Second screening during pregnancy: dates and norms of indicators
Every future mother wants her baby to be born healthy. Perinatal screening is necessary to determine the nature of the course of pregnancy and the timely establishment of various pathologies. This article will tell you about why we need a second screening during pregnancy.
What it is?
Pregnancy screening is a complex of studies necessary for the timely establishment of various violations of fetal intrauterine development. Also with the help of these studies can accurately determine the state of the mother. Evaluation of the results obtained by doctors engaged in several specialties.
For convenience, physicians have divided the entire period of pregnancy into several large time periods, which are called trimesters. Each one lasts 3 of the month. To describe the duration of pregnancy obstetricians use gynecologists for weeks. In this case, each trimester is 12 obstetric weeks.
Screening in pregnant women is a very important procedure that was introduced not so long ago. The first recommendations on the need for it were made by representatives of the Ministry of Health of Russia. According to experts of the Ministry, the introduction of such a measure should have a positive effect on the adverse demographic situation in the country.
Screening during pregnancy is necessary to reduce maternal and infant mortality. Also, without this diagnostic complex, it is impossible to imagine the timely prenatal diagnosis of various genetic and chromosomal diseases.
It should be noted that screening during pregnancy is carried out in all economically developed countries. Different funding programs causes only the difference in the list of necessary for conducting research. In our country, this complex is also gradually expanding. More advanced diagnostics is necessary for the timely detection of dangerous genetic diseases.
In each trimester of pregnancy, certain pathologies are determined by developing a baby in the womb by screening. This is largely due to a specific fetal physiology. The daily changing hormones of a pregnant woman also require a more detailed approach.
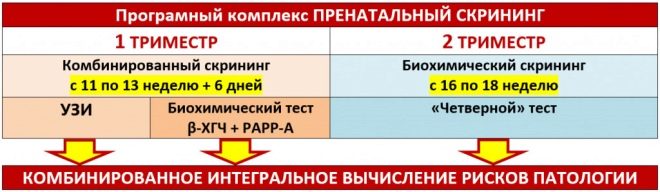
For the entire period of pregnancy, doctors usually recommend expectant mothers to undergo 3 such screenings. In some situations, their number can be reduced to two. This is usually found in the normal course of pregnancy.
What does include?
During the second screening, doctors evaluate a rather large range of different indicators. A pregnant woman must undergo biochemical blood tests, as well as undergo ultrasound.
In some cases, mainly for medical reasons, the diagnostic complex may be somewhat expanded.
At this stage of pregnancy, doctors must check hormone levels. Such studies make it possible to reveal even hidden diseases that were present earlier or developed in the mother already during the carrying of the baby. If the hormonal background in a pregnant woman significantly deviates from the norm, then the doctors may prescribe a special drug therapy.
The determination of genetic pathologies is a very important stage of screening for the second trimester of pregnancy. At this time, research is quite significant focus. The purpose of screening is to exclude from the examined women who do not have any signs of chromosomal diseases.
If the results of the tests revealed any abnormalities in the fetus that are incompatible with its life, then the question of abortion is raised.
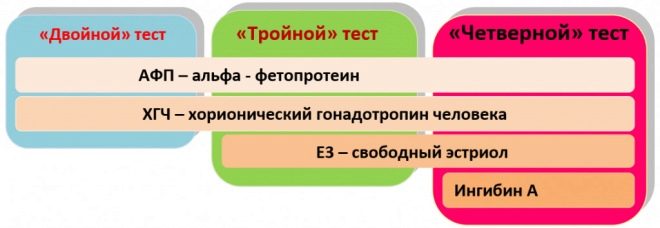
During the screening, experts evaluate both biochemical parameters and ultrasound. The laboratory method used in such an examination is often called “triple” by doctors. The fact is that for its use three basic biochemical indicators:
- HCG;
- free estriol;
- alpha fetoprotein.
In some situations it may be necessary to extend this test.
A gynecologist may recommend a PCR test for 12 infections to a future mother, who had any urinary tract infection during pregnancy. This study will help identify all the "dumb" pathologies that may aggravate the course of pregnancy.
To exclude pronounced allergic pathologies, the doctor may also recommend donating blood for specific antibodies (AT). These proteinaceous substances can be formed in a maternal organism on some fetal structures, which can be allergens (AH). Such an emerging immune conflict can cause the formation of various pathologies.
