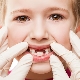
An abscess on the gum in a child
One of the rather unpleasant and dangerous for the child's health situations associated with dental diseases is the formation of an abscess on the baby’s gum. This situation requires an immediate response from the parents, as it can lead to unpleasant consequences.
Why and how an abscess appears on the gums
The main reason for the formation of ulcers in the tissues of the gums of children is their infection, which can occur as a result of:
- Untreated caries of the milk tooth, which caused pulpitis.
- Poor treatment of the tooth (if the doctor has installed a seal on the untreated tooth).
- Infections in cystiform structure, appearing at the site of teething.
- No treatment of pulpitis permanent tooth.
- An infection in the gum after its injury with any sharp object.
Most often the formation of an abscess on the gums is triggered by caries. The first stages of this disease often go unnoticed, so the infection sneaks inside the tooth. As soon as it reaches the root, toxins begin to penetrate through its tissues and cause inflammation of the gums near the root. Since bacteria have become the cause, pus is formed in the process of such inflammation. It goes under the mucous membrane of the gums, which looks like a purulent pouch.
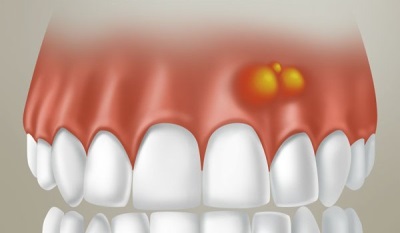
Main symptoms
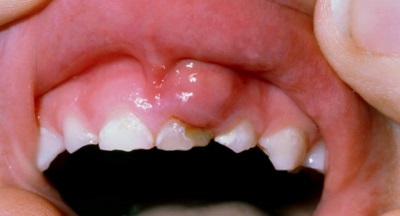
The appearance of purulent formation on the gum is accompanied by quite specific symptoms. First, the child will notice a feeling of distention in the gums, and a little later, in the place that he pointed out, a slight reddish swelling will appear.
Gradually, its size will increase, and a white dot will become noticeable in the center of the bump. It indicates the appearance of pus inside the gums. If you touch such a bump, you will see that it is soft, and the child will notice that it is very painful. Increasing in size, the lump is transformed into a white abscess.
In addition to changes in the mouth, a child may have other symptoms:
- Increased body temperature.
- Moods and restless behavior.
- Refusal of food.
Possible complications
If you do not consult a doctor at the time of formation of the abscess, it will increase in size and as a result will burst. This will improve the general condition of the child (the pain will decrease, and the temperature will decrease), but will lead to the formation of a fistula, through which the pus will go into the oral cavity.
In some cases, the fistula is delayed independently, but still represents a focus of infection, which threatens to activate the inflammatory process in certain conditions (with a decrease in immunity).
If the ulcer appears due to the disease of the baby tooth, it can cause infection of the germ constant. In addition, bacteria from the abscess can fall on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, provoking the development of their chronic inflammation, as well as in the lymph nodes under the jaw, causing lymphadenitis.
Another danger of having a fistula in a child’s mouth is allergy to the body. In the most severe cases, pus can enter the bloodstream, after which it spreads through the body of the child and may cause suppuration in other organs and tissues. No less dangerous is the spread of infection in the deeper tissues of the jaws with the formation of cellulitis or bone inflammation.
What to do
The most correct tactic of parents in detecting an abscess on the gums of their child will be an appeal to a dental clinic. The doctor will examine and determine their further actions, which will be affected by the stage of the process (an abscess is only being formed, already formed or ruptured) and the type of tooth (milky or permanent).
It is best if the child visits the dentist in the early stages of development, when a purulent lump has just appeared, but even after breaking through the baby's abscess, you still need to be taken to the doctor to eliminate the source of infection and prevent the abscess from recurring in the same place or over the adjacent teeth.
Treatment
When an abscess appears in the area of the milk tooth, the doctor first anesthetizes the place of manipulation, then opens the formation and removes pus from its cavity, and then removes the milk tooth, the defeat of which caused the development of purulent inflammation. Next, the child will be assigned a course of antibiotics and rinses.
When an abscess is formed over a permanent tooth, the doctor after examination and local anesthesia will incise the gum and, with a very large amount of abscess, install drainage. If the pulp is infected, the channels of the tooth are opened, depulpation is performed, and then a seal is installed.
How to treat at home
If you immediately take the child to the dentist when an abscess occurs, the parents can provide such first aid to the toddler at home:
- Give the antipyretic drug approved by the child at an elevated temperature.
- Suggest rinsing the mouth with warm chamomile decoction or sage, if the child is already able to perform rinsing, and the abscess is not opened.
- Do not give the child hard and hot food.
- To reduce soreness, apply something cold to your cheek.
- Do not allow the child to touch the abscess.
- Give your baby more drink.
- Call an ambulance if the condition of the child worsens.
If an ulcer is detected in a child, it is strictly forbidden:
- Trying to open education with their own hands. It threatens to enter the bloodstream.
- Heat the site of inflammation with hot compresses or hot rinses.
- Give an antibiotic to a child without a doctor's prescription.
- Rinse your mouth if the abscess has opened.
Prevention
In order to prevent the development of an abscess on the gums of a son or daughter, it is recommended:
- To pay attention to the hygiene of the oral cavity, starting from the moment of the eruption of the first teeth.
- Ensure that the child cleaned the teeth properly in the morning and before bedtime.
- Rinse your mouth after meals.
- Regularly go to the examination in the dental clinic and in time to treat the caries found in the early stages.
- Protect gums from injury.
- Do not allow the child to abuse the sweet and keep the candy behind the cheek.