Obstructive bronchitis in infants
Breath impairment in babies of the first year of life is a fairly dangerous condition. Various reasons can cause a narrowing of the bronchial lumen in an infant. Only timely diagnosis and treatment can help in the elimination of adverse symptoms.
What it is?
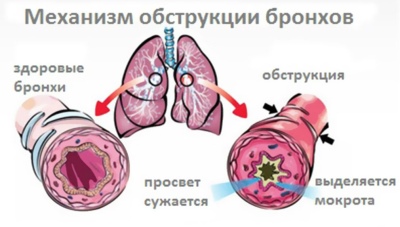
The narrowing of the bronchial lumen in infants as a result of exposure to a provoking cause is called obstructive bronchitis. As a result, respiratory failure occurs. This situation is dangerous due to insufficient intake of oxygen into the children's organism. Prolonged oxygen deprivation leads to disruption of the work of many internal organs.
Both boys and girls can get obstructive bronchitis. Symptoms that occur in the acute period of the disease in infants are much brighter and more pronounced than in schoolchildren. More severe course of the disease occurs in premature babies, as well as children with low birth weight or congenital immunodeficiency.
The reasons
The course of the disease in a newborn baby and baby has its own characteristics. Even the causes that cause this disease can be quite diverse.
TO obstructive bronchitis lead:
Viral infections. Influenza and parainfluenza viruses, PC viruses, adenoviruses most often contribute to bronchial obstruction. These microorganisms have a very small size and easily penetrate the epithelial cells of the upper respiratory tract. Rapidly multiplying in the body, they contribute to the development of a strong inflammatory process in the bronchi.
Bacteria. Streptococci and staphylococci cause severe bronchial damage. Bacterial infections are quite hard, with fever and a strong cough. Antibiotics are required to eliminate adverse symptoms.
Smoke or inhalation of industrial emissions. According to statistics, babies living in urban environments suffer from obstructive bronchitis more often than their rural peers. The smallest components of dust and toxic particles that are in the air near major roads or industrial factories and plants fall into the upper respiratory tract and contribute to the development of bronchial obstruction.
Prematurity The final formation of the respiratory system takes place in the third trimester of pregnancy. If the child was born earlier than expected, then he may experience multiple irregularities and defects in the structure of the lungs and bronchi. This increases the risk of developing bronchial obstruction in the future.
Allergies. Usually appear in babies aged 5 months and older. Often occur after the introduction in the child's diet of new products as complementary foods. Allergic forms of the disease in infants are quite difficult.
Kinds
All obstructive bronchitis can be divided into several groups. Most often, doctors use classifications that reflect the cause of the disease, the form of the disease, and the degree of severity during its exacerbation.
Depending on the duration of the course, all obstructive bronchitis is divided into acute and chronic. The first occurrence of a disease that is registered in a particular child for the first time is called acute. Usually such bronchitis lasts 7-10 days, and for weakened babies - even up to two weeks.
If, despite the treatment, the disease reappears after some time, then this form is called chronic. Periods of exacerbation and remission lead to the development of recurrent bronchitis.Such forms of the disease are most dangerous with the development of complications.
According to the severity of obstructive bronchitis are divided into:
-
Lungs. Proceed without complications and respond well to treatment. The adverse symptoms of the disease are mild. Can flow without heat.
-
Medium heavy. A more protracted course is characteristic. With some bacterial infections even up to 1 month. With this course, various complications may appear.
-
Heavy. It is treated only in a hospital. Accompanied by the appearance of severe dyspnea and manifestations of respiratory failure.
Symptoms
The first signs of the disease appear after the incubation period. It usually takes 3-4 days for viral infections and 7-14 days for bacterial infections. If obstructive bronchitis has become a manifestation of an allergy, the first symptoms may appear after only a few hours from the moment the allergen enters the body.
Clinical manifestations of the narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi include:
-
Cough. It happens exhausting. Often the child coughs with bouts. In the daytime cough worries a baby much more than at night.