Dangerous diseases that can cause congenital diseases in the fetus, can also be further diagnosed during screening. For this, a doctor who is observing a pregnant woman may recommend that she donate blood for the determination of type 1 HIV. Quite often, this analysis is performed along with the definition of specific markers of hepatitis B and C.
Dates
The second screening is carried out in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy.
All studies expectant mothers recommended go from 16 to 20 week. Only a few exceptions are allowed when screening may be delayed. Usually they are associated with contraindications for a woman to conduct any research. Such situations are extremely rare in the practice of obstetrician-gynecologists.
Many mummies are interested in the question of whether it is possible to donate blood for research and undergo an ultrasound scan on different days. This is not prohibited. However, they still need to discuss the terms of the visit with their doctor. Quite often it happens that the doctor himself will recommend specific dates for the performance of laboratory tests or ultrasound.
Who must pass?
High maternal and infant mortality in Russia is due to the fact that doctors recommend screening during pregnancy for almost all women. However, experts single out several “special” or decreed categories of expectant mothers who cannot avoid such a complex of diagnostics.
High risk groups include:
Future moms whose baby conception occurred after their 35th birthday;
Pregnant with pathological course 1 trimester of pregnancy;
Future mothers with a burdened family history of developing chromosomal or genetic diseases, especially along the line of the first and closest relatives;
Pregnant women who have suffered viral or bacterial infections in the first weeks of pregnancy;
Future moms suffering from diabetes, especially insulin-dependent option;
Pregnant women, having any oncological disease or burdened history of neoplasms;
Women whose previous children have severe pathologies and congenital malformations;
Pregnant women who have had several spontaneous miscarriages or who have had many abortions before the onset of this pregnancy;
Future mothers who have been diagnosed with certain intrauterine growth defects by ultrasound during 1 screening.
If during the 2 screening the doctors again reveal certain pathologies, but abortion is not required, then they will recommend to undergo another complex of such studies, but already in the third trimester. Such dynamics is necessary to determine the severity of emerging disorders. If this situation can be somehow changed with the help of drug therapy, then doctors will resort to this.
In some cases, it may be necessary to consult a geneticist to determine the need for the next screening. If after it the doctor excludes all possible diseases, then in the third trimester, the future mom can only be recommended to have an ultrasound examination.
Genetics consultation is a very important component of prenatal screening. If the obstetrician-gynecologist recommends her to go, then it is still worth attending such a reception.
Training
To obtain reliable results is very important to properly prepare. It may take several days between the delivery of biochemical analyzes and ultrasound. In this case, all recommendations should be followed throughout the preparation period for the second screening.
Lipid-lowering diet will help in obtaining more accurate results. Such food completely excludes any fat and fried products. Any cholesterol rich food is also limited. Follow this diet should 5-7 days before screening. In this case, the results of the study will be more reliable.
Limiting protein in your diet to future moms is not worth it. It is necessary for the full growth and development of the fetus. Before testing, they should choose lighter protein products. These include lean fish and white fish, lean beef, turkey. Eat pork and lamb a week before going to the laboratory is not worth it.
Obstetricians and gynecologists do not recommend pregnant women on the eve of research to change their drinking regime significantly. Especially you should not do this to expectant mothers suffering from various edemas. The main limitation is before ultrasound.
In this case, a few hours for research should significantly limit the use of water.
Immediately it is worth noting that in some situations it may be necessary and vice versa, active filling of the bladder. This is usually necessary to perform a transabdominal study for certain medical conditions. To do this, the doctor will recommend the future mom for 1-1.5 hours before the study to drink 3-4 glasses of water. Usually such recommendations are given before the ultrasound.
2-3 days before the ultrasound examination, future moms should restrict fruits and vegetables in your menu. Also under the restriction fall legumes and all kinds of cabbage. These products are rich in coarse fiber that increases gassing and intestinal peristalsis. Also, the appearance of gases in the intestine leads to the use of carbonated beverages or even kvass.
All this contributes to the fact that during the ultrasound the phenomenon of echo negativeness is enhanced. In such a situation, the doctor simply cannot get a high-quality image on the monitor of the ultrasound device.
