Ultrasound of the heart of the child
Heart health of the child is important for a full life and the normal development of each baby. That is why, in case of any suspicion of problems with the heart muscle or blood flow in this organ, it is important to examine the child in time and begin treatment. In order to quickly and accurately identify the pathology of the cardiovascular system, a lot of research methods have been developed. One of the most commonly used in children is an ultrasound of the heart.
What is it?
This is the name of the diagnostic procedure, in which the area under investigation (in this case, the heart) is affected by ultrasonic waves. These waves are generated by the sensor of the apparatus and directed to the heart, as well as to the nearby large vessels. Due to the fact that different tissues reflect or absorb ultrasound in different ways, their condition can be assessed.
Waves that are reflected from the organ being examined fall on the same sensor and then are analyzed in the computer of the device. Everything happens in real time, so the doctor immediately sees the data on the monitor of the device. Since the main principle of ultrasound is the reflection of waves, such a study is also called echocardiography (abbreviated - echoCG) or echocardiography.
You can find out more about the procedure by watching the following video.
Thanks to this study, the doctor can conduct:
- Evaluation of the heart of the child.
- Measuring the size of the heart.
- Determination of the thickness of its walls.
- Monitoring the status and operation of valves.
- Assessment of blood flow inside the heart.
- Visualization of large vessels that depart from the heart and bring blood to it.
- Measurement of pressure inside the heart.
Indications
Ultrasound of the heart is prescribed to children with suspected congenital heart disease and heart disease. The reason for the study may be:
- Refusal of the newborn or baby from the breast, if there are no acute diseases.
- The noise in the heart heard by the pediatrician.
- The alarming changes in the electrocardiogram of the child.
- Increased fatigue baby.
- Periodic (when sucking in babies or during physical activity in older children) or constant blueing of the child’s lips or the skin area above the upper lip, called the nasolabial triangle.
- Episodes of unconsciousness in a child.
- Parents identify the trembling of the chest, if you put your fingers to the lower half of the left or under the sternum.
- Increased body temperature without signs of acute viral infections and complaints from the child.
- Increased sweating for no reason.
- The appearance of shortness of breath at normal body temperature.
- Periodic cooling of the limbs.
- Child complaints of chest pain.
- Periodic or constant pulsation of the child's neck veins.
- Frequent pneumonia.
- The child’s lag in physical development and insufficient weight gain.
- The appearance of dry cough in the normal state of the throat and normal body temperature.
- Heart disease in relatives.

In addition, ultrasound is prescribed to children for prophylactic purposes at 1 month, especially if there are congenital heart defects in the family or the expectant mother has acute infections during gestation.Additionally, this procedure is scheduled according to the schedule for children at the age of 12 months, as well as during adolescence (at the age of 14).
You will learn more about the noise in the sredtsa in a child by watching the following video.
Contraindications
The procedure as a whole is not contraindicated for children of any age, but in some cases it is not performed if the child is opposed to it extremely negative or behaves too restlessly.
Kinds
In addition to the traditional ultrasound, when the child checks the heart, putting the sensor to the chest in a calm state, there are also these types of ultrasound examinations of this organ:
- Extraesophageal echocardiography. In this version of the study of the heart using ultrasound, a special sensor is inserted into the child's esophagus in order to be able to see the sections that are poorly visualized with a normal ultrasound scan. Manipulation is rather unpleasant for a child and requires special preparation, therefore it is rarely used in children. It is prescribed for severe heart disease or in some cases after surgery on this organ.
- Stress test. For such a study, physical activity or the administration of a drug is first required, after which it is checked with ultrasound how the heart does its work in altered conditions. The procedure is performed under the supervision of several specialists, and resuscitation equipment is always at the ready. In addition, this method has its own indications and quite a lot of contraindications, so its use is limited in childhood.
Is the procedure harmful?
Ultrasound examination of the heart of a child is a completely safe procedure. His holding does not impair the work of the heart and does not adversely affect the health of babies. This allows you to carry out ultrasound many times, even in one day. In addition, the manipulation is completely painless and is tolerated by most children without too much difficulty.
What diseases diagnoses?
When echocardiography in childhood can be identified:
- Congenital malformations of the heart, in particular, its walls and valves.
- Blood clots in the cavity of the heart or on its walls.
- The decrease in the volume of the chambers of the heart or their expansion.
- Increased muscle volume of the heart or its reduction.
- The presence of fluid in the heart bag (it is called the pericardium).
- The narrowing of the coronary vessels.
- Heart valve thickening.
- Inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, called the endocardium.
- The dying off of the heart muscle (infarction).
At what age can you do an ultrasound of the heart?
The procedure can be carried out from the first day of life, if there are indications to it. To perform it at a very early age, the ultrasound machine is equipped with a small-sized sensor. It is also important that the examination of newborns is performed by a specialist who has experience in examining such young patients.
Where can I do an ultrasound?
Nowadays, such a procedure is carried out in almost all medical institutions - and in district clinics, and in private medical centers, and in hospitals. Also available is the option of manipulation at home, which is used in case of a serious condition of the child.
