Obstructive bronchitis in children
Diseases for which breathing is impaired are found most often in pediatric practice. The leading symptom of such diseases is cough. Lead to it can expressed narrowing in the bronchi.
What it is?
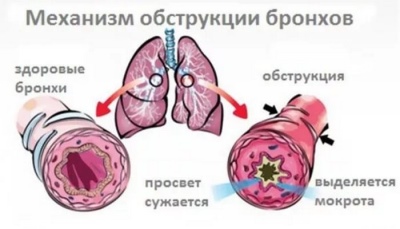
With obstructive bronchitis, there is a strong narrowing of the bronchi - an obstruction. This condition is caused by numerous causes and provoking factors. Breathing is impaired due to obstruction. A few days after the onset of the disease, all the symptoms begin to progress, leading to a worsening of the baby’s condition.
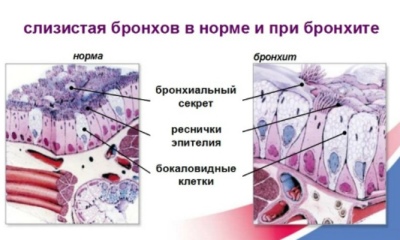
Bronchial tree cover microscopic cilia. They are located on the surface of the cells that form the bronchi. After exposure to provoking factors, the movement of cilia is disturbed, which also contributes to the violation of sputum discharge and increases obstruction.
Causes
Any bronchitis develops only after exposure to the children's body of various provoking factors. They are quite a large number. They are especially dangerous for newborns and infants.
Immunity of babies of the first year has not yet been fully formed. Any agent that is foreign to a child’s body can cause severe inflammation in the bronchi. This immediately leads to bronchial obstruction.
The reasons that can cause illness include:
Viral infections. The most frequent culprits of the disease: influenza and parainfluenza viruses, MS - a virus, adenoviruses. They easily penetrate the upper respiratory tract of the baby and quickly spread through the bloodstream, reaching the bronchi and lungs. Viral infections are the leading cause of bronchial obstruction in babies during the first months of life.
Bacteria. Streptococci, staphylococci and moraccella are the most common causes that can cause bacterial forms of the disease. These microorganisms contribute to the development of severe inflammation, which leads to a pronounced narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi. The disease caused by the bacterial flora has a more severe course and requires intensive therapy.
Allergies. When an allergen enters the body, the immune system is activated. This contributes to a large release into the blood of various biologically active substances, which strongly spasm the bronchi. With allergies, breathing is significantly impaired, and shortness of breath increases.
Inhalation of polluted air. Living near large industrial enterprises or factories, the baby has a higher risk of bronchial obstruction. This occurs as a result of the constant ingress of the smallest toxic substances into the small bronchi. Industrial emissions quickly lead to the development of respiratory failure.
Prematurity In the third trimester of pregnancy, the final formation of the respiratory organs of the future baby occurs. This process takes place almost until the days of birth. If, due to some circumstances, the child is born earlier, then the risk of respiratory underdevelopment increases several times. Such an anatomical defect often leads to impaired respiratory function.
Rapid abandonment of breastfeeding. Children who received their breasts in a very short time have a higher risk of getting bronchitis.To combat various infections you need a good level of immunity. During breastfeeding, babies receive a large number of immunoglobulins G. These protective antibodies help them not to get sick during the period of seasonal colds and protect against the development of diseases of the bronchopulmonary system.
How does it come about?
Influencing provocative factor leads to the development of severe inflammation. Most viruses and bacteria enter the body through the upper respiratory tract. Deposing on the epithelial cells lining the respiratory organs, they begin to have a strong toxic effect.
The incubation period is different and depends on the characteristics of the particular microorganism that causes the disease. On average, it is 7-10 days. At this time, the child does not show any complaints. There are no specific signs of the disease during the incubation period. Only weakened children can feel a little fatigue and drowsiness.
After the end of the incubation period, the first specific symptoms characteristic of this disease appear. An active inflammatory process that occurs in the bronchial tree, contributes to the violation of the discharge of mucus and sputum.