Blood tests should be done in the morning. This should be done strictly on an empty stomach. Doctors have long noted that tests taken in the evening often do not become informative. In the evening on the eve of the laboratory tests should be eaten as easily as possible.In the morning after waking up, you cannot eat.
The results of biochemical tests are quite dependent on the effects of many factors. Even eating seafood, citrus fruits, chocolate and honey can lead to their distortion. Quite often this happens in those situations when these products are used on the eve of testing.
Exercise is another possible factor that will lead to distorted results. Even the usual cleaning of the apartment, which the future mom will start to do on the eve of the trip to the laboratory, can lead to the fact that the doctors find the test results unreliable.
You should also not attend special classes or yoga for pregnant women before screening. It is better to postpone them in this case for a couple of weeks. Daily walks in the fresh air will be for future mothers an excellent alternative to physical exertion in this period. Such a promenade will appeal to the future baby. During walks in the air, a large amount of oxygen enters the bloodstream, which is an excellent preventive measure for the development of fetal hypoxia.
Exclusion of psycho-emotional stress is a very important step. before screening. Doctors found that if the future mom often worries or worries while carrying her baby, the risk of developing neurological disorders in her child increases significantly. Strong psychoemotional stress can also affect obtaining reliable ultrasound results. It provokes a pronounced spasm of blood vessels, which may adversely affect the performance of uteroplacental blood flow.
Test Rates and Reasons for Abnormalities
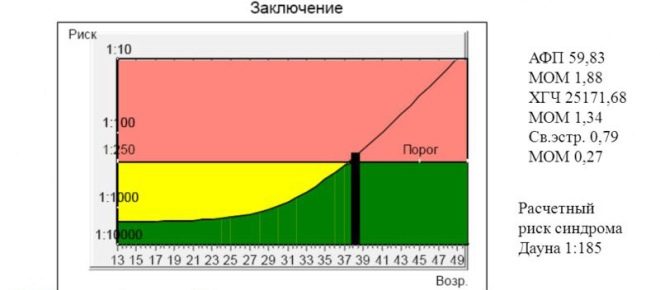
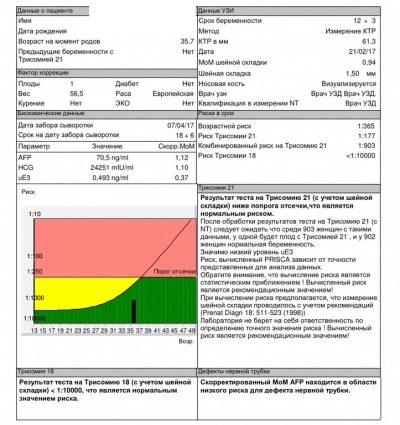
Any deviations from the norm must be evaluated by experts. What matters is the increase and decrease in these indicators. Compiling a comprehensive report after screening requires the mandatory interpretation of all the results obtained.
The doctor will never set the diagnosis for only one result of biochemical analysis. In some cases, to determine the pathology without an ultrasound is impossible.
HCG
Chorionic gonadotropin, or hCG - is one of the components of the "triple" biochemical test. It is also a biologically active substance called by doctors pregnancy hormone. Its concentration gradually increases to the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. Only immediately before birth, it falls somewhat.
- By week 16, this figure is 10 000- 58 000 IUU / ml.
- At week 17, the values are 8000-57 000 honey / ml.
- By the 20th week of pregnancy - 1600-49 000 IU / ml.
Elevated
High levels of gonadotropin in the blood are found when carrying twins or triplets. In this case, doctors even use special tables in which the normal values of this hormone are entered. Elevated blood levels of hCG may indicate the presence of preeclampsia or certain tumors in the mother. A similar situation develops also in the event that the expectant mother is forced to take immunosuppressive or hormonal drugs during pregnancy.
Reduced
Reduced hCG in the blood is found in many pathological conditions. Concentration of gonadotropin decreases markedly with an increased risk of miscarriage. Reduced blood hCG concentration indicates intrauterine fetal delay or Edwards syndrome. Critical level of gonadotropin occurs during fetal death of a child.
Alpha fetoprotein
This specific substance is formed under the influence of the functioning of the embryo. In the first weeks of fetal development, it is synthesized in the yolk sac. Then it is formed already under the influence of the liver and in the organs of the baby’s gastrointestinal tract.