-
Deep and noisy breathing. Even at a distance, wheezing and gurgling in the chest can be heard.
-
Dyspnea. The baby begins to breathe more often. Symptom can be checked at home. To do this, you should count the respiratory movements that are performed by the chest in one minute. Increased dyspnea is an unfavorable symptom. It may indicate the development of respiratory failure.
-
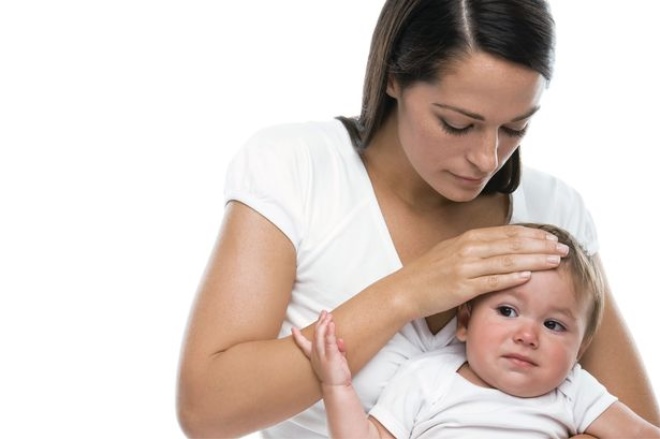
Temperature rise. It can rise to 37-39 degrees. At the height of temperature in infants often vomiting occurs.
-
Violation of the general condition. Kids refuse to breastfeed, naughty, more asking for pens. Drowsiness and general weakness increase.
-
Violation of nasal breathing and redness of the oropharynx. Occurs with viral and bacterial infections.
-
Soreness in the chest after coughing. A hacking cough with difficult sputum leads to a baby’s rapid fatigue and pain in the chest during breathing.
Diagnostics
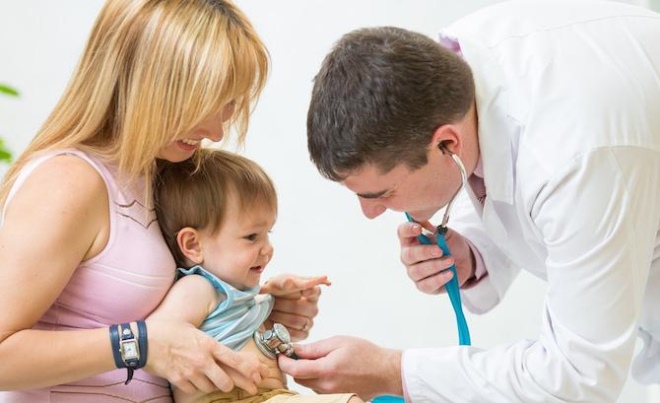
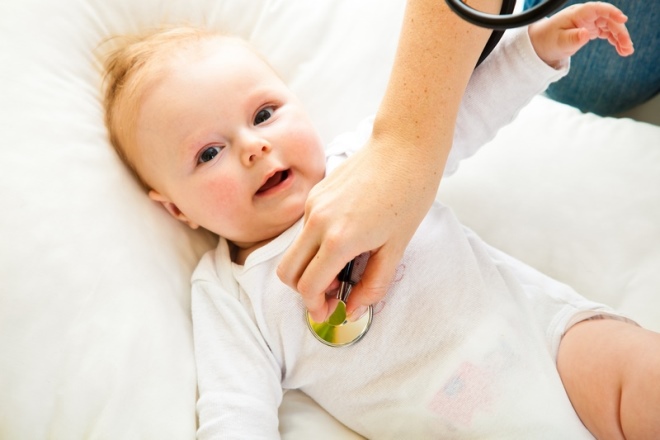
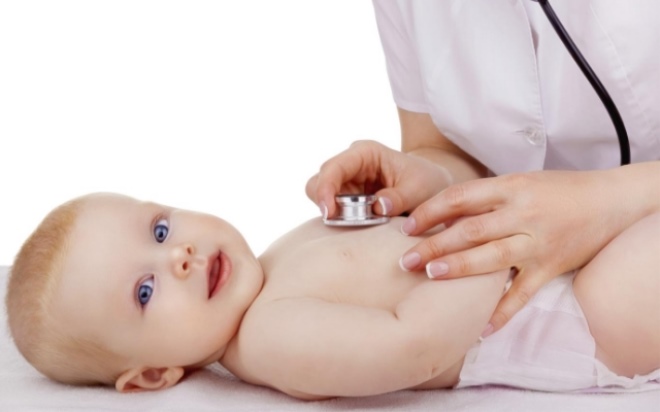
When the child has the first symptoms of the disease, it must be shown to the pediatrician. With the help of auscultation (listening to sounds with a stethoscope), the doctor will be able to detect the presence of wheezing and an impaired breathing conduction.
