Treatment of milk teeth in children
There is an erroneous opinion that it is not so important to treat teeth at an early age while they are dairy. Many parents pay more attention to permanent teeth, not knowing that diseases of milk teeth can worsen the condition of indigenous teeth. In addition, such diseases develop very quickly and can proceed without serious consequences, often causing complications.
Should I treat milk teeth?
Treatment of diseases of milk teeth is important because of such reasons:
- Too early destruction of a baby tooth, which resulted in its removal or loss, threatens improper development of bite and changing the location of permanent teeth. Because of this, at an older age, the child will have to wear braces or suffer from psychological complexes.
- Because of caries, a child may develop complications such as periodontitis, pulpitis, or a cyst. Besides, infection from the affected baby tooth can fall onto the primordial germ. In some cases, the bacteria spread to the bone tissue of the jaws, which is even more dangerous for the health of the crumbs.
- Also, because of problems with the teeth, the child's digestive tract will suffer. Due to the absence of teeth, the food will not be processed sufficiently, which will impair digestion.
However, there are situations when the treatment of milk teeth is not shown, but they are only determined by the dentist after examining the child.. For example, if the affected tooth falls out within 6 months and the disease is sluggish (chronic), it can be left without treatment.
Frequent problems and treatments
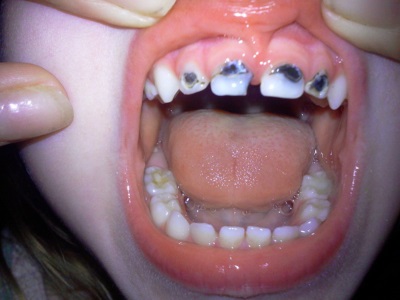
Caries
This is the most common dental problem, which is found in 70% of children under 6 years old. Most often, the disease affects milk molars, which is associated with the nutritional conditions of children and the relief structure of these teeth. Because of the accumulation of plaque, microorganisms quickly develop there, and as a result of their vital activity, caries becomes a result.
It is quite difficult to notice how it starts in a child, because at the beginning, white spots on the teeth affected by caries cause no discomfort to the crumbs. If the disease develops further, the spots become dark, and when the child eats salty, sour or sweet, the teeth can react with painful sensations. And then the baby needs to start treatment.
If you miss the time, the lesion will spread to the internal tissues, the teeth will become sensitive to cold and hot food. In the worst cases, when caries penetrates very deeply, the affected tooth will have to be removed.
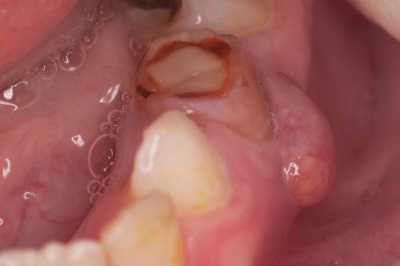
Periodontitis
This is a serious complication of caries caused by the spread of bacteria that have infected the root of a tooth on the tissues surrounding it. The disease is manifested by constant aching pains, which eventually become pulsating and intense. The child also complains of pain when bitten by a sick tooth, and his general condition may worsen (headaches appear, the temperature rises).
Flux
This is the name of an abscess caused by dental diseases, in which the child’s cheek becomes swollen.The disease is quite serious, because it is caused by purulent inflammation. It is manifested by pains in the tooth and jaw, redness of the gums and the appearance of "bumps" on it. As a rule, the child's body temperature rises, and the general condition is worsened.
Flux can only be treated in a dental clinic, and treatment should be as fast as possible to prevent the spread of infection and the ingress of bacteria into the blood.

Stages of treatment
If caries is found in a child at an early stage, he will be recommended to do fluoridation. A special compound is applied to the teeth, which will protect them from further destruction. Silvering is used in children younger than 1–2 years, however this causes darkening of the teeth and requires frequent repetition of the procedure.
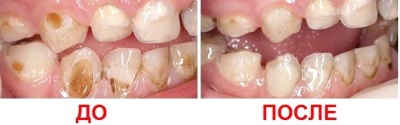
More advanced stages of caries require filling, as is pulpitis and periodontitis. The affected tissues of the tooth are removed and fillings are placed in their place. If several teeth are affected, they are treated gradually - so that the child does not get tired, one visit should not last more than 30 minutes. Besides, in many clinics offer fillings of different colors to interest the child.
When filling the roots of milk teeth, a special material is used that can be absorbed in the future. To remove the resort only in cases where the tooth tissue is almost completely affected or the tooth is very mobile, which indicates its readiness for loss.
How to make anesthesia for children?
Anesthesia is not required in all cases of dental treatment in children. As a rule, it is resorted to with strong caries (deep or medium). For anesthesia, use spray or injection, that is, in most cases, anesthesia will be local. At the same time, the concentration of the active substance in medicines used in children is low.
General anesthesia at the age of less than 6 years old is resorted to only for serious indications. Most parents fear such anesthesia, but in reality it is a fairly safe method used in many countries. Modern drugs effectively affect the child, and the frequency of complications is very low.
Opinion Komarovsky
Famous doctor names among the main causes of the destruction of milk teeth. genetic factor considers other factors provoking caries sweets (especially sweet drink) and the drying of saliva in a child. If the child’s teeth have already begun to deteriorate, the popular doctor advises not to wait, but to go to the dentist.
At the same time, Komarovsky complains about the poor quality of dental care for children in our country and emphasizes that it is better to prevent the need for dental treatment with proper prophylaxis (limiting sweets and moisturizing the mucous membranes).
Prevention
- Starting to take care of dairy, and at the same time at the same time the baby’s permanent teeth should be taken from the gestation period. For this, the expectant mother should consume enough foods rich in calcium, fluorine and phosphorus.
- Also important is the daily care of the teeth, which should be started not from the moment of the appearance of the molar teeth, but after the first milk tooth is “hatching”. Careful cleaning of food debris is essential to prevent tooth decay.
- When the baby began to cut teeth, you should pay special attention to his diet, in particular, the number of sweets. Excess sugar intake contributes to the more rapid development of diseases of milk teeth. It is especially important not to give the child sweet foods and sweet drinks at night.
- Another important condition for the prevention of dental diseases in children is regular visits to the dentist. This doctor should see the baby for the first time at the age of up to a year, as soon as the crumbs begin to erupt the first teeth. Next, the child must visit the dentist's office every year.
Tips
- Many children are afraid of the dentist’s office, soThe parents' task is to reduce fears and convince the baby of the need for visits to this doctor.
- To clean the first milk teeth, it is recommended to use a special soft fingertip.. An older child should get a toothbrush, which has soft bristles, a rounded small head and a comfortable handle.
- Teach your child to brush their teeth in the form of a game, controlling cleansing and helping your baby. Use of paste is recommended only after two years.