Use of calcium gluconate during pregnancy
During pregnancy, for a woman there is nothing more important than caring for the health of your baby. In order for these nine months to proceed sufficiently well for both the expectant mother and the fetus, there are many different recommendations.
A future mother can minimize the risk of various comorbidities, following a diet, adhering to the optimal mode of alternating physiological loads and rest, avoiding psycho-emotional stress.
Also, a pregnant woman can use various vitamin complexes or supplements, wanting to strengthen her health and “supply” the baby with useful substances. One of these drugs that are popular among pregnant women is calcium gluconate. Is the use of this remedy justified during pregnancy, what are the rules of calcium gluconate intake for future mothers?
Function
Deficiency of any vitamins is a fairly common problem that occurs during pregnancy. This is explained by the fact that now the organism of the future mother is forced to “share” all the most necessary things with the future baby, which requires serious resources for its active growth and development.
It often happens that after the birth of one or several children, a woman will have a “bouquet” of problems related to the health of bones and teeth. This is mainly related with a lack of calcium in the body, provoked by pregnancy.
We will understand in more detail what the main functions in the body are calcium:
- The level of calcium in the body depends on the health of the entire musculoskeletal system, as well as the strength of teeth, nails and hair.
- This trace element plays an important role in the formation of certain hormones and enzymes, and also participates in the mechanism of blood clotting.
- Calcium has an antioxidant effect, is involved in the regulation of insulin levels and glucose in the blood.
- Is a probiotic.
- During pregnancy, the woman's body suffers an even greater need for enough calcium: it affects the strength of the fetal skeleton, as well as hair and nails.
- In addition, this chemical element is actively involved in the formation of the nervous system of the baby. Therefore, it is important that a sufficient level of calcium is always maintained in the body of the future mother, otherwise the child will “take” the necessary amount of calcium with significant damage to his mother.
In order to compensate for the deficiency of any useful substances in the pregnant woman’s body, the doctor may prescribe her intake of various vitamin complexes. To compensate for the lack of calcium, a woman may be recommended to take drugs enriched with this trace element.
One of these tools is calcium gluconate. It may be in tablet, powder or liquid form as an injection. This drug is already prescribed. at 13-14 weeks of fetal development, just when he begins intensive formation of the musculoskeletal system.
In the narrow-minded view, calcium gluconate is “harmless vitamin supplements”, the administration of which does not need to be coordinated with a specialist observing pregnancy.However, this opinion is erroneous, since the excessive content of a trace element, including calcium, may adversely affect the health of the expectant mother and her baby. Therefore, the use of any additives is justified only on the advice of a doctor.
Clinical picture of calcium deficiency
As already mentioned, all sorts of drugs should be used for the purpose and the fact of pregnancy is not the reason for the uncontrolled intake of various vitamin supplements.
Your doctor may recommend starting to apply calcium gluconate if a woman has the following disorders:
- paresthesias (false sensations, for example, “goosebumps”);
- convulsive syndrome;
- regularly occurring pain in the bones;
- deterioration of skin health, dental diseases;
- decreased performance;
- irritability, emotional lability.
Possible threats of calcium deficiency in pregnant women
If a woman is in a "position", experiencing an acute calcium deficiency, in time not to prescribe a drug to fill this deficiency in her body The following negative changes may occur:
- in 1 trimester, symptoms of toxemia may appear, such as nausea, vomiting, dizziness, loss of consciousness, general malaise, and others, as well as the threat of abortion;
- preterm delivery;
- late gestosis (may occur in the second or third trimeter);
- weak uterine activity during labor;
- underdevelopment of the musculoskeletal system of the fetus;
- congenital abnormalities of the internal organs of the fetus.
Reception mode
With a calcium deficiency in a pregnant woman, calcium gluconate is most often prescribed in tablets, since this pharmacological form is the most convenient. On average, 2-3 tablets are prescribed per day, although the dose may vary in each case depending on the individual characteristics of the course of pregnancy.
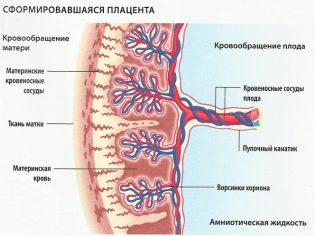
The fetus receives about a third of the entire dose of the drug that enters the mother’s body, while the baby receives calcium not only with maternal blood. His own body is also able to synthesize this trace element in certain quantities.
Method of use of the drug: you need to drink tablets an hour after eating, preliminarily grinding them to a uniform consistency. For better absorption, the drug should be taken with milk.
With a high level of calcium deficiency in the expectant mother, the doctor may prescribe parenteral (in the form of injections) administration of the drug. Enter the drug before warming it up.
Interaction with other drugs
If other drugs were prescribed to the woman during pregnancy, it is necessary to find out how they are combined with calcium gluconate.
It is forbidden to combine this remedy with medicines that contain salicylates, carbonates, and ethyl alcohol. In addition, calcium gluconate increases the toxic effects of quinidine and cardiac glycosides.
If it is taken in parallel with the antibiotics of the tetracycline group, the therapeutic effect of the latter will be significantly reduced.
This drug not recommended in combination with iron, since such a combination reduces the level of absorption of iron. Calcium gluconate reduces the toxic effect of taking fluorides and biophosphonates, besides improves the absorption of drugs containing estrogen, as well as vitamins D and K.
"Safety rules" admission
In most cases, taking this drug does not harm the health of the future mother and baby, subject to the dosage and method of use. However, with excessive admission may occur a number of unpleasant consequences.
This is especially true for those women who do not consider it to be a medicine at all, drink it with or without reason, relying not on the expert’s qualified recommendations, but on Internet reviews and the advice of illiterate persons. For example, in case of heartburn, they are able to swallow a whole handful of pills at once, without thinking about the consequences.
Excessive calcium levels in the mother's body are very harmful to the baby and can lead to early ossification of the musculoskeletal system of the fetus. In this case, the structure of its bones will lose the elasticity necessary for physiological passage through the birth canal. The consequences of this pathology can be birth trauma and soft tissue tears in the woman's birth canal.
An excess of this trace element in the structure of the placenta, due to which the fetus communicates directly with the maternal organism, can cause a deterioration of its carrying capacity, which will lead to the fact that the baby will not receive the necessary nutrients and oxygen for its normal development.
When excess calcium increases the load on the urinary apparatus of the expectant mother, which can also adversely affect the entire course of pregnancy.
Increased calcium in the blood can trigger the appearance of the following symptoms: increased maternal heartbeat, muscle weakness, decreased performance, drowsiness.
However, with calcium deficiency, taking the drug in compliance with the instructions will bring a better feeling to the pregnant woman. In addition, it will have a positive effect on the contractility of the heart muscle and the work of the adrenal glands, as well as reduce the risk of allergies.
How to apply calcium gluconate during pregnancy, see the following video.