Arrhythmia in children
Any heart problems in children cause anxiety in their parents, because the heart is one of the most important organs, and its work affects the health of the toddler in general. One of the fairly common "heart" diagnoses in childhood is arrhythmia. In approximately 40% of cases, arrhythmia is detected in children by chance during the examination, but in some cases it disrupts the child’s well-being and requires immediate medical attention.
What is it
So called the violation of the functioning of the heart, which is manifested by a change in the frequency or frequency of contractions of this organ. It can appear at any age, but most often arrhythmia is detected in newborns and infants, in children 4-5 years old, in schoolchildren aged 7-8 years, and also in adolescence.
The reasons
All factors provoking the development of arrhythmia are divided into cardiac (also called cardiac) and extracardiac (they are called "extracardiac").
Arrhythmia can occur with such cardiac pathology:
- Congenital malformations.
- The postoperative period in the surgical treatment of congenital malformations.
- Rheumatism.
- Myocarditis.
- Hypertrophic or dilated cardiomyopathy.
- Myocardial dystrophy.
- Heart tumor.
- Trauma of the heart.
- Pericarditis.
- Manipulations on the heart.
- Congenital rhythm disturbances.
For extracardiac causes of heart rhythm disorders include:
- Infections with dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
- Prematurity
- Intrauterine growth retardation.
- Emotional overload.
- Vegeto-vascular disorders.
- Diseases of the thyroid gland.
- Anemia
- High physical exertion.
- Diseases of the adrenal glands.
- Pathology of the CNS.
Symptoms
For arrhythmias, some specific symptoms are often uncharacteristic. In childhood, it can manifest itself:
- Weakness
- Shortness of breath.
- Pale skin.
- Increased fatigue.
- Discomfort in the chest.
- Refusal of food.
- Sleep disturbances.
- Bad weight gain.
- The restless behavior of the child.
- Dizziness.
- Pulsation of blood vessels in the neck.
- Cyanosis of the skin.
- Poor exercise tolerance.
- Feelings of disruption of the heart.
- Fainting
Kinds
Arrhythmias arising in childhood are classified on the basis of disorders in the heart that provoke them:
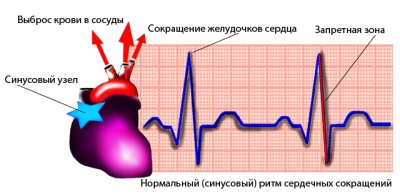
- Impaired automatism. They are represented by sinus arrhythmia, which may be in the form of tachycardia (rapid sinus rhythm), respiratory arrhythmia (disturbances associated with breathing) and bradycardia (slow sinus rhythm). With impaired automatism, the pacemaker migration is also encountered.
- Violations of excitability. When it occurs, beats, paroxysmal tachycardias, flutter and flicker of the heart chambers (both ventricles and atria),
- Conduction disturbances. Such arrhythmias are called blockades.
Clinically distinguish unstable arrhythmias that are not dangerous and pass on their own, as well as persistent arrhythmic disorders requiring treatment. Depending on the severity, the arrhythmia is moderate (most often diagnosed in children) and severe (a rarer variant).
What is dangerous
In case of pronounced arrhythmias, the development of brain tissue hypoxia and heart failure is possible. Some types of arrhythmias are characterized by a high risk of sudden cardiac arrest.
Diagnostics
You can suspect the occurrence of arrhythmia in a child when you listen to his heart during a routine examination by a pediatrician, as well as when counting the pulse, which can be done by both the doctor and mother at home. The main method for detecting arrhythmias is ECG recording. To clarify the diagnosis, daily monitoring (Holter), stress tests, ultrasound, radiography, consultations of narrow specialists are carried out.
Treatment
If the arrhythmia in a child is caused by functional reasons, it is not treated, but pay attention to a balanced diet, moderate physical exertion, proper organization of the child's day regimen. In case of pronounced arrhythmias, the child needs treatment, which can be medical, as well as surgical, depending on the cause of the heart rhythm disorder.

Drug therapy for arrhythmias is aimed at normalizing the balance of electrolytes and improving metabolic processes in the heart. If necessary, prescribed antiarrhythmic drugs. In some cases, they resort to surgery, for example, they destroy arrhythmogenic zones in the myocardium or implant a pacemaker.
What parents, whose children have an arrhythmia, can do, you can find out by watching the next video.