The presence of this substance in the blood is vital. It allows the fetus to provide all the necessary nutrients, and also protects it from the aggressive effects of estrogen.Alpha-fetoprotein minimizes the risk of developing immune inflammation between the mother and the fetus.
This substance penetrates the maternal organism through the common system of uteroplacental blood flow. A rather high concentration of alpha-fetoprotein is also observed in the placenta.
During different periods of pregnancy, the indicators of this hormone are different. This is due to the physiology of fetal development.
- At 16-18 weeks of pregnancy, alpha-fetoprotein values are 15-95 U / ml.
- At week 20, the concentration of this substance changes to 27-125 U / ml.
Elevated
Increased levels of alpha-fetoprotein are found not only in pathological conditions. Increased concentration of this hormone indicates the presence of multiple pregnancy. This condition is also found in preeclampsia. This pathology can be extremely dangerous for the development of multiple complications.
The increase in blood alpha-fetoprotein indicates a possible formation of malformations. In this case, to exclude pathologies, an ultrasound scan is required. Doctors note that an elevated level of this hormone is also found with various defects and neural tube incision.
Congenital nephrosis of the kidneys in the fetus is also manifested by a significant increase in alpha-fetoprotein during mid-pregnancy.
Reduced
Reduced levels of alpha-fetoprotein may indicate the possible development of some genetic defects - Edwards syndrome and Down syndrome. Also, this situation can be a very unfavorable symptom of the manifestation of a "frozen" pregnancy. In this case, unfortunately, abortion is required, since its further development is no longer possible.
Free estriol
The increase of this biologically active substance occurs immediately after conception. This hormone is also quite strongly associated with gonadotropin. This substance is synthesized by the placenta and the liver of the fetus.
Increased concentration of estriol is necessary for normal uterine-placental blood flow. Also thanks to this substance the necessary tone of the blood uterine and placental vessels is provided. The increasing concentration of this hormone affects the formation and further work of the ducts of the mammary glands.
In different periods of pregnancy, the values of this indicator may be different.
- At week 16, the hormone values are 5.4-21 nmol / l.
- By the end of the 18th week, the concentration of the substance changes to 6.7-26 nmol / l.
Elevated
This condition during pregnancy can also be quite physiological. It develops in future moms who have twins or triplets. In this case, the concentration of free estriol increases relative to the norm by a factor of 2-3.
Pregnancy by a large fetus is another factor that can lead to an increase in the serum of a given substance. The various emerging pathologies of the urinary tract in the fetus are also manifested by an increase in the concentration of estriol. Quite often, diseases of the urinary tract or the mother’s kidneys become the primary cause of the development of this condition in a child.
Reduced
Low estriol can occur in a variety of genetic diseases, such as Edwards syndrome or Down's disease. Pathology in the fetus, accompanied by a decrease in the concentration of estriol, may also be associated with impaired development of nervous tissue.
Reduced uteroplacental blood flow is also manifested by a decrease in the concentration of estriol in the blood. This feature is manifested in the pathological course of pregnancy. Also, a change in the hormonal background leads to taking certain hormonal drugs that the expectant mother has to take in order to treat concomitant diseases.
Inhibin A
The analysis for the determination of this substance is carried out only for certain medical reasons. Usually it is assigned to women whose previous test results were unreliable.Also, this study can be used to clarify the presence of pathologies.
The blood concentration of this hormone increases significantly during pregnancy. Before conception, inhibin A is synthesized by the ovaries. Then this function takes over already the placenta of the fetus. This test is used to determine various congenital defects of intrauterine development.
Elevated
This auxiliary test helps to determine quite a lot of different genetic diseases even in the period of fetal development. Some chromosomal pathologies also manifest as an increase in the substance in the serum.
An elevated level of inhibin A in the blood precedes a very dangerous state - the gallbladder. Often, fetoplastic insufficiency is manifested by an increase in this biochemical index.
Reduced
Reduced Inhibin A is found when a threatened abortion is pronounced. In this situation, doctors may order a rerun of this analysis. The absence of any positive dynamics will indicate that pregnancy, unfortunately, does not develop. In this case, it may be necessary to urgently hospitalize the future mom to the hospital for intensive treatment.
