Acute bronchitis in infants and young children
Diseases of the respiratory system in children are more common than other ailments. Among them, one of the leaders in terms of prevalence is acute bronchitis. Not everyone knows how to distinguish it from other respiratory diseases, what it is and how to properly treat such a disease.
About the disease
Bronchitis in children is acute and chronic. The disease may acquire a chronic form if the acute illness was treated incorrectly or not treated at all. That is why it is important in time to identify bronchitis in its initial form and in time to cope with the problem.
With bronchitis, the bronchial tree is inflamed, the production of bronchial secretions (mucus) increases, and the bronchial patency is impaired. This condition can occur as an independent illness or be a complication after another disease - for example, acute respiratory viral infections so common among children.
Most often, bronchitis is caused by viruses. When foreign agents enter the bronchi, the mechanism of the formation of abundant mucus is triggered, it performs an important immune task - to bind and neutralize virus particles. At this stage, it is important to prevent thickening of mucus, because the thick bronchial secretion no longer saves, it is now dangerous, since it is almost an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. Bacterial lesion of the bronchi is a rather severe pathology.
Bronchitis can be localized only in the bronchi, and can spread to the trachea, and then the disease will be called a little differently - tracheobronchitis. Depending on the condition of bronchial mucus, the disease may be:
- catarrhal (acute current, moderate amount of liquid mucus);
- slimy (acute course, a large amount of mucus increased viscosity);
- purulent (complicated course, the accession of a bacterial infection due to dried out or severely thickened mucus or microbes that fell from the outside).
Inflammation may be minor, spread only to the shell of the bronchi, and may be more profound, when the inflammatory process moves to the submucosa and muscle layer.
The reasons
The most common cause of bronchitis in a child is viral infections. Pediatricians say that often bronchitis is a complication of influenza, parainfluenza, rubella, sometimes - measles. Rarely enough, bronchitis is initially bacterial in nature (associated with contact with the bronchial mucosa of pneumococci or staphylococci). If the fact of bacterial bronchitis is ascertained, we are talking about a secondary, joining infection.
Noncommunicable bronchitis can be caused by the following reasons:
- inhalation of dust, smoke, chemicals, chlorine vapors;
- polluted or too dry air;
- allergens.
In childhood, the appearance of bronchitis in the acute stage is influenced not only by the unfavorable ecological situation and the presence of a virus or bacteria, but also by the state of immunity, which in children is much weaker than in adults. In children who are malnourished, they lack vitamins, often suffer from a head cold and have a chronic infection in the nasopharynx, bronchitis occurs more often, and the number of complications and the transition to the chronic stage increases markedly.
The probability of occurrence of complications increases, if not to prevent the dilution of bronchial mucus.In the thickened secretion, bacteria multiply rather quickly, and as early as 2-3 days after the onset of bronchitis, it can become complicated. The affected mucous membranes are usually restored on their own, if this does not happen, doctors put another diagnosis - chronic bronchitis.
Allergic bronchitis usually develops in children with a strong genetic predisposition to allergic reactions. One contact with an allergen is not enough for this; a child must experience such an impact for a long time.
Symptoms
The onset of bronchitis is always closely associated with the symptoms of the underlying disease - it can be fever or high fever, rhinitis, a violation of nasal breathing. However, the main symptom of acute bronchitis is the appearance of cough. At first it has the character of unproductive and dry. At night, such a cough increases, which does not give the baby a good sleep. During the day you can notice severe shortness of breath, especially after exercise or active games.
After 3-5 days, the cough changes to a moist, productive one. This is easy to hear, as characteristic “gurgling” sounds appear, and coughing spells always end with sputum separation (with excess bronchial mucus). During this period, a child may have a low subfebrile temperature - 37 degrees. The child becomes lethargic, drowsy, apathetic. Older children may complain of headaches.
These accompanying symptoms usually pass quickly enough within a week, but the cough can remain for a long time, since the healing process of the affected bronchus is very slow. It is this feature of the bronchial tree that sometimes causes such serious consequences as asthma. It is important to understand that recovery will not be quick, but a prolonged bronchitis that lasts more than a month should alert the parents and necessarily cause a visit to the pulmonary doctor.
Toxic or allergic bronchitis is always accompanied by painful long attacks of dry cough, sometimes hoarseness (due to the development of edema). This condition is very dangerous for babies up to a year. In infants already narrow airways, cramping and swelling can lead to death from suffocation.
