Cortexin for children: instructions for use
In order to improve brain activity, intensify metabolic processes in brain tissues and eliminate various neurological pathologies, nootropic medications are often prescribed for children. One of them is the drug of the domestic pharmaceutical company Geropharm, called Cortexin. When is it prescribed to a child and how to properly treat babies with this medication?
Release form and composition
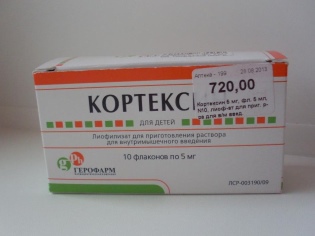
Cortexin is presented in pharmacies only in one form - injection. It is sold in boxes, inside of which there are 10 glass bottles with white or yellowish-white powder (lyophilized). It may also look like a porous uniform yellowish or white mass.
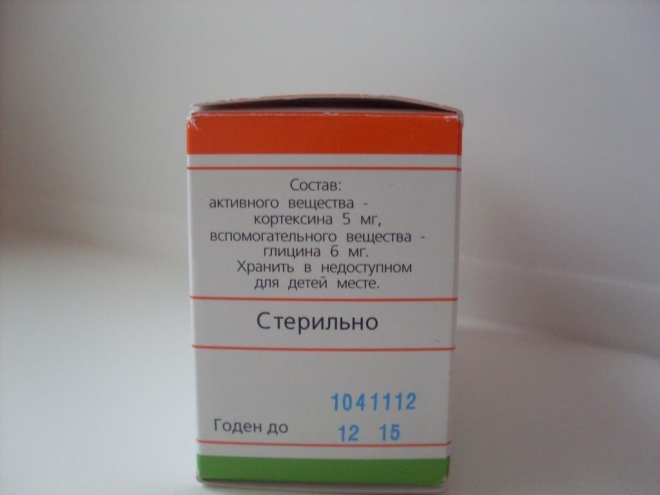
The main ingredient of such a powder is polypeptide fractions, the molecular weight of which does not exceed 10 thousand Da. Such protein molecules with a small length and mass are a water-soluble complex and are also called Cortexin. Their number in one vial can be 5 mg or 10 mg. These polypeptides are extracted from the brain of pigs or cattle (from the bark).
Glycine is added to the drug as a stabilizer. Its dosage is 6 mg in vials with 5 mg of the active complex (the drug contains 11 mg in total, and the volume of the bottle is 3 ml) and 12 mg in the preparation with 10 mg of cortexin (22 mg of powder is inside, and the volume of the bottle is 5 ml) .
Operating principle
After the injection, low molecular weight protein molecules Cortexin pass through the blood-brain barrier and have such an effect on the brain:
- Both nerve cells and neurotrophic factors are stimulated, due to which information is better and faster transmitted through the fibers, and the balance of excitatory and inhibitory mediators is normalized.
- They protect neurons from various damaging factors, for example, from hypoxia, free radicals or calcium ions. This therapeutic effect of the drug is called cerebro-or neuroprotective. It makes nerve cells more resistant to any external influences, including stressful situations and taking various psychotropic drugs.
- They activate metabolic processes in the brain tissues and accelerate the regeneration of nerve cells, as a result of which the overall tone and function of the CNS improves.
- Positively affect the ability to learn new material and work. Such an action is called nootropic. It consists in improving the functions of thinking, among which attention and memory are especially important.
- Reduce seizure activity in brain tissue lesions. Due to this effect, Cortexin can help prevent seizures.
- Oxidative processes in brain cells are slowed down, that is, they act as an antioxidant.
Indications
Cortexin in childhood is prescribed:
- With traumatic brain injury or to eliminate their effects.
- When encephalitis or encephalomyelitis.
- When speech is delayed.
- With epilepsy.
- When neuroinfections caused by viruses or bacteria.
- With delayed psychomotor development.
- When circulatory disorders in the brain.
- When encephalopathy.
