What does the head presentation of the fetus during pregnancy, how it happens and how the delivery proceeds?
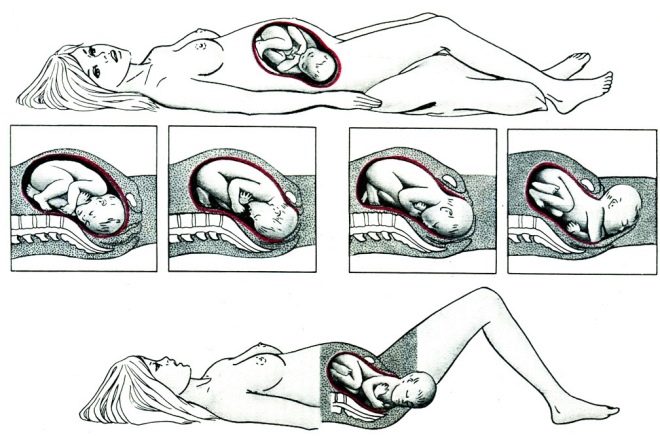
During the passage of the next ultrasound, the expectant mother can hear that her baby is located in the main presentation. What this means is not difficult to guess: the baby is head down. This position is most convenient for its development, growth and subsequent birth into the world. This position is provided for the baby in the womb itself nature. But is headache presentation always normal and safe for mother and fetus? We will tell more about this in this article.
What it is?
The fetus in the mother's womb during pregnancy changes its position more than once or twice, in early terms and in the second trimester, the baby can tumble and roll over freely and naturally several times an hour. Until a certain period of time, the size of the uterus, the amount of amniotic fluid, allow it.
However, from the 30th week of pregnancy, the baby becomes less mobile, it is already big enough to practice gymnastic upheavals, and its movements become more limited as the gestational age grows.
It is believed that the body's position relative to the exit to the small pelvis, from where his journey through the genital tract in labor begins, is finally established by the 34-35th week of pregnancy. After this period, the change of presentation is unlikely.
After the 23-25th week of pregnancy, 80% of babies occupy the correct, most comfortable head position, in which the head is the part that leads to the exit into the pelvis.
By the 34th week of pregnancy, 95% of babies are turned head down. By the 38th week, the number of such children grows to 97%.
In the cephalic presentation of the development of the fetus is more harmonious, in accordance with the nature and laws of evolution. For childbirth headache presentation is considered optimal.
A child who sits on the priest in the uterus, that is, is in pelvic presentation, in the last months of pregnancy has a chance to turn to the correct position. And if the baby is in headache, there is almost no risk that he will suddenly “sit down” or settle across the intrauterine device.
It would seem that the doctor’s statement that the baby is in the head position should calm the pregnant woman. But in practice, things are not so simple. Some types of head placement do not imply routine delivery and require the appointment of a planned cesarean section. Let's find out what types of this presentation exist and what might be their danger.
Classification and causes
Claiming that the baby is in headache, the doctor will certainly pay attention to the child’s posture and position, its position relative to the middle central axis of the uterine cavity, and the position of the child’s arms and legs relative to the body itself (articulation).
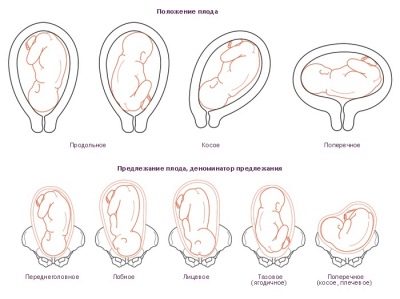
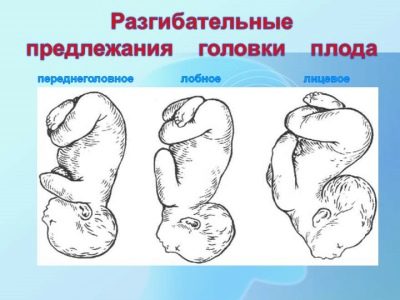
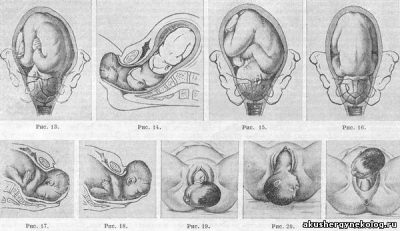
So, headache presentation is different, and here are its main types:
- occipital when the adjacent part of the head is the nape of the baby;
- anteropteraleum, in which the baby is pressed against the exit of the mother’s uterus by the parietal head;
- facial (the child is pressed against the exit face);
- frontal, when the baby is adjacent to the pelvic area of the forehead.