In babies who have anatomical defects in the structure of the bronchi, the bronchi are very narrow. Bronchial obstruction in such children develops much more often and is much more difficult.
Kinds
The course of diseases associated with bronchial obstruction may be different. It depends on the initial state of immunity of the baby, the characteristics of the anatomical structure of the organs of the respiratory system, as well as the cause that caused the disease.
According to the frequency of occurrence, all obstructive bronchitis can be divided:
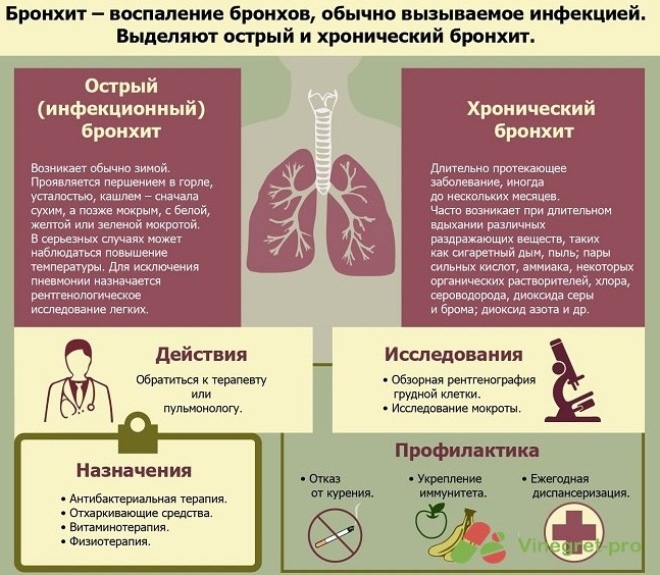
Sharp These variants of the disease appear for the first time. They last, on average, 1-2 weeks. After the treatment, the baby is completely cured.
Chronic. May be recurrent. Progress with periods of exacerbations and remissions. In case of insufficiently high-quality treatment or the presence of concomitant diseases in a baby, acute forms become chronic.
By severity:
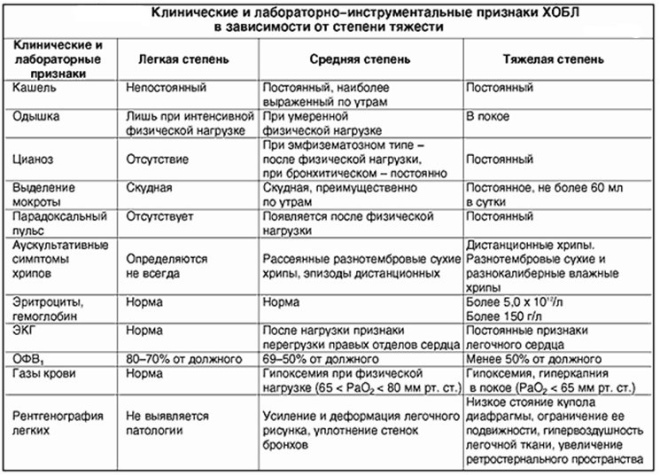
Lungs. Proceed with minimal symptoms. Well treated. After the treatment, the babies fully recover. Long-term effects of the disease does not occur.
Medium degree. Cough stronger, hacking. Body temperature in moderately severe obstructive bronchitis rises to 38 degrees. Dyspnea may increase. The general condition of the child suffers greatly. In some cases, hospitalization and more intensive care are required.
Heavy. Proceed with a marked violation of the general condition and well-being of the baby. Body temperature rises to 38.5-39.5 degrees, severe shortness of breath, accompanied by signs of respiratory failure. The treatment is carried out only in the conditions of a children's hospital, and with the development of cardiopulmonary insufficiency - in the intensive care unit.
Symptoms
The narrowing of the bronchial lumen and the violation of sputum discharge causes the child to have specific signs of the disease:
Cough. Appears on 2-3 days after the end of the incubation period. The hacking cough bothers the baby more during the daytime. May be paroxysmal.