- With hydrocephalic syndrome.
- If you have problems with memory or with attention.
- When asthenia.
- When cerebral palsy.
How old is allowed?
Cortexin can be administered to children of any age, including infants in the first year of life. Such a tool is used even in premature babies, if there are serious indications for this, for example, in birth trauma, neuroinfection, or hypoxia during labor.
Contraindications
The drug is not used in children with intolerance to its components. Other contraindications for such drugs are absent. However, if the baby is sick during the course of therapy, you should definitely consult a doctor and discuss the cancellation of the medication. As a rule, for colds, flu and other acute respiratory viral infections injections do not do, and suffer treatment for the period when the child is fully recovered.
Side effects
Sometimes treatment with Cortexin provokes an allergic reaction, such as a rash or itchy skin. If the injection site is red, there are rashes or the child complains of pain and burning, the baby should be shown to the doctor.
Instructions for use
Cortexin is administered only intramuscularly. Before making the injection, the lyophilisate must be diluted. Dilution of the powder is performed immediately before the injection. For this purpose, apply sterile water intended for injection, as well as sterile saline.
A medicine can also be diluted with a 0.5% solution of novocaine, but this solvent is used much less frequently. Although it reduces the painfulness of the procedure, when diluted with an anesthetic, the therapeutic effect of Cortexin decreases, and the risk of an allergy to an injection increases. For this reason, the use of novocaine is recommended only if the child is difficult to tolerate injections and they are very painful for him, and the allergy to novocaine in a small patient is absent.
In order to dilute Cortexin, you must first collect a solvent in a volume of 1-2 ml with a sterile syringe, then remove the foil from the vial of lyophilisate and puncture the rubber stopper. Next, the solvent should be gently released into the vial so that no foam is formed (for this purpose it is advised to send a stream of liquid to the wall so that the solvent flows slowly onto the powder).
Having released all the water or saline and not removing the needle, it is necessary to gently shake the bottle until the powder is completely dissolved. As soon as the solution becomes homogeneous and transparent, it is collected back with the same syringe, and then intramuscular injection is performed.
It is important to remember that for one injection, the entire lyophilisate is diluted, and then the required amount of medication is collected. To divide the powder into parts, and then dilute only one of them is unacceptable.
The drug is advised to enter the muscles of the shoulder or thigh. To reduce pain, the injection should be done with a thin needle, and the medicine should be injected very slowly. The next injection is done, departing from the previous place at least 1 cm.
Dosage
- Babies weighing up to 20 kg need to calculate the dose by weight. To do this, the number of kilograms is multiplied by 0.5, for example, if a child weighs 8 kg at 10 months, then he needs 8 x 0.5 = 4 mg of cortexin per day. For such a baby, take vials with 5 mg of the active ingredient, dilute 2 ml of water for injection and inject a grit of 1.6 ml of the finished medicine (it is from this amount that the baby will receive 4 mg of the active complex). If the medication is diluted with 1 ml of saline or sterile water, then the child needs to enter 0.8 ml. The remainder of the drug is discarded.
- For a child weighing more than 20 kg, Cortexin is prescribed 10 mg per day. One bottle with the content of the active complex is diluted with 1 ml of water for injection or saline.
- The drug is administered daily 1 time for ten days. The injection is recommended to do in the morning, because the medication has a stimulating effect. After a 10-day course of treatment, they take a break for 3-6 months, after which the therapy can be repeated.
- For stroke, 2 injections of 10 mg are taken daily. One of them is given in the morning, and the second - in the daytime, as the injection made in the evening may prevent sleep.
- If for some reason the injection was missed, the next day you do not need to enter the drug in double dose.In such a situation, the course is extended in order to make a total of 10 shots.
Overdose
For the entire time of use of the drug in children, no cases of overdose have been reported.
Drug interaction
Cortexin does not have any negative effect on other drugs, so it can be used in conjunction with various medications. In this case, the drug should not be mixed in the same syringe with any other solutions, except approved solvents. If several injections are prescribed, they should be given in separate injections.
