Application of No-shpy in the treatment of children 2-5 years
No-shpu It can be called one of the most popular antispasmodics often used by adults for abdominal cramps, headaches and other pains. Can children be treated with this drug when it is used in childhood and what dosages are used?
Release form
No-shpa produced by the Hungarian pharmaceutical company in two forms:
- In the form of small round yellow with an orange or greenish tint pills with the words "spa" on one side. One pack contains from 6 to 100 tablets, which are sold both in blisters and in plastic bottles.
- In the form of greenish-yellow transparent the solution poured into dark glass ampoules of 2 ml. One box holds 5 or 25 ampoules.
Composition
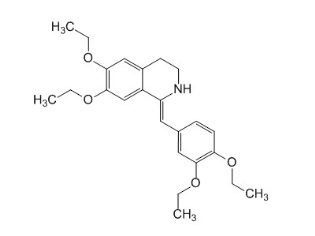
Both forms of the drug contain drotaverine hydrochloridewhich is their main ingredient. Its quantity both in 1 ampoule and in 1 tablet is 40 mg. So that the tablet No-shpa was dense and kept its form, talc, magnesium stearate and povidone, as well as lactose and starch obtained from corn are added to its composition. In the injectable form of the drug is sodium disulfite, sterile water and 96% alcohol.
How does it work?
In No-shpy, a rather strong effect on smooth muscles is noted, the result of which will be the elimination of spasms and muscle relaxation. The drug affects the walls of the digestive tract, biliary and urinary tract, as well as vascular walls.
The result of his admission will be a decrease in pain caused by cramps in the smooth muscles of the intestine, stomach, bladder and bile ducts.
Due to the effect on the vessels, No-shpa helps with fever, which is called “white”. A child with such a fever will have pale skin and cool limbs. A state of dangerously high risk of seizures, called febrile. Application of No-shpy helps to expand blood vessels, improving blood flow to the limbs and heat transfer.
When is appointed?
No-shpa claimed if a child has:
- Intestinal colic.
- Inflammation of the gallbladder or cholangitis.
- Inflammation of the bladder.
- Constipation, which is called spastic.
- Gastritis or gastric ulcer disease.
- Dry cough (medication can be applied at bedtime to prevent cramps in the airways).
- Toothache.
- High fever with simultaneous spasm of skin vessels.
Application
The instructions for the tablet No-Spee contain information that this form of the drug is not prescribed to children under 6 years of age. Annotation to the solution for intramuscular or intravenous injections prohibits the use of such a drug in children at all, referring to the fact that no clinical studies of the effect of No-shpy on young patients have been conducted. However, in practice, doctors often dispense No-shpu children in pills and injections.
According to doctors, these drugs are prohibited for children under one year old, and at the age of 1 to 6 years, they can be used, but with one important qualification, only a doctor should prescribe a medicine to children under six years old.
The specialist will determine whether No-shpa is really needed in the treatment of a particular child, and will also recommend the correct dosage according to age.
Contraindications
The treatment of No-spa is prohibited:
- With serious kidney disease, due to which the excretory function is impaired.
- With severe heart failure.
- When severe violations of the liver.
- When hypersensitivity to any ingredient of medication.
- With hereditary diseases due to which carbohydrate absorption is impaired (this is the reason not to prescribe pills).
- With severe pain in the abdomen (the drug can "smear" the clinical picture of surgical pathology and prevent timely treatment).
If a child has low blood pressure, the drug is applied very carefully, because it can provoke collapse.
Side effects
Judging by the reviews, patients in most cases tolerate No-shpu well, but occasionally the medication causes constipation, allergic rash, insomnia, skin itching, hypotension, dizziness, nausea, or headache. Such side effects are diagnosed in less than 0.1% of those who receive No-silos. When they appear, the medicine is canceled or its dose is reduced.
Dosage
If a patient is not yet six years old (for example, a child is only 4 years old), a pediatrician, urologist, gastroenterologist or other specialist who prescribes the baby No-silo should determine the single dose of medication. This can be a quarter, third or half pills. If a small patient still does not know how to swallow solid medicine, No-shpu in the dosage prescribed by the doctor is ground into powder, and then mixed with water or a sweet syrup.
The frequency of taking the pill will depend on the severity of the child’s condition. Sometimes a single dose of medication is enough, and some patients are given the drug up to 4-6 times a day. The duration of treatment must also be determined by the doctor, taking into account both the clinical picture and the response to therapy. The drug injections is prescribed in exceptional cases, for example, if the child is unable to take pills or there is a high risk to the health of the baby. Most often, the injection form of No-Shpy is used in children with fever, combining with antipyretic drugs (often Analginom) and an antihistamine (Diphenhydramine or Suprastin). For a single injection to a patient under 6 years of age, from 0.5 to 1 ml of No-shpa solution is taken.
Overdose
A very high dosage of No-shpy adversely affects the rhythm of the heartbeats and the conductivity of electrical impulses in the heart, which in severe cases can even result in cardiac arrest. For this reason, giving No-shpu to children under 6 years old without consulting a doctor is unacceptable. If an accidental overdose occurs, an ambulance is immediately called in to the child.
Terms of sale and storage
Tablet No-shpa is an over-the-counter medicine and is freely marketed in many pharmacies. On average, 6 tablets cost 60 rubles, and a box of 24 tablets costs about 120 rubles. As for ampoules with a solution, for their purchase you need a prescription from a doctor. For 5 ampoules often need to pay about 100 rubles.
Keep both forms of medication recommended at room temperature. At the same time, the storage space for No-shpy should be dry and hidden from small children. The shelf life of the liquid form is 5 years, and tablets - depending on the packaging 3 years or 5 years.
Analogs
The most common No-shpu replace DrotaverineDroverin, Spasmol, Spasmonet and other drugs containing drotaverine. In addition, instead of No-shpy, children 2-5 years of age are often prescribed Papaverineallowed from the age of six months.
In the next video, see the pharmacist's story about the drug, its composition, method of use, side effects and contraindications.