Dyspnea. Occurs with moderate and severe disease. When dyspnea increases the number of respiratory movements in one minute. Babies often breathe. This symptom can be seen from the side, paying attention to the movement of the chest during breathing.
Soreness in the chest during expectoration. With bronchial obstruction, sputum becomes very dense and thick. All clearing attempts lead to increased pain in the chest area.
Increased body temperature. It increases to 37-39.5 degrees.Bacterial forms of the disease are accompanied by a higher temperature.
Blue nasolabial triangle. The skin in this area on the face is very thin and sensitive. A pronounced decrease in the level of oxygen in the blood leads to the development of acrocyanosis (blue) in this area. On the background of the pale face, the nasolabial triangle contrasts strongly.
Violation of nasal breathing and redness of the throat. These secondary symptoms are found in viral and bacterial infections and often appear in a child with obstructive bronchitis.
Severe drowsiness and impaired well-being. Sick kids refuse to eat, begin to be capricious. Little kids are more asking for pens. Long coughing attacks cause the baby to start crying.
Thirst. Manifested during severe intoxication of the body. The more severe the disease, the more pronounced this symptom in the baby.
Active movement of the ribs during breathing. Respiratory movements have a large amplitude and become visible from the side.
Loud breathing. During breathing movements, there are bubbling sounds. They result from the passage of air through tightly closed bronchi.
Diagnostics
When the first signs of bronchial obstruction appear, the child should be shown to the pediatrician. The doctor will conduct a clinical examination and will recommend additional examinations. Such tests are needed to determine the severity and cause of the disease.
For the diagnosis of obstructive bronchitis is used:
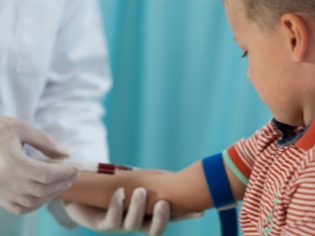
General blood analysis. The increase in the number of leukocytes and accelerated ESR indicate the presence of an inflammatory process. Changes and shifts in the leukocyte formula allow to clarify the viral or bacterial nature of the disease.
Blood biochemistry. Allows you to identify the presence of complications that develop with respiratory pathology. Also used for differential diagnosis.
Radiography of the chest. This method is used in children older than one year. This study allows to establish the degree of narrowing of the bronchi, as well as to identify associated lung diseases.
Spirometry Helps assess functional impairment. Indications of forced inhalation and exhalation allow doctors to conclude about the presence and severity of bronchial obstruction.
Specific laboratory tests for the identification of allergens. Necessary to establish the cause of bronchial obstruction in children with an allergic form of the disease.
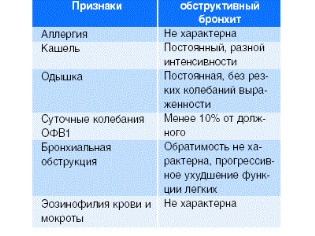
Differential diagnostics
The narrowing of the lumen of the bronchi is found not only in obstructive bronchitis. The syndrome of bronchial obstruction can be in various diseases. In order to correctly establish the diagnosis, a differential diagnosis is required.
Most often obstructive bronchitis can be confused with:
Stenosing laryngotracheitis. Most often caused by viruses. It usually occurs 3-4 days after the onset of a viral infection. Characterized by the appearance of barking cough and severe shortness of breath.
Obliterating alveolitis. In this disease, the growth of the internal epithelial layer of the bronchi occurs, which leads to the appearance and accumulation of frothy sputum. Usually cough is paroxysmal. Often the disease leads to the appearance of various complications.
Acute bronchitis. Symptoms are similar. Only spirometry can accurately establish the correct diagnosis.
Infection with parasites. Some worms during development in the body with a blood stream can fall into the bronchopulmonary tree. Developing, they emit numerous products of their vital activity, which have a toxic effect.