The most optimal and safe for the child and his mother is flexor occipital presentation. With him, the baby will go forward in childbirth, the point of advancement will be a small spring, just for this and provided for by nature. The remaining parts of the body of the crumbs will come out much easier, because the occipital part is the largest. The first to be born is the back of the head, the neck will be bent, the baby will not be able to straighten it and will receive a birth injury to the cervical spine. According to this scenario, up to 90% of all natural genera passes.
However, the head can be "inserted" in the small pelvis and at a different angle, and here much will depend on what part of the head and with what extension of the neck of what corner the baby is preparing to “start” into our world.
Anteropagia - the first degree of extension of the head. The point of moving along the sexual ways at birth in this position is the second (large) spring. The area of the pushed head part is larger, which means that the baby’s passage through the birth canal will be longer. Can a woman in this case give birth independently? Yes, quite, but the risk of injury to her and the baby is much higher than at birth back of the head. Such labors have a longer duration, there is a chance that contractions will become weaker, primary or secondary weakness of labor forces will develop, and hypoxia (oxygen starvation) may occur in a baby.
Frontal presentation is the second degree of extension of the head. The largest part of the head enters the pelvic area of the mother, which can cause significant difficulties during childbirth. "Punch" the way baby in childbirth in this position will be forehead. This increases tens of times the likelihood of spinal cord, brain and spinal cord injuries, the onset of acute hypoxia, which can lead to irreversible consequences and even to the death of a child. For mothers, such births are dangerous by ruptures of the uterus, cervix, perineum, injuries of bones and pelvic ligaments.
That is why it is believed that independent childbirth in the frontal presentation is very dangerous. A cesarean section is recommended.
- Facial presentation is the third degree of extension of the head, which is considered to be extreme in obstetrics - there is simply no place to extend the head. With natural childbirth through the mother's genital tract, the child will come forward with the chin. That chin will be the main point of the application. Theoretically, a woman can give birth on her own, but only if her baby has small sizes and light weight and at the same time the size of the woman’s pelvis is large enough. The risks of injury exist, however, not as big as in the case of a frontal presentation.
In most cases, a caesarean section is also offered to the woman to minimize possible complications.
In practice, extensor positions are less common. Only 1.5-2% of head presentations require surgery. Among the reasons for which the baby is located with extension in the cervical region, we can note the narrowness of the woman's pelvis, the presence of tumors, fibroids in her uterus, scars from previous operations. The fact is that the kids instinctively try to take the most comfortable position for themselves so that the pressure on the head is minimal.
If a tumor or fibroids seize the lower uterine segment, then the child may well get the head down, but with a few adjustments, which will be extensor.
Often, irregular head positions are associated with a low placenta, with its presentation. A common cause of this situation is high water. There is also a hereditary relationship - if the woman herself was born with her chin forward, then there is a very high probability that her children will also want to repeat the path in the facial presentation.
Sometimes the cause of the pathology is a weak distended abdominal wall - this happens in women who have given birth to a lot. Also, children can remain in the wrong headache with a certain type of extension in pregnant women who have congenital anomalies of the uterus - a saddle or two-horned uterus.