MoM
The calculation of this important coefficient is carried out using a special computer program into which all the basic initial values are entered. This indicator allows us to estimate the risk of possible deviations of intrauterine development relative to normal values.
Normal performance of this criterion is 0.5-2.5 MoM.
What is it for?
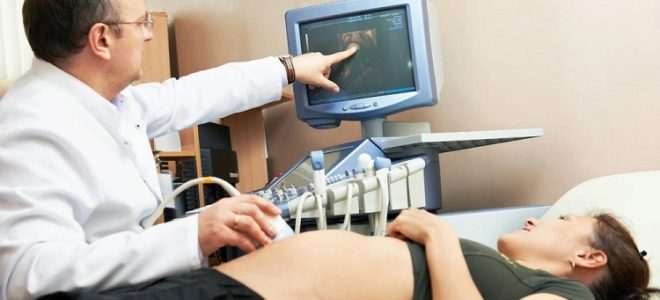
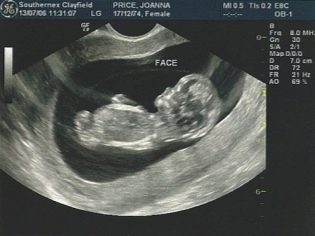
Dates ultrasound screening fall on the 20-22 week of pregnancy. Doctors say that ultrasound expert class can be held much later - at 22-24 week. It is better that such studies are carried out by experienced and qualified professionals with significant clinical experience with pregnant women.
The second screening is conducted mainly transabdominal way. To obtain an image in this case, an ultrasonic sensor is used, with which the doctor leads the skin of the future mom's belly.
Transvaginal ultrasound in the second trimester of pregnancy is practically not performed.
To obtain a good image on the monitor of the ultrasound device, a special transparent gel is used. It is applied to the skin of the abdomen before the procedure. This gel improves the reflective properties of ultrasonic waves. Its use can not provoke the development of allergic conditions or somehow harm the unborn baby.
With the help of ultrasound at this time of pregnancy, you can determine the main vital organs of the fetus. Experts, conducting research, determine the size of the liver, gallbladder and intestines. Examination of the brain and its basic structures plays a very important role in the diagnosis of many pathologies.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, doctors also determine circumference of the chest and abdomen. Abnormalities of these indicators indicate various pathologies that have arisen in the fetus. Also, to assess the development of the baby, doctors determine the size of some tubular bones. The absence of some bone formations at this stage of intrauterine development may indicate very serious pathologies.
Evaluation of the facial bones of the face plays a very important role in the diagnosis of many diseases. To do this, an ultrasound specialist examines in detail the frontal bone, eye sockets, the area of the nasolabial triangle. Facial architecture is estimated both in front and in profile.
Definition pathologies of the cardiovascular system very important at this stage. At this period of development, the baby already has a heartbeat. Experienced ultrasound specialists can identify and developing heart defects. To identify regurgitation (abnormal blood flow), the study is performed using Doppler.
Fetal membranes are very important anatomical elements that are also evaluated during such an examination. In the second trimester of pregnancy, the basic parameters of the placenta are determined. To do this, determine its thickness, volume, as well as the blood vessels that feed the organ.
Amniotic fluid volume - an important criterion for ultrasound screening. Excess of this indicator over the normal value is a consequence of high water. An insufficient amount of amniotic fluid indicates a lack of water. Both of these pathological situations are extremely unfavorable for the development of the fetus.
Internal genitals pregnant women are also evaluated during screening. It is especially necessary to conduct such research if the future mom has any pathologies of the reproductive system. In this case, it describes not only the inner layer of the uterus, but also its appendages, as well as the ovaries.
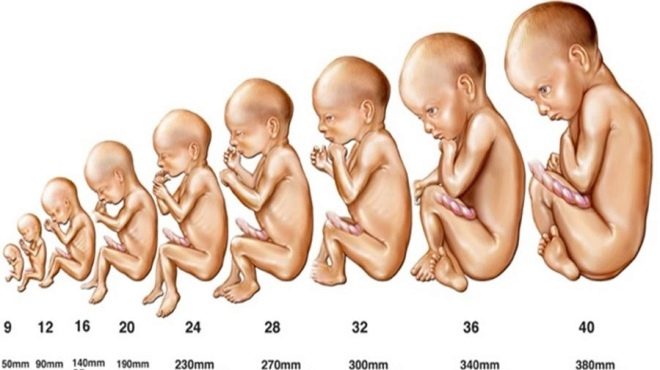
Fetometry - This is the baseline study included in the screening. It allows you to determine the size of the fetus, as well as the main components of its body. To assess the results obtained, doctors apply certain standards of the norm. The combination of all signs will help the doctor to identify pathologies that have developed in the fetus during its prenatal development.
