WBC blood test in children
Unknown abbreviations in the analysis of the blood of children are alarming for many parents, especially if their indicators are above normal or underestimated. One such designation is the WBC. What is behind these letters, why do we need this analysis and how to decipher its result?
What it is
Through an analysis of the WBC, the doctor finds out the state of the child’s immunity, which will help him in making a diagnosis or monitoring the treatment.
Norm and deviations
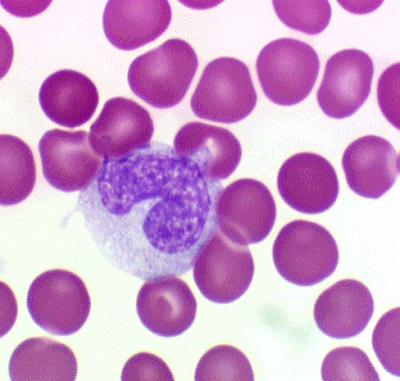
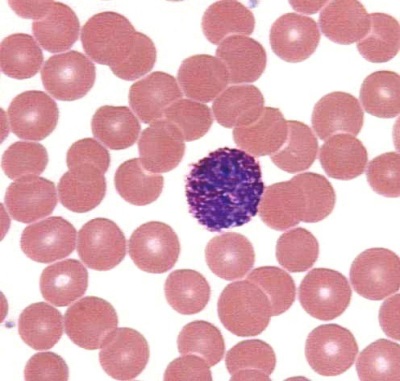
Leukocytes are very important blood cells that are involved in immune responses and protect the child from any negative effects. They form in the bone marrow and some other organs, and then go into the bloodstream and move through the body of the child. It is these cells that protect children from bacteria, viruses, toxins and many other influences. Therefore, a sufficient number of them is important for maintaining the health of babies, and any changes in the number of white blood cells can be a sign of illness.
Leukocytes are normal - decoding in the table
To understand whether the child’s immunity is in order and whether the baby has any dangerous diseases, one should know which WBC indicator is considered the norm. For kids of different ages, it will be like this:
|
In the first month of life |
5.5 to 12.5 x 109/ l |
|
From 1 month to 1 year |
6 to 12 x 109/ l |
|
From 1 year to 5 years |
5 to 12 x 109/ l |
|
From 5 to 12 years |
4.5 to 10 x 109/ l |
|
From 12 to 15 years |
4.3 to 9.5 x 109/ l |
|
In children over 15 years |
4 to 9 x 109/ l |
In the first days after birth, the number of white bodies may increase to 30 x 109/ l, which is also considered normal, but by the fifth day of life the number of leukocytes decreases and does not exceed 15 x 109/ l.
Increased rate
Also, leukocytosis is normal for several hours after a meal, so a blood sample for WBC should always be taken on an empty stomach.
Increased WBC is characteristic of such pathological processes:
- Bacterial infections.
- Acute surgical diseases.
- Chronic inflammatory processes.
- Viral infections.
- Allergic reaction.
- Fungal infection.
- Parasitic diseases.
- Autoimmune processes.
- Neoplasm.
- Severe bleeding or hemolytic anemia.
- Extensive burns.
- Injuries.
- Removal of the spleen.
- Leukemia
Also, the WBC index may increase due to the intake of certain drugs, for example, hormonal drugs.
We recommend watching a video in which the famous doctor Komarovsky answers questions about elevated white blood cells:
Below normal
With a decrease in WBC in a child is diagnosed leukopenia. It occurs if a child has:
- Exhaustion or hypovitaminosis.
- Poisoning.
- Bacterial infection.
- Viral disease in the stage of recovery.
- The bone marrow is affected by chemicals, radiation, an autoimmune process, a tumor.
- Reduced blood pressure.
- Anaphylactic shock.
- Systemic disease.
- Diabetes or hypothyroidism.
- Enhanced spleen function.
- Tumor.
Also, a decrease in WBC is possible after treatment with certain drugs, such as cytotoxic drugs, anticonvulsants, or antibiotics.
Leukocyte formula
Simultaneously with the counting of the number of all leukocytes in the analysis of the blood of children, they can also decipher their different types, representing their number as a percentage of the total number of white blood cells.
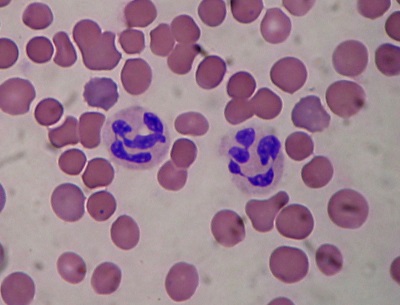
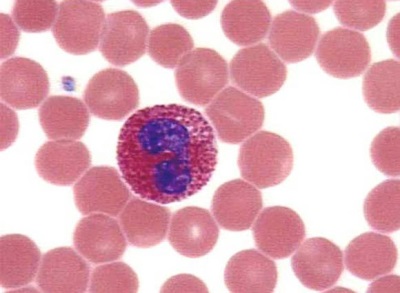
The most numerous among all leukocytes are neutrophils. Such cells are designed to protect the children's body mainly from bacterial infections, so their increase usually indicates infection with bacteria or active inflammation. Neutrophil reduction is dangerous for a child by the lack of protection against bacteria. If the analysis determines the lack of these cells, the child risks “catching up” the disease; therefore, neutropenia cannot be ignored.
Only a few percent of all leukocytes occupy eosinophils. The main function of these cells is to protect the body of children from allergens, as well as from parasitic diseases. That is why, with an increase in their percentage, the doctor first of all examines the child for worms, and also assesses his allergic history. Reduced eosinophils are found in cases of poisoning and severe infections.
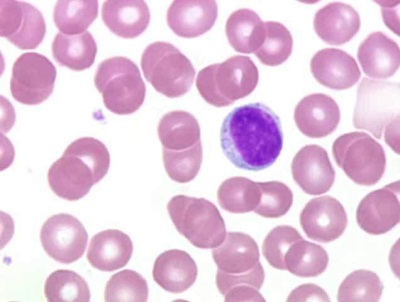
A small group of leukocytes act and monocytes. These cells protect the child’s body not only from pathogens, but also cleanse it from diseased cells and dead tissue. Their increased number is observed in infections, tumors and other pathologies, and a decrease in monocytes in the blood is characteristic of serious lesions of the bone marrow.
Another group of leukocytes, determined in peripheral blood in a small percentage, is represented by basophils. These cells are involved in allergic reactions.therefore, their high percentage often indicates allergies, but is also found in some other pathologies.
What to do when WBC changes
If the WBC indicator deviated from the norm in a child’s blood test, it is necessary to retake the blood, not forgetting the influence of factors that may give unreliable results (food intake, overheating, physical activity, stress, etc.). If changes are also present in the reanalysis, this is a reason for turning to a pediatrician to examine the baby more carefully.
As soon as the doctor establishes the diagnosis and prescribes the necessary treatment for the child, the level of white cells in the blood also normalizes as the baby's condition improves and he recovers.
When a child is diagnosed with leukopenia, it is important to find out its cause as soon as possible, since the low number of white cells in the blood indicates a decrease in protective forces and a high risk of infection. After determining the cause of lowered white blood cells, treatment should begin immediately, during which the WBC index will return to normal.
We recommend to watch the video prepared by the Union of Pediatricians of Russia dedicated to clinical blood analysis: