child has any abnormalities in the state of reproductive health, they are tried to treat them conservatively or use “observational” tactics.
In many babies with various pathological conditions in childhood, by adolescence they completely disappear without treatment. In any case, the baby should always be observed and monitored for any changes in his state of health.
Causes
There is currently no single reason that leads to the development of the disease. Many andrologists and pediatric urologists still argue about what contributes to the development of phimosis in babies. They identify several causes that can cause this pathological condition in boys. In some cases, the influence of several causal factors simultaneously can lead to the development of the disease.
This pathological condition leads to:
- Disorders of fetal development. The impact of adverse environmental factors or chronic diseases in a pregnant woman contribute to the formation of various pathologies during gestation of the unborn child. The fetus disrupts the stage of organogenesis, which contributes to the onset of various diseases in the future. Usually the clinical signs of phimosis in this case occur in a child under one year old.
- Traumatic effects. The external genitals in boys is fairly easy to damage. Especially in young children. A blow to the area of intimate organs, a fall, or independent attempts to uncover the head of the penis can cause a pronounced injury to a child.The consequence of this, as a rule, is the formation of resistant phimosis.
- Infectious and inflammatory pathologies in the area of the external genitalia. The children's body, due to the fact that it has reduced immunity resources, is easily exposed to any infectious agents. Usually they are a variety of viruses and bacteria. Getting into the intimate area together with the bloodstream or through the household contact, they can cause a strong inflammation in the child. The consequence of this, as a rule, is the formation of persistent andrological pathologies.
- Complications of urological operations. Improperly chosen operational benefit in most cases leads to the formation of various long-term complications. Phimosis is considered one of them. Damage to the tissues of the glans penis or foreskin contribute to the formation of pathologies and acquired anatomical defects in this area.
- Insufficient number of connective structures. This feature is individual and occurs only in babies with a special predisposition.
Kinds
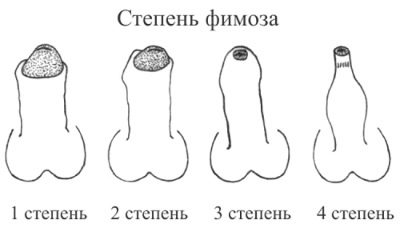
Doctors distinguish several forms of this pathological condition. This classification is necessary in understanding the essence of the disease, as well as for drawing up the tactics of examination and treatment in the future. So, phimosis can be congenital, hypertrophic or cicatricial.
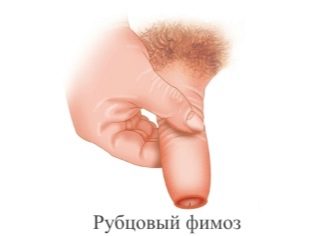
A large number of cases of cicatricial phimosis occurs due to violation of personal hygiene. This leads to the fact that an infection easily penetrates the area of the external genital organs, and the inflammatory process develops.
Much less often, cicatricial stenosis is a congenital pathology. This pathological condition is characterized by a rather long foreskin that prevents the head of the penis from fully opening. Due to the pronounced inflammation, various cracks appear on the skin and scars are formed.
In this case, it becomes extremely difficult to carry out hygienic procedures. If the inflammation increases, then phimosis can even turn into a very dangerous state - paraphimosis. Tactics of treatment of cicatricial phimosis - the appointment of conservative therapy or surgery. The choice of treatment tactics remains for the attending urologist. The prognosis of the disease is favorable. The risk of complications is medium.
According to statistics, most often the development of the hypertrophic form of phimosis is caused by the presence of excess weight in the child. The most dangerous in this case is obesity in the lower abdomen and in the groin area. The abundance of fat cells in the reproductive zone contributes to the fact that there is easy fat folds. It is important to note that this form of the disease occurs not only in the smallest patients, but also in adult males.