During ultrasound screening, the maturity of the lungs must be determined. An experienced ultrasound diagnostic specialist can also determine the presence of structural pathologies of the kidneys and urinary tract.
To assess fetal growth and development on week 16 some averages are applied.
- A 16-week fetus should weigh about 100 grams.
- Its length is 11.5-12 cm.
- The abdominal circumference is 10.2 cm and the head is 12.4 cm.
- The biparietal size is 30-37 mm.
- The length of the femur in a 16-week fetus is usually 1.7-2.3 cm, and the bones of the forearm - 13-18 mm.
- The length of the seed of the leg is 2.0 cm.
- The volume of amniotic fluid in this period of intrauterine development is 80-200 ml.
Also evaluated indicators 20 weeks of pregnancy. By this time, the baby is already significantly growing up.
- The weight of the fetus at this stage of its development is 300 grams.
- Body length does not exceed 16.5 cm.
- Indicators of abdominal circumference at the same time can be from 125 to 165 mm, and heads - from 155 to 186 mm.
- Biparietal size is 43-53 mm.
- The length of the femur is 36-37 mm, and the shoulder is up to 34 mm.
- The bones of the forearm grow to 5 cm.
- In this period of pregnancy, the thickness of the placenta is 16.5-28.5 mm.
- The index of amniotic fluid is 93-130 mm.
During the second trimester, the size of the brain is necessarily evaluated. In a 16-week fetus, the cerebellum is 13-15 mm. Also determined by the size of the lateral ventricles and brain tanks. At this time they are 10-11 mm.
What pathology determines ultrasound?
Pathologies of the brain are perhaps the most severe. By week 16, hydrocephalus is already quite well manifested. With this pathology is determined by the excess amount of cerebrospinal fluid. Experienced professionals can determine this condition already at 11-12 weeks of pregnancy. If this pathology continues to progress, it may lead to the need for an abortion.
A hernia of the brain or encephalomeningocele is a very dangerous manifestation that is also easily diagnosed during the second screening. This pathological condition is quite often coming. To eliminate this pathology requires the mandatory appointment of treatment. To assess the course of pregnancy in the future, several consecutive ultrasounds will be performed.
Anencephaly is a pathological condition in which the brain has not formed in the fetus. In this case, unfortunately, pregnancy cannot develop. In this situation, doctors may recommend to interrupt the development of pregnancy.
Heart pathologies require mandatory diagnosis. Some of these diseases require mandatory surgical treatment immediately after the birth of the baby. To identify the disturbed operation of the valves, several ultrasound modes are used at once. The presence of regurgitation in the heart is a bright sign of a developing heart defect.
Anomalies of the nervous system often lead to the development of neurological disorders in a child after birth. Some of them are also accompanied by the formation of mental disorders. Failure of the neural tube - a very dangerous pathology, which can be identified through ultrasound.
Pathology of uterine and placental vessels lead to the formation of placental insufficiency. The prolonged course of this pathology can lead to a spontaneous miscarriage or the development in the child of various disorders of intrauterine development. A prolonged course of placental insufficiency often leads to the development of persistent fetal hypoxia.
Experienced ultrasound specialists can also reveal many orthopedic pathologies. They are determined by the baseline length of the limbs of the legs, forearm, and thighs. If the fetus abdominal circumference is much larger than the head, then this sign can be extremely unfavorable. It may indicate that the child has a pathological accumulation of fluid (ascites) in the abdominal cavity. This situation can develop with serious liver pathologies or tumors of the hematopoietic system.
The shortening of the lengths of the main bones may indicate some genetic diseases. This is how some chromosomal pathologies, including Down syndrome, are manifested. In this case, a mandatory comparison of the results of ultrasound with biochemical analyzes is required. Also in this situation, consultation of the family genetics is necessary.