Cystic fibrosis. This disease is congenital. Usually, children develop poorly, lagging behind in physical development from their peers. During an exacerbation, there is a strong cough with difficult and very viscous sputum.The course of the disease is quite difficult. The disease requires systemic treatment.
Consequences and complications
Frequent obstructive bronchitis can lead to the development of persistent respiratory disorders in children. With reduced immunity in the baby, all new exacerbations occur in a relatively short period of time.
Poor treatment or late diagnosis of the disease contribute to the development of complications in the future. Persistent bronchial obstruction may lead to development bronchial asthma, especially if the cause of the narrowing of the bronchial lumen was an allergy.
Long and hacking cough contributes to the formation of bronchiectasis. In this pathology, the distal sections of the bronchi are expanded to form additional cavities. Bronchiectasis contributes to the appearance of shortness of breath with an increase in respiratory failure. Surgery is performed to eliminate this condition.
During the exacerbation of obstructive bronchitis caused by a bacterial infection, the inflammatory process may spread to the lungs.
In this case, pneumonia or abscesses appear. They, in turn, lead to a deterioration of the child's well-being. Intensive antibiotic therapy is required to eliminate purulent tumors.
Treatment
Various methods of treatment are used to eliminate the adverse symptoms of the disease. After examining the child and making a diagnosis, the pediatrician will recommend a specific treatment regimen, which is provided in the clinical guidelines. These medical developments contain the necessary algorithm of actions of doctors in identifying a specific pathology.
Treat obstructive bronchitis follows from the first days, after the onset of symptoms. Early prescription of drugs helps to cope with all adverse manifestations of the disease and prevent chronicity. Preparations that eliminate the bronchial obstruction and contribute to a better sputum discharge are prescribed by the attending physician.
For the treatment of obstructive bronchitis use:
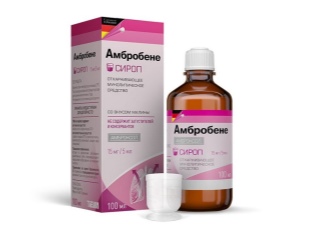
- Means with mucolytic action. They help to dilute the thick sputum and contribute to its easier discharge through the bronchopulmonary tree. Ambroxol-based preparations are widely used in pediatric practice. "Ambrobene", "Lasolvan", "Flamed"Help to eliminate even a strong cough. Appointed by age, 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days.
- Antipyretic. Appointed when the temperature rises above 38 degrees. In babies, various paracetamol-based products are used. Not assigned for long-term use. May cause allergic reactions and side effects.
- Bronchodilating. PDesigned to eliminate blockages in the bronchi and improve breathing. Appointed usually in the form of aerosols or inhalations. The effect is achieved in 10-15 minutes. Short acting bronchodilators on the basis of salbutamol act in 5 minutes.
- Combined products containing bronchodilators and anticholinergic preparations. To improve the bronchial conductivity in children is used "Berodual". It is administered by inhalation. The dosage and frequency of inhalation is carried out taking into account the age of the child. Usually the drug is prescribed 3-4 times a day.
- Antihistamines. Helps to cope with adverse symptoms in allergic forms of the disease. Children use drugs based on loratadine, "Claritin"," Suprastin ". Appointed 1-2 times a day, usually in the morning. Discharged for 7-10 days. With a more severe course - for 2-3 weeks.
- Vitamin complexes enriched with selenium. These substances are needed to combat intoxication. Biologically active components that are present in the vitamin complex, help the baby to fight infection and improve the immune system. Selenium is needed for the active work of immunity.
- Glucocorticosteroids. Used with severe and prolonged course of the disease. Usually appointed inhalation "Pulmicort". Prescribed medication for long-term use. Apply 1-2 times a day to achieve a stable good result. May cause side effects with prolonged use.
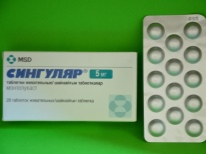
- Leukotriene receptor blockers. Helps to quickly eliminate bronchospasm. Have a lasting effect. A drug "Singular"Begins to have an effect within 2 hours after ingestion. It is applied 1 time per day.