A large accumulation of adipose tissue leads to the fact that the head of the penis is somewhat compressed. The skin begins to get wet, which causes the formation of various macerations and irritations. Squeezing adipose tissue of organs located in the reproductive zone, leads to the fact that the foreskin of the penis begins to tightly cover his head. This greatly aggravates the course of the disease. The pronounced moisture of the skin leads to the appearance of various irritations on the skin, which become an excellent environment for the development of pathogenic bacteria.
In the treatment of hypertrophic obesity, the normalization of the daily regimen and the prescription of a therapeutic low-calorie diet are very important. For such kids, the necessary mode of physical training is selected. Therapy of hypertrophic phimosis in most cases is conservative.
Doctors of several specialties take part in the treatment of a child at the same time.
Congenital forms of phimosis are quite common.Many doctors agree that the cause of this pathological condition are congenital anomalies of fetal development and genetic predisposition. In some cases, specialists can not identify a specific reason that caused the appearance of adverse symptoms in a baby. Congenital phimosis is characterized by the presence of a pronounced narrowing of the orifice of the foreskin, which is manifested by the inability to exit the glans penis. Quite often, these conditions are accompanied by the presence of multiple synechiae in a baby.
Doctors are not engaged in active treatment of congenital phimosis in infants. Basically, they choose waiting tactics that allow you to control the course of the disease and predict the outcome of the disease in the future. Pediatric urologists deal with the treatment of congenital forms of phimosis.
If the doctor found signs of the disease during the examination of the child, he “puts” the baby on the dispensary registration. In this case, you should visit the doctor at least 1-2 times a year.
Some children during the examination doctors diagnose “proboscis phimosis”. This pathological condition is hypertrophic. It is characterized by excessive skin formation in the area of the glans penis, which creates a "proboscis". Tactics in this case is the same as in other forms of the disease. With the ineffectiveness of conservative treatment is performed surgery.
Symptoms
The clinical signs of this pathological condition are primarily associated with a violation of the opening of the glans penis due to a pronounced narrowing of the orifice. This symptom is the most characteristic. As a rule, it is noticed by parents during regular hygienic procedures.
Some fathers and mothers make an extremely inadmissible mistake. They try to “open” the head of the penis themselves through overcoming efforts. This should not be done categorically! Such self-medication can contribute to injury to the baby. To treat this pathological condition should only pediatric urologist. Independent replenishment - is unacceptable!
In addition to the main symptom of the disease, there are other clinical signs of the disease. These include:
- Painful urination. This symptom does not always occur, however, significantly aggravates the well-being of the baby when he appears. Mild disease is not accompanied by a violation of urination. Heavier and more complicated forms of the disease contribute to the appearance of irregularities in the discharge of urine. A baby may feel soreness when urinating or even a pronounced pain syndrome.
- Urination disorders In some babies, especially those with fairly pronounced phimosis, urine can be excreted with some “interruptions” or flow in a thin stream. If pain syndrome joins this symptom, then the child’s well-being is sharply disturbed. The youngest patients usually show this by weeping. Older children begin to act up, more often run to the toilet to urinate.
- Soreness in groin area. Usually this symptom appears when the inflammatory process spreads throughout the intimate area. If phimosis is complicated by a secondary bacterial infection, then the child has additional adverse symptoms. These include: suppuration from the orifice of the glans penis, swelling and swelling of the foreskin, marked increase in body temperature and swelling of the testicles.
The severity of symptoms may vary. Lighter variants of the course of the disease, as a rule, are almost asymptomatic.
The main clinical sign in this case is a narrowing of the orifice of the head of the penis and inability to fully open it.
Severe course of the disease is accompanied by the appearance of numerous symptoms that require the appointment of conservative treatment.When the first signs of phimosis appear, you should immediately contact your pediatric urologist with your child.
What does newborn look like?
In all boys born, the head of the penis and the foreskin are spliced. As the child grows up, this situation changes. To hurry with the conduct of surgical treatment is not worth it. Physiological phimosis completely disappears in almost 90% of babies by the age of three. Doctors recommend that only the smallest patients be monitored carefully and that proper regular hygienic care be carried out.
