Sinus tachycardia in a child
Any problems with the heartbeat of the child are alarming and worrying, but parents need to know that some of the rhythm disturbances are not only in diseases, but also in healthy children. One of these disorders is sinus tachycardia.
What is it
The diagnosis “sinus tachycardia” refers to the change in the number of heartbeats per minute, at which the frequency of contractions increases, but the rhythm remains normal (it is called sinus because this rhythm comes from the sinus node).
For each age, the number of heartbeats at which they talk about tachycardia will be different, since the rate of heart rate at different ages is different. Tachycardia is the excess of the norm by 10-20% or more.
The reasons
The main reason for the appearance of sinus tachycardia is the activation of the sinus node, however, an increase in its automatism may be associated with non-dangerous physiological states and diseases.
Physiological
To this group of factors provoking the occurrence of sinus type tachycardia, include:
- Physical activity
- Excitement and experience.
- Fear.
- Stay in a stuffy room.
- Emotional stress.
- Temperature difference.
- Increased body temperature.
- Swaddling or inspecting a newborn.
Pathological
Such causes of sinus tachycardia are associated with damage to the heart or non-cardiac diseases. Heart palpitations occur with:
- The defeat of the central nervous system.
- Congenital heart disease.
- Myocarditis
- Acidosis
- Anemia
- Dehydration.
- Falling blood glucose levels.
- Violation of the thyroid gland.
- Tumors of the adrenal glands.
- Obesity.
- Heart failure.
Age
In newborns and children 2-3 years
The automatism of the sinus node in newly born babies is increased, so short-term episodes of an increase in the number of heartbeats for babies up to a year are considered the norm if such attacks pass on their own without medical intervention.
However, in some cases, the appearance of sinus tachycardia in an infant of 1 year of life is a sign of problems with the myocardium or other organs. This can be a congenital defect or a disease of the nervous system.
Schoolchildren and teenagers
At the age of 6-7 years and older, sinus tachycardia can be provoked by emotional or physical overload, and acquired heart disease.
In adolescence, the occurrence of such arrhythmias is often associated with active growth and hormonal changes.
Among the pathological causes causing sinus tachycardia at the age of 10 years and older, iron deficiency anemia and endocrine gland diseases are most common.
Symptoms
Tachycardia, which is triggered by physiological causes, often does not manifest itself in a child with some dangerous symptoms. Such light sinus tachycardia quickly passes and many children do not notice any discomfort.
Tachycardia caused by heart disease can be complemented by symptoms such as shortness of breath, dizziness, pain in the chest, severe weakness, and darkening of the eyes. Sometimes there is a loss of consciousness. This clinical picture is called a tachycardia attack.If it lasts more than 10 minutes, it can affect the metabolic processes in the heart muscle.
What to do
If a child's tachycardia occurs as a result of a physiological cause (due to fear, anxiety, or physical exertion), as a rule, it quickly passes by itself and does not require the intervention of a physician.
An attack of tachycardia in children of the first year of life is stopped only with its long duration in order to prevent heart failure.
The onset of sinus tachycardia in children of school or adolescence requires the attention of parents and doctors, as this condition can cause complications.
Diagnostics
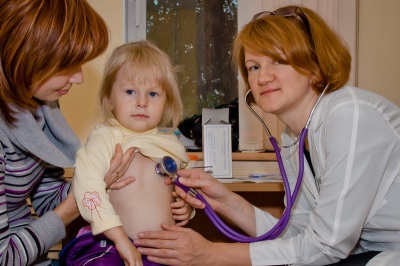
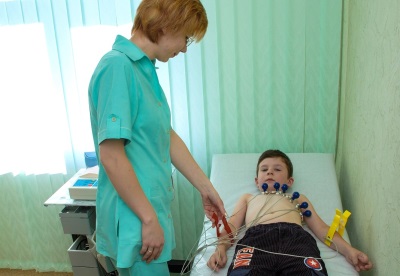
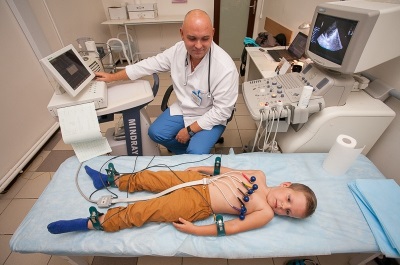
It is easiest to identify sinus tachycardia on an ECG, since this study allows you to accurately calculate the number of heartbeats, and to determine the changes in the complexes and segments, is it really sinus tachycardia. To clarify the diagnosis can be used and Holter monitoring, in which the ECG of the child is continuously recorded during the day.
To identify cardiac pathology, manifested by tachycardia, the child can prescribe echocardiography. To exclude extracardiac pathologies in a baby, it is required to have a complete blood count, to assess the level of thyroid hormones and to make an EEG. Of the narrow specialists, the child may need to consult an endocrinologist and a neurologist.
Treatment
If a child has a tachycardia attack, parents should be given a crumb such first aid:
- Provide access to oxygen by unbuttoning or removing clothing from the upper part of the body, as well as opening a window.
- Wash the toddler with cool water or attach a cloth dipped in water to the baby’s forehead.
- Ask your baby to take a breath and hold your breath for a while.
- Call the doctor, even in a situation where the attack has already passed.
Treatment for tachycardia should be prescribed only by a doctor, since it will depend on the cause of the attack.
Prevention
To prevent problems with heart rhythm in childhood, it is important to teach the baby to a healthy lifestyle. To do this, the baby must have an optimal daily regimen, moderate physical activity, a balanced varied diet, and full sleep.
The pediatrician in the next video will tell more about child tachycardia and will give some advice to parents who are faced with this ailment.