Frequent problems with gums in children
Like caries, gum disease occurs in childhood quite often, which is associated with both physiological causes and hygiene problems in children. Toddlers are more vulnerable to various infections, they often pull contaminated objects into their mouths and fall, as well as not sufficiently clean the oral cavity from food debris and bacteria. All these reasons can cause problems with the gums, and it is important for parents to know what to do if the crumb has broken the gums, the baby’s gums are bleeding or itchy.

Most common problems
Most often, when gum changes are found in a child, they are a symptom of inflammatory diseases or injuries.
Gingivitis
This is a very common inflammatory gum disease in children, which can be caused by various causes, such as poor care for the gums, cuts with sharp edges of a toy, improper bite, infectious diseases, lack of vitamins and many other factors.
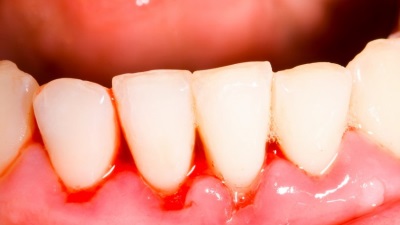
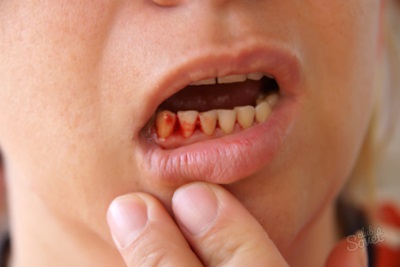
In its development, the disease goes through several stages. First, catarrhal inflammation develops, in which the baby feels discomfort and itching in the gums, as well as pain when the temperature changes. If such gingivitis is not treated, the loose gums of the child begin to bleed and become covered with areas of erosion. Further, the development of an atrophic form is possible, or hypertrophic gingivitis develops, in which a child has thick gums on examination.
In treating such an illness, it is important to thoroughly clean the teeth of plaque, after which the doctor will prescribe the child to rinse and irrigate with antiseptics (for example, chamomile infusion, rotocan or miramistin), as well as the treatment of gums with anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs (for example, holisal, solcoseryl, kamistad , sea buckthorn oil, gingivit gel or gel metrogil denta).
Periodontitis
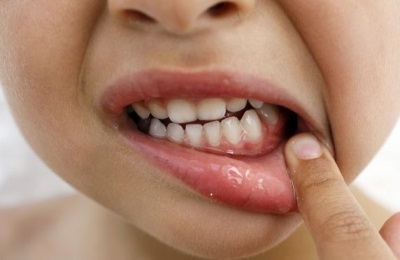
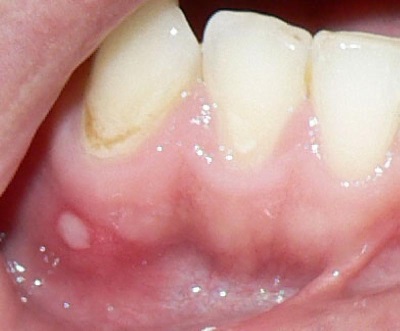
So called one of the complications of caries, in which the infection penetrates so deeply that toxins affect the gum tissue next to the sick tooth. The result is the formation of pus inside the gums. He tries to find a way out and forms a pus-filled bladder on the surface of the gum. If such a blister is opened by itself, a fistula appears in the gum. With a strong suppuration, the infection gets into the soft tissues, which causes swelling of the jaw (flux appears).
In the treatment of periodontitis, it is important to eliminate the source of infection, so if it is represented by a baby tooth, such a tooth should be removed. If such a complication appears around a permanent tooth, it is opened and treated with the installation of a seal, trying to keep the child molar.
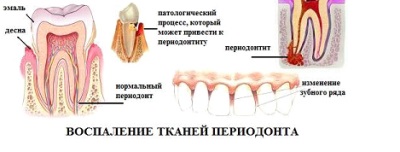
Periodontitis
Such a disease develops with untreated gingivitis, affecting not only the gum tissue, but also their connection with the teeth. It is manifested by bleeding gums and unstable teeth, frequent appearance of fistulas and abscesses. The main danger of such a pathology is the risk of losing teeth, and the treatment of the disease must be comprehensive.
Stomatitis
Such a disease, often affecting the gums of a child, can be caused by fungi, germs, injuries, viruses, poor hygiene, allergies, or other causes. At an early age, thrush is most often diagnosed in children. This disease is manifested by redness of the gums, white bloom, fever and other symptoms.Antifungals, antiseptics, painkillers, and folk recipes are used in its treatment.
No less often children develop such types of stomatitis as herpes (its main manifestation is a bubble rash on the gums) and aphthous (this stomatitis looks like a white sore). Their treatment should be monitored by a doctor, since herpes stomatitis is highly infectious and requires the prescription of antiviral drugs, and in the treatment of aphthous it is important to prevent the occurrence of its recurrence.
Injury
Since babies often fall or gnaw something hard, gum injuries are quite common. The manifestation of injury is usually a dark spot, which is a hematoma. If a lot of blood is collected inside such a hematoma, the spot becomes purple or almost black, which frightens parents. If such a stain is detected, you should consult a doctor so that he examines the child. Quite often, the doctor does nothing and allows the hematoma to dissolve on their own, but at very large sizes or at risk of inflammation, the formation is opened.
Rarer problems
In some babies on the gum can be found and such formations:
- Pearl cysts. So call the small round white points consisting of epithelial tissue. Their name is due to the fact that each cyst looks like a tiny pearl. Such cysts are not dangerous and eventually dissolve without a trace.
- Wen. It is a benign tumor that does not affect the health of the child. Remove this formation only in the case of active growth or when changing the appearance of the tumor.
- Papilloma. So called benign growth of the mucous membrane, protruding above the surface of the gums in the form of a small papilla. If the papilloma does not bother the child, do not touch her.
For gum disease, see the next video.