Often, parents of boys independently discover some physiological features in a child. The skin of the foreskin of newborn babies is very delicate and thin-skinned. It is tightly spliced with the head of the penis. When trying to self-expose the head, the child feels sore, begins to be naughty and even cry.
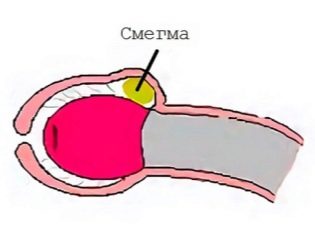
The skin of the foreskin secrete a special substance - smegma. It has a white color and a specific smell. With age, its number and composition varies somewhat. The formation of smegma is quite a physiological process. It is necessary so that the inner leaflet of the foreskin "peeled off" from the glans penis. This physiological situation helps to improve the opening of the head.
If the smegma is formed too much or its composition changes significantly due to chronic diseases, then the process of normal development of intimate organs is disturbed. Also, this situation may lead to the fact that the baby appears clinical signs of a variety of infectious diseases. Smegma is an excellent nutrient medium for microorganisms. Conducting a thorough hygienic care of a newborn baby is necessary as a prevention of diseases of the intimate area.
Diagnostics
The appearance of the first adverse symptoms of the disease should motivate parents to consult a doctor. The doctor will conduct the necessary clinical examination, as a result of which he will be able to establish the correct diagnosis. In some cases, phimosis is accompanied by other pathological conditions that require careful observation or the appointment of adequate treatment.
Diagnosis of phimosis is usually not a significant difficulty for doctors. To establish the diagnosis is quite clinical examination is sufficient. Additional diagnostics may be required only in difficult cases or in case of complicated course of the disease. To do this, appointed: general blood and urine tests, biochemical research (if there are complications), ultrasound, Doppler and other methods according to indications.
Complications
The prognosis of phimosis is conditionally favorable. Usually the disease occurs without the development of long-term negative consequences. However, phimosis can be dangerous. Especially in weakened babies or children who have immunodeficiency states or concomitant chronic diseases. Treatment of all complications is carried out only in the hospital. For this baby are hospitalized in the urology department.
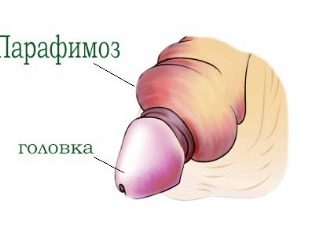
Quite frequent complication of phimosis is paraphimosis. This pathological condition is characterized by the appearance of pinching the glans penis with the foreskin. Most common when attempting to force its discovery. Quite often recorded in children aged 7-10 years.
Paraphimosis is accompanied by the appearance of a strong pain syndrome, which brings the child considerable discomfort. This pathological condition requires emergency treatment in a hospital.
Organs in the intimate area are very sensitive to any infections. The spread of the inflammatory process leads to the fact that the inflammation passes to the adjacent anatomical structures. A common complication in this case is urethritis.This pathological condition arises due to the fact that the bacteria fall on the mucous membrane of the urinary tract. Urethritis is accompanied by the appearance of various adverse symptoms: a violation of urination, pain during going to the toilet, pain in the groin area and the lower third of the abdomen.
It is important to note that physiological phimosis does not affect conception. This pathological condition independently passes to school age.
Only complicated versions of phimosis can cause difficulties in the future with the conception of a child. However, this is extremely rare. Treated phimosis is not a problem in the future for the planning of children.
Home treatment
Self therapy should be carried out only under the close supervision of specialists. Usually this home treatment is reduced to the implementation of all medical recommendations, as well as the proper conduct of hygiene procedures. All manipulations should be done in a fairly gentle way. Follow the daily hygiene should be from the very first days of birth. Also it is necessary to gradually accustom this to the baby.
Some doctors practice the method of gradually opening the head of the penis. This is done gradually, no more than 0.5 -1 mm per day. All movements should be smooth, of weak intensity. Usually they are performed after a warm bath, when the pelvic floor muscles are as relaxed as possible. As an adjuvant therapy using various ointments, which were prescribed by a doctor.