Diagnostics
Parents on the totality of symptoms can only suspect bronchitis, only a pediatrician should make the final diagnosis. For this, the doctor will evaluate not only the symptoms and signs, but also the characteristic features of respiration.
With the help of a phonendoscope, the doctor will be able to detect hard breathing and scattered dry rales in a child with bronchitis. In the second stage, when the cough becomes productive, wet, the doctor, when listening, will be able to identify gurgling sounds that disappear immediately after a coughing fit. Allergic bronchitis is accompanied by hard breathing and moderate wheezing.
In addition, the doctor prescribes a number of tests - a general analysis of urine and blood, bacterial sputum culture, blood test for the determination of viruses and antibodies to them. The doctor may refer the child to an x-ray of the lungs to rule out tuberculosis and pneumonia, and also perform bronchoscopy. These same two studies must be prescribed for prolonged bronchitis to find out if there are signs of another infection.
Treatment
Treatment of acute bronchitis is usually carried out at home. The need for hospitalization sometimes arises only for young children and children with severe disease. Viral acute bronchitis does not need special treatment, as a rule, it takes 7-10 days on its own - if the parents provide the right conditions. The baby should breathe with clean, sufficiently humidified air (the relative humidity of at least 50% can be created with the help of a humidifier or hanging wet towels).
As long as the temperature holds, the child should lie down more, rest.As soon as she declines, it is important not to spend time in bed, but move as actively as possible.
Drinking plenty of water will speed up the process of sputum formation, and drainage massage and active motor regimen in the second stage of the disease will contribute to its timely discharge. In no case can viral bronchitis be treated with antibiotics, since they are ineffective against the causative agent of viral nature, and the risk of complications does not decrease, as many people think, but significantly increase.
Complicated by bacterial infection, bronchitis is usually treated with antibiotics, although recently doctors are not trying to prescribe antimicrobial therapy in all cases. In allergic bronchitis, antihistamine therapy is prescribed.
The temperature of bronchitis rarely rises above 38.0 degrees. If this happens, children are given antipyretic drugs. At the initial stage of the disease associated with a dry, painful cough, mucolytic expectorant drugs can be recommended. In no case should the child be given antitussive drugs. They suppress the cough reflex itself - and can thereby create an obstacle to the discharge of sputum, which will lead to the most dire consequences.
At the stage of recovery children are shown physiotherapy treatment and physical therapy sessions.
Treatment of bronchitis is always a set of measures, which includes the creation of favorable conditions for recovery, and medications, and medications are not central to this complex. If a baby is being wrapped, he sweats, if he breathes dry air and lives in an apartment where heaters work, if he is hot, then no syrups and pills will help.
Medicines
To reduce the high temperature in acute bronchitis, if it has risen above 38.0 degrees, the preparations allowed for use in childhood will help. This is "Paracetamol" and all funds based on it ("Nurofen", "Cefecone D"(Candles)," Panadol "and others). Effectively reduces the temperature and relieves inflammation nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory "Ibuprofen".
With a strong dry cough, such preparations as “Alteyka” syrup will contribute to the formation and further discharge of sputum.Mukaltin». Children from 3 years old can be given "Codelac Broncho ", and babies 2 years and older - syrups"Herbion"And"Libexin Muko". Everyone, including children in the first year of life, can be taken "Lasolvan", And babies after 6 months are allowed"Bromhexine". Perfectly dilutes phlegm and even nasal mucus during viral infection "ACC».
Antibiotics, which are prescribed for serious bacterial bronchitis, most often belong to the penicillin group. The specific drug is prescribed by the doctor after the sputum culture is ready, depending on the type of germ found in it. The most active against most of these pathogens has "Amoxicillin».
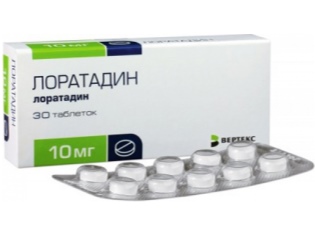
In allergic bronchitis, treatment is aimed at finding the allergen that caused the disease and at eliminating it. It is not always possible to find it, so it is recommended to remove all potential allergens from the nursery - soft toys, books, carpets. To reduce the negative impact the doctor may recommend "LoratadineOr Suprastin.