How much is the procedure?
The cost of an ultrasound examination of the heart is influenced by several factors, among which the qualifications of the doctor, the authority of the medical institution and the accuracy of the equipment are particularly significant. In a normal clinic, manipulation can be performed free of charge, but it is necessary to register in a queue, which is not suitable in case of an urgent need to carry out a heart diagnosis. In private clinics, prices for the procedure range from 600 rubles to 5 thousand rubles.
Preparation for diagnostics
Special preparation for echocardioscopy is not required and there is no special diet in front of an ultrasound of the heart.If baby is a baby, it can be fed immediately before the procedure, so that the baby falls asleep and calmly transfers the manipulation.
If the child is older than infancy, it is important to pay attention to the psychological preparation of the child:
- Tell your baby why and how exactly they will perform the manipulation.
- Tune your child in a positive way and emphasize that the study will not hurt.
- Ask your child to listen to the instructions of the doctor and behave calmly.
- Do not discuss in the presence of a child the symptoms of the disease and the possible risks.
Mom should remember to grab a referral, a diaper, a bottle of water, napkins and a favorite toy of the baby.
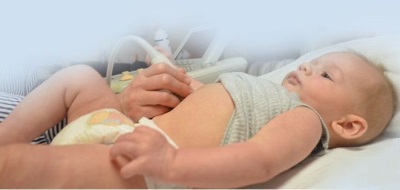
How is the procedure?
The child is not injected into anesthesia, but for an ultrasound it is important that the crumb be quiet for about 15 minutes. To do this, there are parents in the office, trying to distract and calm the toddler, for example, with the help of toys. The process of echocardiography itself looks like this:
- The child is stripped to the waist and laid on the couch.
- A small amount of gel, which is water soluble and hypoallergenic, is applied to the baby’s breast skin.
- The sensor device is applied to the gel and moves through the chest of the child during the study.
- Older babies may be asked to hold their breath several times during the procedure.
Decoding results
Analysis of the data obtained by ultrasound of the heart is performed by an ultrasound doctor, referring to the standard indicators typical for children of a certain age. Noticing deviations, he describes them in conclusion, for example, that the wall of the ventricle is thickened.
At the same time, the state of the valves is assessed, in which the specialist detects whether enough blood leaves the heart when it contracts into the blood vessels (this parameter is called the ejection fraction), and whether part of the blood returns to the heart (this phenomenon is called regurgitation).
With the results of the ultrasound, parents should go to a pediatric cardiologist or their local pediatrician. The doctor evaluates the data taking into account the clinical picture and determines the tactics during treatment, if any problems are identified.
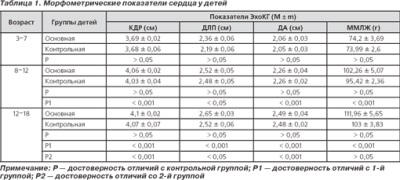
Here are some average ultrasound results of the heart normal in millimeters:
|
In 1-3 months |
11-14 years old |
|
The size of the left ventricle at the end of diastole |
|
|
16-24 |
34-51 |
|
The size of the left ventricle at the end of systole |
|
|
9-18 |
21-35 |
|
The thickness of the posterior wall in the left ventricle |
|
|
2-5 |
5-9 |
|
Aortic diameter |
|
|
9-15 |
15-30 |
|
Interventricular septum thickness |
|
|
2-6 |
5-8 |
|
The diameter of the left atrium |
|
|
10-19 |
19-32 |
|
The thickness of the walls of the right ventricle |
|
|
1-3 |
1-4 |
|
The diameter of the right ventricle |
|
|
2-13 |
7-18 |
|
Ejection fraction |
|
|
65-75% |
55-60% |
Possible pathologies
During the ultrasound of the heart can be diagnosed:
- Open oval window. It is detected normally in children of the first year of life in the septum between the atria. In some children, its overgrowth occurs by 5 years of age. For older kids, the presence of an oval window is a pathology.
- Mitral stenosis. The problem is manifested by the reduced size of the chambers in the right ventricle and the left atrium, as well as the thickened walls of these parts of the heart. In addition, when stenosis reveals a thickened mitral valve and a smaller opening that separates the left heart.
- Mitral valve insufficiency. Its presence is judged by the non-closure of the valve leaflets with the contraction of the heart and the return of part of the blood to the left atrium from the ventricle.
- Stenosis of the mouth of the aorta. This pathology is diagnosed on the basis of the thickened walls of the right atrium, as well as the left ventricle. In addition, ultrasound reveals a narrowing in the aorta.
- Aortic valve insufficiency. Its presence is detected in the absence of closure of the valves of this valve.
- Endocarditis. With such an illness on the valves will be revealed growths.
- Myocardial infarction. On ultrasound, it will look like a portion of the heart muscle that is not functioning.
- Myocarditis. This pathology is manifested by the expansion of the cavities of the heart and a decrease in the ejection fraction.

You will learn more about ultrasound examination of the heart by watching the following video.