In the bath, which is carried out before the procedure, you can add a variety of ready-made antiseptic solutions and decoctions of herbs. As such tools are perfect: pharmacy chamomile, calendula, a weak solution of potassium permanganate, sage and others. Such baths are prescribed 2-3 times a week for 10-15 minutes. The temperature of the water should be pleasant and not cause discomfort in the child.
After the procedure, the foreskin should be smeared with a special ointment, which the doctor will prescribe. These drugs have good wound-healing and regenerative properties. It is necessary to carry out such home treatment only with obligatory control of the treating pediatric urologist.
Drug therapy
To eliminate adverse symptoms, doctors prescribe various drugs. According to their mechanism of action, they can be different: anti-inflammatory, wound healing and regenerating, improving blood supply, painkillers. The choice of treatment regimen depends on the pediatric urologist. In children under 6-7 years of age, active therapy is not carried out. Preference is given to conservative methods performed by gentle methods.
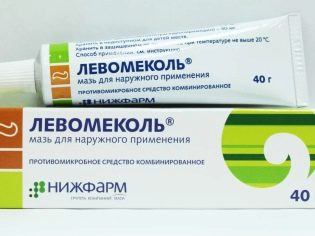
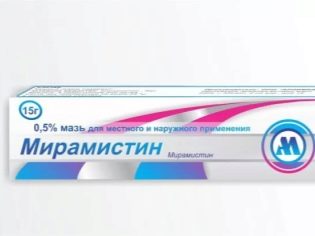
As a local treatment, doctors prescribe various ointments and creams. They are usually applied to the skin in the region of the foreskin after the hygienic bath. "Diprosalik", "Miramistin», «Levomekol», «Akriderm» help prevent secondary infection and promote the speedy healing of tissues. These products have an excellent antiseptic effect, which is necessary for the prevention of complications of phimosis. Hormonal ointments and antibiotics should be prescribed by a doctor according to strict indications. Independent use of such drugs without consulting a doctor will significantly aggravate the course of the disease, since these drugs have a number of side effects with long-term use.
Tetracycline ointment is usually used to treat pathological conditions. The dosage, frequency and duration of use of this drug is determined by the attending physician. All antibacterial drugs are prescribed for course admission. During treatment, strict control of the effectiveness of the prescribed therapy is required.
Hormonal drugs are prescribed for cicatricial phimosis, as well as in cases where previous therapy is ineffective.
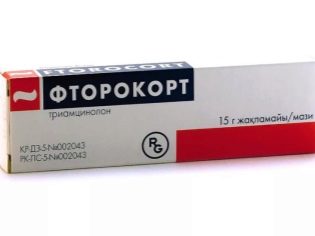
Hydrocortisone ointment and "Ftorokort" have a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect, heal minor wounds and cracks in the skin, and also help to improve the exposure of the glans penis. Hormone therapy is also applied course. With prolonged use of drugs, adverse systemic and local side effects may occur.
In children up to 6-7 years old, in most cases only conservative therapy is performed. As a rule, it helps to improve the condition and reduce adverse symptoms. To cure, this treatment leads to more than 90% of cases. In the same situations when conservative therapy is unsuccessful, various invasive techniques and even operations are used.
Surgical treatment
To date, there are several methods of surgical treatment of phimosis. These include both very common methods and are used only in some countries. In some states, a number of operations are not carried out for ethnic and spiritual reasons. In any case, the choice of treatment tactics remains with the attending physician and must be coordinated with the parents of the baby.
