When does the fetus's heart begin to beat? When can you hear a heartbeat or see it on an ultrasound?
Future mothers with trepidation and special excitement are waiting for the moment when you can hear the baby's heartbeat in the womb. It appears long before other signs of vital activity of the crumbs, and for future parents it becomes the most reverent touch with the mystery of the origin of a new life.
Moms are interested to know how a baby's heart is formed, at what time it starts to beat and when it can be heard and seen.
Body formation
The cardiovascular system in the body of a developing fetus is formed one of the first. Already in the earliest terms, an important “mission” rests on it - to ensure the embryonic blood flow. It depends on her normal development whether the baby will grow or the pregnancy will be interrupted, the heart will remain healthy or its defects will be detected.
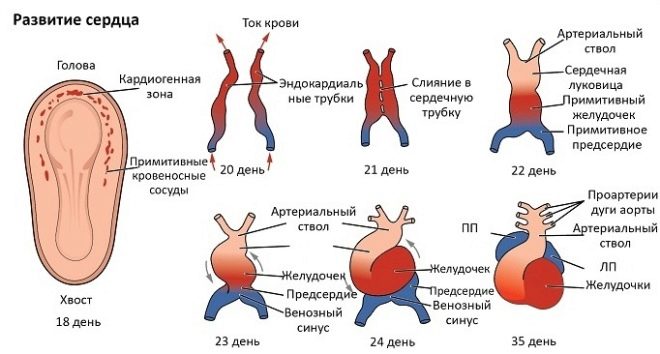
Formed a heart in the fetus at the end of the 2nd week of gestation. This means that mom may have already begun to suspect that she is pregnant. The first are two heart tubes. They gradually merge into one. The blood is already flowing into it, but so far in one continuous stream.
By the end of the 3rd week of gestation (the week since the beginning of the delay) the structure of the tube is changing and becoming more complex.
During this period, it is important to avoid contact with chemicals, radioactive substances, do not take medicines without the knowledge of the doctor, who has already been informed of the "striped" test.
At this stage, any adverse external or internal factor can affect the development of cardiac pathologies. - severe stress, mother's experiences, viral infections, bad habits.
By the beginning of the 4th week from the moment of conception (only about 9-10 days will pass from the moment of the beginning of the delay) the child's heart will become sigmoid (in form resembling Latin S). A primary ventricle and atrium will be formed in it. By the end of the 4th week of gestation, the single-chamber is still beginning to contract in the heart, but you still cannot hear a knock. - Too tiny size of the body.
On the 4th-5th week of gestation, a proliferation of the heart’s sections occurs, a partition is formed between them - the organ becomes a two-chamber organ. So far, the child has only a big circle of blood circulation (after all, there are no lungs yet).
On the 6th week of pregnancy, the heart becomes 3-chamber, and after a few days, and 4-chamber, since the ventricular division is divided by a flexible partition.
The process of forming partitions in the fetus is completed by the 7th week.
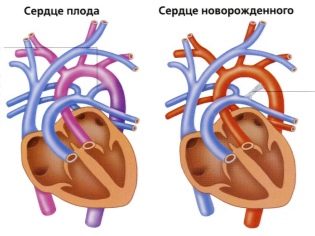
The body the remaining 7 months will only increase in size and smoothly work, supplying other organs and systems of the child with blood. Indicators of the frequency and rhythm of the baby's heartbeat is an important indicator during pregnancy. According to him, doctors will judge how well the child feels, how well he develops, whether he has enough oxygen.
When and how to listen?
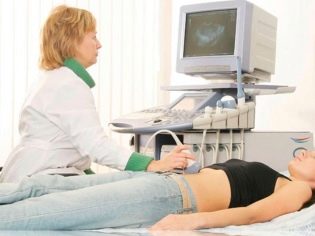
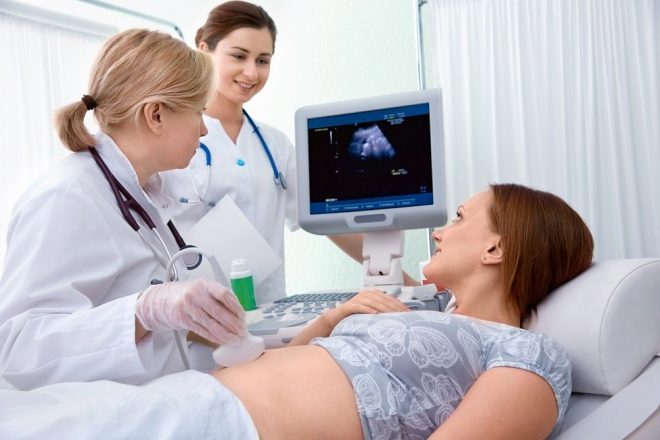
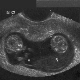
3 weeks after the delay of the menstrual period, a woman can go to the ultrasound diagnostic room - it is during this period that the embryo is already visible and you can hear its heartbeat if you do an ultrasound scan with a vaginal sensor.