Diagnostics
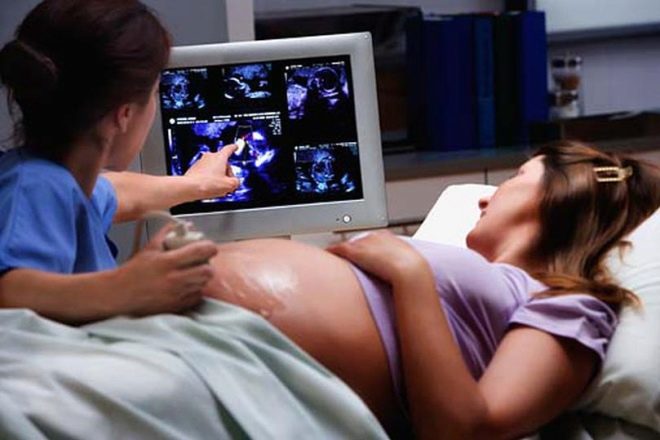
The location of the fetus in the womb is determined by ultrasound from the 12th week, but these data do not have any practical value in such early pregnancy. No attention can be paid to this item in the ultrasound protocol, because the doctor describes only the pose in which the baby was “caught” at the time of the ultrasound scan. From the 28th week of pregnancy, the obstetrician-gynecologist begins to determine the type of presentation, which monitors the pregnant woman.
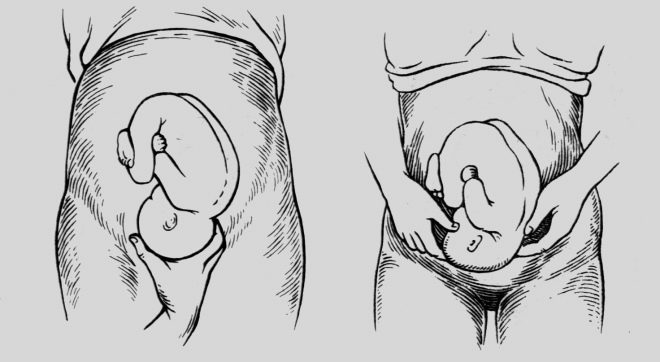
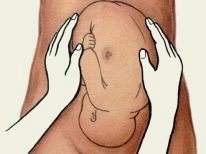
He uses methods of external obstetric research: he measures the height of the uterus bottom and probes the part that is presenting through the belly of a pregnant woman. When pelvic previa in the lower abdomen above the pubis, the butt is palpable, which is softer and less mobile than the baby’s head, and the height of the uterus when the pelvic previa is higher than the norm. With transverse previa, the head is found in the right or left side, and the height of standing of the uterus often lags behind the standard values.
At the head position, the baby’s heartbeat is heard in the lower abdomen, below the navel, and in the pelvic or transverse - in the navel of the expectant mother or above it. That is why On each examination after the 28th week, the doctor measures the stomach with a measuring tape and feels the presenting part. However, even the most experienced obstetrician-gynecologist cannot feel or determine the degree of extension of the head, if available, through a vaginal examination.
Therefore, the most accurate method of diagnosis is ultrasound. It allows you to determine the exact type of longitudinal headache, to determine the estimated weight of the baby, especially the location of its back (front or back) relative to the mother’s anterior abdominal wall, and also shows how other parts of the body are located, whether there is no cord embryo and placenta previa. All this information is mandatory for making decisions about the mode of delivery.
How is the birth?
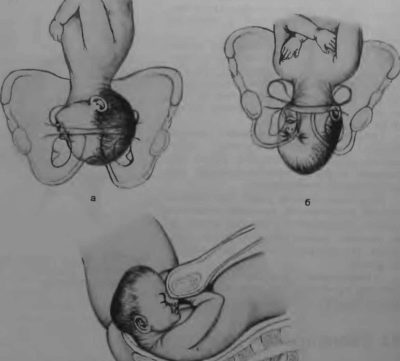
As already mentioned, childbirth most often occurs in the flexor occipital presentation. This is a classic childbirth, a kind of "gold standard" of obstetrics. With them, the risks of injury to the baby and mother are minimal. With occipital presentation, the proportions between the size of the nascent head and the size of the pelvis of the woman are in perfect agreement.