Terms of sale and storage
Buying Cortexin in pharmacies is possible only if you have a prescription for such a medicine, obtained from a pediatrician, a neurologist or another specialist. The average price of 10 ampoules, which contain 10 mg of the active compound, is 1,200 rubles. Separately, you should purchase a package with ampoules of saline or water for injection with a volume of 1-2 ml.
Keep a box of bottles at home is recommended at temperatures below +25 degrees in a place where the tool will be hidden from the sun's rays and inaccessible to children. The shelf life of sealed vials of powder - 3 years from the date of manufacture. Diluted medication can be stored for no longer than 20 minutes. If, after mixing with the solvent for any reason, more time has passed, the syringe with the drug must be discarded, and then diluted and collected lyophilisate from a new bottle.
Reviews
On the treatment of children Cortexin found a lot of good reviews. In them, mothers note that after the course of injections, the child speaks better, easily learns poetry, memorizes new information, becomes less nervous, expands his vocabulary. The smallest medicine accelerates motor development. According to the parents, the kids after the injections learn to roll over quickly on the tummy, sit, stand, hold a spoon, learn to crawl, and so on.
In the treatment of schoolchildren, mothers confirm the positive effect of Cortexin on thinking, attention and memory. In children of this age, the drug effectively helps with low learning, difficulties with the assimilation of the material, problems with speech. Doctors also emphasize that the injections help eliminate the negative effects on the brain of stress, hypoxia, trauma and other factors. However, many doctors, among whom Komarovsky, include Cortexin and other nootropics to drugs whose effectiveness is not proven.
It is well tolerated by most young patients. Local reactions to injections occur very rarely and often when diluted with Novocain powder. In the negative reviews complain about the high cost of treatment, a strong pain of injections, and in some children there is no positive effect on the nervous system. Also, many parents do not like that the drug is released only in an injection form, so they choose analogues in tablets.
Analogs
Instead of Cortexin, children may be given other drugs with a similar therapeutic effect:
- Kogitum. This medication in the form of a sweet banana solution in ampoules is in demand for ZRR, asthenia, perinatal CNS damage, neurosis, and other problems. It is prescribed from the age of 7.
- Cerebrolysin. The action of this drug in ampoules for intravenous or intramuscular injections is provided by peptides that are obtained from the brain of pigs. The drug is used in children with traumatic brain injuries, organic or metabolic brain diseases. Children are prescribed at any age, if there are indications for this.
- Aminalon. Such coated tablets act due to gamma-aminobutyric acid. They are discharged for problems with attention, cerebral palsy, mental retardation, depression, drowsiness, motion sickness, prescribing for children older than a year.
- Pantogam. This product, in the form of syrup or tablets, contains hopantenic acid and is used at any age.The drug is indicated for mental overload, neurosis, attention disorders, stuttering, enuresis and other problems.
- Gliatilin. These capsules or ampoules for injections contain choline alphosphate and are prescribed for circulatory disorders in brain tissue, memory loss, birth injuries of the brain, hydrocephalus, tics, developmental delay and other problems. The drug is allowed at any age.
- Vinpocetine. Such a drug in injections or tablets used for encephalopathy, stroke, autism, epilepsy and other diseases. In children, it is used only under the supervision of a physician.
- Nootropil. The basis of this medicine is piracetam. The drug is produced in tablets, solution, injections and capsules. Children are prescribed from the age of 1 with reduced learning, brain injuries, stroke and other neurological disorders.
- Glycine. Such a drug in pills is used for stress, attention disorders, developmental delay and other problems, prescribing it to children from birth.
- Fezam. The composition of such capsules includes two components that affect the brain - cinnarizine and piracetam. The drug is recommended for children 5 years and older with motion sickness, tinnitus, memory loss, asthenia and other disorders of the central nervous system.
A few words about the effect of nootropic drugs on the brain and the rules of admission in the following video.