If an ultrasound examination is performed by an external sensor through the anterior abdominal wall, then hear how your baby has a heartbeat, it will turn out no earlier than at 6-7 weeks of gestation.
Of course, a woman on such a short time cannot feel the rhythmic heartbeats of a child. Such it is possible only in the late stages, and then only on the condition that the baby will occupy a comfortable position in the uterus, in which its chest is turned towards the anterior abdominal wall of the mother.
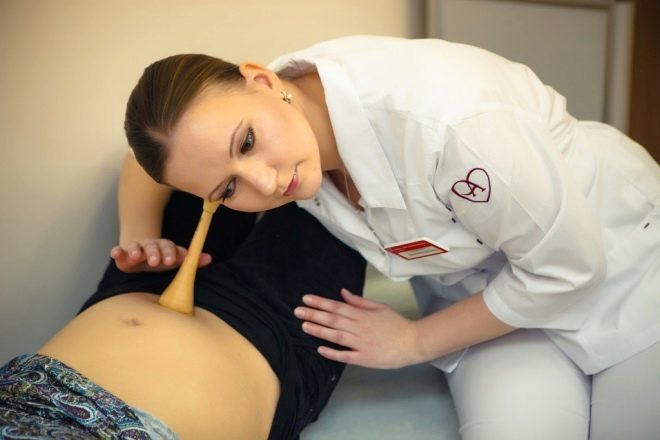
Many future mothers have seen and heard that doctors are listening to the belly of a pregnant woman with an obstetric stethoscope - a special tube with an extended lower end.
When a heartbeat appears, the baby is still too small and floats freely in the uterus. The dimensions of his heart are microscopic, and therefore heart in the 1st trimester is not bugged by a stethoscope.
The doctor will repeat the procedure at each scheduled admission at the end of the 2nd and 3rd trimester, when the child grows up, and with it the heart will increase.
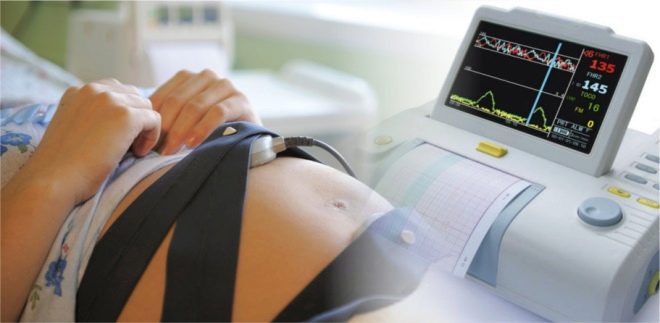
The method of cardiotocography (CTG), based on the registration of cardiac activity and motor activity by sensors located on the future mother's abdomen, is used after 30 weeks of pregnancy (rarely - after 28-29 weeks - for individual indications).
Also, CTG sensors can be connected in the process of childbirth, so that obstetricians can assess in real time the condition of the child who is born.
A woman can listen to the baby’s heart with a stendoscope from a 28-30th week of pregnancy, but it depends on what size the future mother is and how exactly the baby is located in the uterus. If the pussy turns its face to its mother's intestines, then it will be problematic to hear something at a later date.
In the 3rd trimester of pregnancy, the future father and other members of the household can hear the baby’s heartbeat - this is possible already two months before delivery.
Pregnant women don't have to mess with the stethoscope today. there are special home fetal monitors that quickly and accurately calculate the baby’s heart rate. It is enough to attach the sensor to the mother's stomach and find the point of reception of the audible signal.
Facts and figures
Since the heart is formed from the 2nd to the 7th week of gestation, in this and the subsequent period the heart rate of the baby will be uneven. To assess the indicator of organ development in obstetrics, the abbreviation HR is used - heart rate.