As we move along the birth canal, the baby naturally unfolds, and the back of his head has turned to the womb, and his face - to the sacrum. When the head is cut, the baby turns his shoulders and face is turned to the mother's thigh. This ensures the safest and easiest passage of the child’s body.
If the baby is in the back of the occipital presentation, childbirth can be somewhat delayed. This situation requires more careful attention from the medical staff. If necessary, contractions are stimulated so that the child does not spend too long without water and does not suffer from hypoxia.
Sometimes these genera require the use of obstetric forceps, although in recent times they have been trying to use them as little as possible, since their very imposition represents a great risk of injury to the little ones.
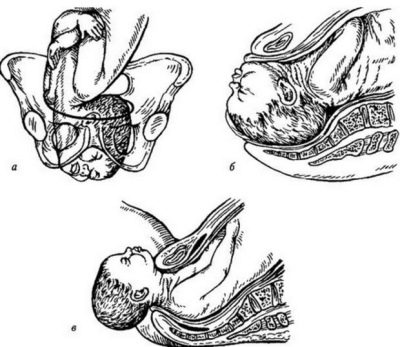
When the facial presentation of childbirth, if a decision is made about natural delivery, are classically, however, doctors are closely watching that the baby does not injure the facial structure, because it will go out with your chin forward. If there is a threat of injury or rupture of the uterus and cervix, urgent caesarean section is performed.
In case of frontal presentation, independent labor is undesirable; usually, a planned caesarean section is performed.If, for some reason, spontaneous labor occurs, they risk to be protracted, the process of expelling the fetus from the uterus will be long and may be accompanied by a decrease in the strength of contractions.
Of course, an experienced obstetrician can theoretically make a turn of the baby manually, but it is in the process of childbirth poses a certain risk of injury to the cervical spine of the child. After such injuries, disabled children are most often born.
For any type of headache presentation other than the frontal one, independent delivery is possible if the doctor considers that the size of the child and the size of the woman’s pelvis are quite comparable. Even a perfect occipital presentation can result in a cesarean section if the child is large and does not fit the size of the pelvis.
The decision on the choice of tactics of childbirth is usually made at the 36-37th week of pregnancy. If a caesarean section is prescribed, the woman needs to come for hospitalization in advance, not waiting for spontaneous contractions to begin. Usually, doctors try to perform planned operations on a period of 38-39 weeks of pregnancy.
If the presentation of the baby does not cause questions and concerns, the woman may well be at home until the appearance of signs of the onset of labor activity: discharge of water, mucus plug or the onset of labor.
How to avoid complications?
To avoid birth injuries and trauma to women in labor during childbirth, a pregnant woman should responsibly and competently approach the visit to the antenatal clinic. You should not miss the scheduled visits to the doctor, especially in the third trimester of pregnancy, you should follow all the recommendations of the specialist, in time to pass all scheduled examinations and take the required tests.
By the 35-36th week, it is desirable to determine the choice of obstetric institution. Now that women receive a birth certificate, they can dispose of it at their discretion, choosing any maternity hospital not only in their region. This right can and should be used to find a maternity hospital or perinatal center, about which there are most positive reviews.
Trust in a doctor during childbirth is half the success, it is important that a woman believes in her own strength and in the competence of a doctor who helps her baby to come into the world.
If a woman is diagnosed with one of the types of extensory positions of headache presentation, in no case can one accept home births or water births, since the outcome of such births can be very sad.
Even if the baby is perfectly normal, it is best to give birth in a specialized medical institution, because no one can ever guarantee that the birth will be easy and uncomplicated. This process is unpredictable. Do not risk your health and the health and life of your long-awaited child.
If you have to go to the hospital on an ambulance on an urgent basis, be sure to tell the doctor in the emergency department about your baby's location, if any, and give the exchange card, which should contain the latest ultrasound data. This will help save precious time when the doctor makes an important decision about how best to give birth to your child.
For information on how to determine the position of the fetus in the uterus, see the following video.