Inhalation
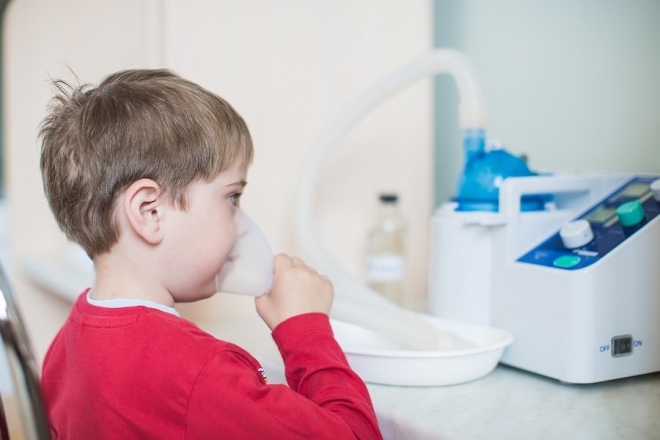
Inhalation should not be administered independently, it is a big parental mistake. The fact is that with bronchitis, these procedures are very useful only if they are done with the use of special medicines, which the child will breathe through a nebulizer. The device creates small particles of the drug, which easily penetrate into the lower respiratory tract and act exactly where it is needed. Inhalation using a nebulizer is needed when the bronchitis has a severe course, if it is complicated or (according to the doctor's assessment) the risk of developing such complications is very high.
It is very important that the child inhale the medication, and not the decoction of chamomile or plantain.
Most often, children are prescribed inhalation with Lasolvan, Berodual, Fluimucil. However, you should not choose the medicine yourself, because it can greatly harm the child.
Steam inhalers, which produce steam, are excellent in moisturizing nasal mucus and mucus in the larynx, but this vapor does not reach the bronchi, and therefore conducting such procedures (as well as the popular procedure “breathing over potatoes”) does not have any therapeutic benefits for bronchitis. They can hurt, and quite often this is exactly what happens.
Caring parents who give a child with bronchitis to breathe steam, then go to a doctor who finds burns of the mucous membranes of the respiratory organs in a patient, purulent congestion that begins with bacterial inflammation, repeatedly intensified by heating and steam inhalation.
Breathing exercises
At the stage of formation and discharge of sputum, when the cough becomes wet, the child is shown a drainage massage and breathing exercises. The massage is based on light tapping movements with the tips of the fingers over the ribs, across the chest and back. Breathing exercises are a fairly easy way to speed recovery.
Most often, doctors recommend that parents use the Strelnikova technique. The child should take an intense, quick inhale with the nose and a relaxed, slow exhale with the mouth. To carry out such breaths and exhalations need to rhythmically.
Such exercises are very useful closer to the stage of recovery, when there is no temperature, and the child should walk more in the fresh air. It is the breathing exercises carried out on the street according to the Strelnikova method that usually give the best results.
The most simple and interesting exercise for children is performed with a ball. The kid should take it in hands, take a sharp breath, press the ball to the stomach - and on the exhale, start to bend forward, as if hugging a ball with the rib cage. At the end of the exhalation, the arms with the ball are pulled forward and then lowered. Exercise should be repeated at least 8-10 times in one set.
Infants who cannot repeat breathing exercises should undergo a drainage massage more often. Usually it is enough for recovery.
Prevention
Prevention should be based on the timely and proper treatment of viral infections. The child does not need to be given antibiotics at the first symptoms of flu or ARVI, this only increases the risk of complications, which is bronchitis.
In case of viral respiratory disease, at high temperature (whatever they are caused), you should give the child as much warm water as possible, this will help keep the bronchial mucus in a normal consistency, prevent it from thickening and dry out, clog the bronchi.
The cleaner and fresher the air in an apartment, the less often children have bronchitis, and indeed, such children suffer less. Favorable conditions are air temperature not higher than 20 degrees and humidity in the range of 50-70%.
Walking in the open air, if they are long enough, at any time of the year, contribute to the formation of normal local immunity of the respiratory system. In addition, walks will help the child recover faster if bronchitis still happened to him.
The child should definitely be given all the vaccinations prescribed by age. At the first sign of incipient bronchitis, it is imperative that you call a doctor or take the child to the clinic for examination. Folk remedies to treat acute bronchitis is dangerous.
Read more about acute bronchitis in children You can find out in the next video.