Home treatment
Help your child cope with the disease can not only with drugs and pills. The use of drugs prepared at home, also helps to eliminate the coughing hamper and improve the child's well-being.
The methods that are safe and effective for self-application include:
Plentiful warm drink. Perfectly suitable alkaline mineral water, heated to a temperature of 40-45 degrees. They are appointed 20 minutes before or one hour after meals, 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. You can use "Essentuki" or "Borjomi".
Liquorice root. This wonderful remedy improves sputum discharge and promotes better expectoration. It should be used carefully, bearing in mind possible allergic reactions. It copes well even with a strong cough.
Breast fees. The composition of such pharmaceutical preparations includes several medicinal plants with expectorant and anti-inflammatory effects. Licorice, coltsfoot, sage help to cope with coughing and improve bronchial conductivity.
Radish juice. For the preparation of such a homemade medicine, ordinary black radish will do. To make 250 ml of the drink, you only need 1 teaspoon of juice. Before use, add honey to taste.
Breathing exercises
It is applied after the subsidence of the acute process. Usually such a gymnastics is conducted on the 5-6 day from the beginning of the disease. The correct sequence of respiratory movements helps to normalize the work of the respiratory system and cope with adverse symptoms.
In order to improve the outflow of sputum, when performing breathing exercises, a sharp and short breath is taken. The exhalation is rather slow and smooth. During exhalation should be considered to 5. Each set of exercises consists of 3-4 repetitions. It is recommended to practice every day. Even in remission, breathing exercises will be very helpful.
How to conduct breathing exercises look in detail in the form below.
Nutrition
The diet of a child suffering from bronchial obstruction should be complete and contain all the necessary nutrients and vitamins.
Breastfeeding in the acute period of the disease should not be canceled. Together with mother's milk, the baby receives all the necessary protective antibodies that help it fight the infection causing bronchitis.
Older kids should eat fractional, at least 5-6 times a day. In the diet of the child should include a variety of protein foods. It is better that with each meal the baby gets some kind of protein source. Perfect veal, rabbit, chicken or fish.
Try to choose more lean varieties. Fatty foods are absorbed longer by a weakened child’s body. You can supplement proteins with cereals and vegetables. Fresh fermented milk products are also well suited as protein foods. They will be a great afternoon snack or second dinner.
All dishes are better steamed, baked or stewed. They should be more fluid consistency. Fruit and vegetable purees are perfect for younger children. It is not necessary to give the child food from the jars. A good choice would be mashed cauliflower or potatoes, cooked at home.
The kid must drink enough liquid.As drinks, you can use compotes, various fruit drinks and juices made from fruits and berries. Frozen fruits are also suitable for making healthy decoctions. Try to give your child more boiled water. This will help eliminate the adverse symptoms of intoxication.
Prevention
In order for the baby not to suffer from obstructive bronchitis, use the following recommendations:
Visit your dentist regularly. Often the presence of carious and untreated teeth leads to the development of various infectious pathologies. Make sure your baby regularly brushes his teeth.
Do not allow colds. Any frequent respiratory diseases, which mainly occur in the cold season, lead to disruption of the respiratory organs and reduce immunity. The risk of bronchial obstruction in frequently ill children increases several times.
Strengthen immunity. Active walks in the fresh air, good nutrition and the correct daily regimen contribute to the normal functioning of the immune system.
Treat on time inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Children suffering from chronic otitis or sinus have a higher chance of becoming ill with obstructive bronchitis in the future. To prevent this, visit otolaryngologist with your child regularly.
Use special room humidifiers.. Too dry air contributes to respiratory failure. Room humidifiers help create a comfortable and physiologically favorable microclimate in any room.
After the treatment complex, the babies feel much better. They have normal breathing, shortness of breath. With a properly selected therapy, the transition of an acute to a chronic process does not occur. Compliance with preventive recommendations helps to prevent the emergence of new exacerbations in the future.
Dr. Komarovsky will tell you more about obstructive bronchitis in the video below.