So, on the 5th week of pregnancywhen the doctor gives the expectant mother (who has not yet had time to get used to her new "position") to listen to the crumbs on the ultrasound, it can beat with frequency from 90 to 115 beats per minute. On the 6-7th week heart rate changes (this is due to the transition of the organ to the 4-chamber level) and ranges from 105 to 130 beats per minute.
On the 8-9th week gestation baby will please the doctor and mother with a heart beat with a frequency from 130 to 155 beats per minute, and at 10-11 weeks your heart knocks even faster - up to 160 beats per minutey Peak in speed the tiny heart reaches on the 13-15th week, when the heart rate can reach up to 185 beats per minute.
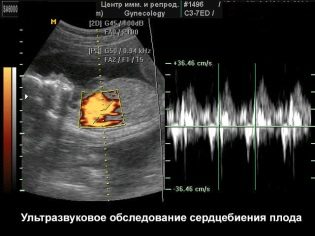
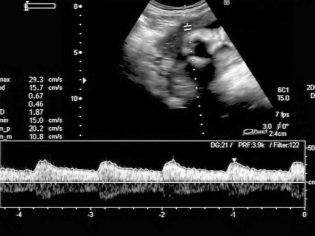
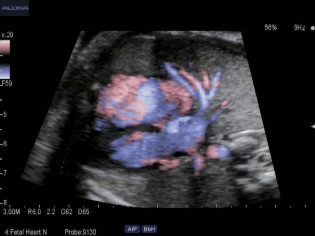
Then, almost until birth, the heart rate remains at 130-170 beats per minute, and before delivery, it normally ranges from 120 to 160 beats per minute. Look at the heart and see how it pulses, the mother can doppler ultrasound (Doppler ultrasound) on the 7th week of pregnancy.
To those women who did not go for an ultrasound, the crumbs of the heart are shown on the first screening ultrasound in 10-13 weeks.
Causes of deviations
The heart rate of the fetus is very important for its normal development. Wherein exceeding the norm is considered less dangerous than slowing the heartbeat. Frequent rhythm can be a sign of started hypoxia or circulatory disorders. With an increased heart rate (relative to the heart rate), babies in the mother's womb often respond to violations of the structure and function of the placenta, to placental insufficiency, and to low hemoglobin in women.
Sometimes frequent heart rate is a sign of some heart defects or other organs.In the period of the threat of miscarriage of a baby, an excess of the normal heart rate is often noted. With an increased heartbeat, the fetus may react to the diseases of its mother - for example, to catarrhal or viral infections in an acute form.
Slow heartbeat is a dangerous sign. At any stage of pregnancy, a decrease in heart rate relative to the norm can be caused by severe uncompensated intrauterine hypoxia (oxygen starvation), severe congenital defects, metabolic disorders in the mother and baby, impaired hemostasis in the mother and baby.
With a short delay in heart rate, a child in the mother’s womb may react to the mother’s long rest in the supine position (posture not recommended for expectant mothers, because the uterus squeezes the pelvic and vena cava).
As soon as the woman changes her body position, the heart rate of the crumbs returns to normal values within literally several minutes.
A woman must remember that the baby's body in the 3rd trimester of pregnancy is already fully formed: the child can hear what kind of intonation the mother is talking to, picks up her emotional state. At this time, the fetal nervous system is also laid, on which it depends on how psycho-emotional it will be stable, how it will perceive the world around it.
If a woman is worried, worried, anxious, then her body reacts very sensitively to this. The blood flow increases, the heartbeat quickens, adrenaline is released into the blood. All this may adversely affect the health of the unborn child.
Already proven that the state of physical health of the mother directly affects the development of the fetus. If she takes alcohol, smokes, does not eat properly, takes drugs or psychotropic substances, then the child can be born with serious disabilities.
Heart disease - a terrible disease that gives a chance for survival is not for all children. A carefree mom after conceiving a child should seriously think about whether she wants to follow her wishes, risking the life of the crumbs, or prefers to give birth to a healthy and happy baby, not poisoned by poisons and toxins. The answer is obvious, but you will have to make an effort, show willpower, so that once a decision is made, it becomes a way of life, not a momentary whim, which is easily forgotten in the future, and everything returns to normal.
More on fetal heart rate and its rates - in the next video.