To clarify the diagnosis may require a complete blood count. Expressed leukocytosis will be evidence of the presence of an inflammatory process in the children's body. Examination of the child by the doctor and a general blood test, in most cases, is sufficient for establishing the diagnosis and treatment. Radiography of the chest in infants-babies do not apply.
Treatment
If the course of the disease is severe or complications have developed, and there are symptoms of respiratory failure, then hospitalization is required. In other cases, treatment at home under the supervision of the attending physician is sufficient.
To eliminate the adverse symptoms of the disease is used:
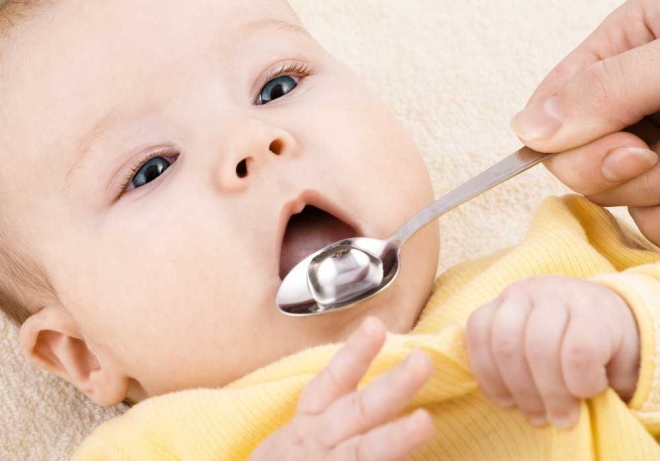
Expectorants and mucolytics. They make viscous sputum more liquid, and help the baby easier to cough up.
Antipyretic. Appointed when the temperature rises above 38 degrees. Long do not apply. Medicines in syrup or solutions are prescribed for infants.
Antispasmodics. Drotaverine and papaverine-based preparations help to eliminate bronzospasm well, and also contribute to a better sputum discharge.
Plentiful warm drink. Alkaline mineral waters are actively used in babies from 4 months. Fruit drinks and fruit compotes made from apples and pears, as well as dried fruits are also good.
Good nutrition with the exception of allergenic foods. If obstructive bronchitis develops in a baby, as a result of an allergic reaction, it is necessary to completely exclude the provoking allergens from its diet.
Bronchodilators. These drugs help eliminate bronchospasm and normalize breathing. Appointed by inhalation. The dosage and frequency of use is chosen by the attending physician, taking into account the age of the child and the presence of concomitant pathologies.
Antiviral drugs and antibiotics. Appointed after establishing the cause of the disease. Antivirals are prescribed for 4-5 days, antibiotics - for 7-10 days.
Special air humidifiers. Such devices allow you to maintain the correct humidity in the premises and help eliminate the pronounced dryness of the mucous membranes.
Treatment of obstructive bronchitis in babies of the first year of life requires a more careful approach. With the wrong treatment, the disease can become chronic. Strengthening immunity and preventing infection during the cold season will allow infants to not get sick with obstructive bronchitis in the future.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell us about the treatment of obstructive bronchitis in children in the next video.