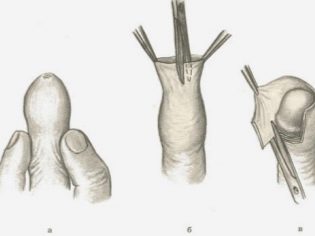
You can perform operations in the traditional way. In this case, the surgeon cuts the foreskin and makes axial cuts on it. All excess skin is removed. Then the doctor stitches the foreskin area. This contributes to a pronounced expansion of the orifice of the head of the penis. It is easily exposed without the appearance of pain. Such an operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Another quite popular method of surgical treatment is considered Shkloferu operation. In this case, the excision of the foreskin is carried out in a zigzag manner. Then the wound edges are sutured. This technique also allows excision of excess skin areas that significantly violate the movement of the glans penis. This operation is usually performed under local anesthesia.
Circumcision is a fairly common procedure all over the world. Prerequisites for its implementation are usually not only medical. Circumcision in young boys is also carried out on spiritual and ethnic grounds. This procedure is painless if performed in very young patients. In older children, it should be carried out with mandatory prior anesthesia.
One of the most minimally invasive procedures to date is the excision of excess skin with a laser. This technique is quite safe and can be applied even in pediatric urological practice. During this procedure, the child has practically no complications.
The laser allows you to minimize blood loss, reduce the risk of postoperative scars and long-term adverse effects.
In polyclinic conditions, children's urologists resort to excision of various adhesions using probes. This technique will have a positive result only when carried out in children with mild forms of uncomplicated phimosis. For this procedure, no type of anesthesia is usually used. The doctor inserts a special medical metal instrument, a probe, into the space between the foreskin and the head. Making movements of small amplitude, the probe "opens" the anatomical zone.
After all medical invasive procedures with external genital organs, special hygienic procedures are required.
This is an important component for a successful postoperative period. You can hold these events yourself - at home. After the operation, all the babies are in the dispensary at the urologist.
Care after surgery
After the surgical treatment, the doctor must make a number of recommendations that are required for the successful healing of tissues and preventing the development of postoperative complications. These medical advice should be followed for 3-4 months.Then you can return to the usual, but daily hygiene procedures.
For the fastest recovery of the child’s body after surgery is required full protein nutrition. For tissue regeneration, a whole complex of a wide variety of amino acids is needed. The diet of the baby must necessarily include fresh foods containing different sources of protein. These include: lean bird, fish, veal, turkey. Each meal should be accompanied by seasonal fruits and vegetables.
In the first month after surgery, all active physical activities are limited. Special restrictions are imposed on sports where injuries can occur. As physical activity in the first month after surgery, walks in the fresh air are well suited. Active games can also be present in the mode of the day of the baby. The expansion of the physical regime is carried out systematically, under the supervision of the attending physician.
For the rapid healing of damaged tissue, doctors prescribe various anti-inflammatory ointments. Usually they are used 2-3 times a day topically. They are applied on the skin of the foreskin, and in some cases, on the head of the penis, after conducting daily hygiene procedures.
To improve the absorption of drugs should leave the drug for a few minutes on the skin until completely absorbed.
Prevention
The main task in phimosis is to prevent various infections of the foreskin and the glans of the penis.
Prevention of secondary infection is an important goal in this pathological condition.
To do this, use the following tips:
- Perform regular hygiene procedures.. To do this, suitable special children's cosmetics, which do not contain alcohol and aggressive perfume fragrances that can cause pronounced allergic reactions in the child. To accustom the child to the conduct of a daily toilet should be from an early age. To preserve reproductive health for many years, such hygienic procedures should be carried out 2 times a day: in the morning and before bedtime.
- Change diapers in a timely manner. in newborns and infants. Prolonged wearing of diapers can cause various macerations or inflammation to appear on the baby’s skin. Weeping skin becomes an excellent nutrient medium for the development of the most dangerous microorganisms.
- Regularly undergo examinations at the urologist. If your child has urological diseases, visit the doctor at least 2 times a year. Be sure to talk with a specialist the tactics of future treatment and observation of the baby.
- Do not allow complications of chronic diseases.. Concomitant diseases of internal organs can significantly aggravate the course of pathological conditions in the area of the intimate zone. Observance of the recommended regimen, optimal healthy nutrition and active physical exertion contribute to the well-being of the baby and strengthen its immunity.
About what a boy's phimosis is, see the next video.