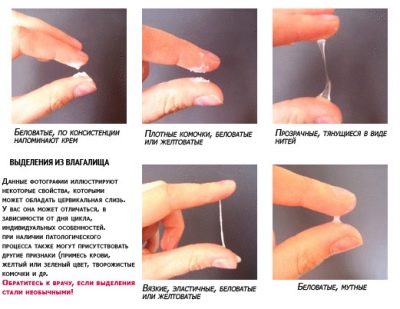
Brown discharge during pregnancy
During pregnancy, the type of vaginal discharge will inevitably change. This is due to changes in the hormonal background, with some anatomical changes in the process of carrying a child. Normally, the vaginal secretion should be light or yellowish throughout the gestational period. Brown discharge usually scares future moms. Should they be afraid of and what they can talk about at different times should be considered in more detail.
Special features
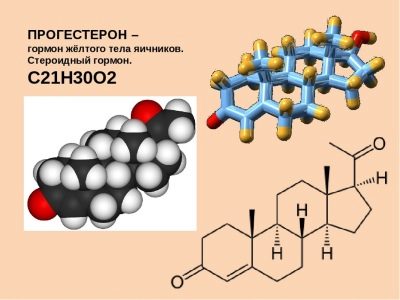
Highlight can not be underestimated. Vaginal secretions produce cervical epithelium cells. At different stages of pregnancy, they can tell a lot about the state of the future mother and fetus. Immediately after conception and up to 8–9 weeks of pregnancy discharge from a woman in the norm is rather scanty, and sometimes, in general, is practically absent. So affects the action of progesterone, which conducts the basic preparation of the body for long-term bearing of the fetus.
From week 10 the vaginal secretion becomes more abundant, and by the end of pregnancy not only abundant, but also watery. So acts on the vaginal secretion of the hormone estrogen. The task of the secretory function of the genital tract of a woman is to maintain a healthy, stable microflora. The genital tract will be the first to reach the baby in the generic process after it leaves the uterus. The health of the baby depends on their health.
Existing medical literature describes normal discharge during pregnancy as light, odorless or with a slight fermented milk smell. Other variants of the norm are also considered, but only under certain conditions and on certain terms.
Brown discharge is no exception. They can not only talk about dangerous complications, but also be a natural variant of normal vaginal secretion. Erythrocytes - blood cells - give brown secretions. This means that the brown discharge refers to the type of blood discharge.
Norm
A small amount of blood in the earliest discharge can be the norm when a fertilized egg is implanted into the uterus. This phenomenon is called implant bleeding. It occurs due to endometrial integrity problems when the blastocyst is attached. One of the options for such natural bleeding may be a light brown discharge in a small amount of about 8–9 days after the intended conception (or after ovulation - for ease of counting).
Brownish smears on daily pads or underwear are not long lasting. Usually a day or two of them does not remain a trace. There is nothing alarming in this phenomenon.
In addition, such an early sign of pregnancy is not manifested in every woman. You should know that the appearance of dark brown discharge with clots before the delay can hardly be considered a sign of implantation. Rather, it is a hormonal failure, in which menstruation began prematurely.During the first 2-3 months of pregnancy, yellow-brown moderate or scanty discharge may be due to global hormonal adjustment.
Progesterone raging in the body of the future mother usually gives a vaginal secret a yellowish tint, brown “notes” in it can appear due to high or low levels of progesterone, due to the vulnerability of the genital tract due to looseness under the action of hormones. Normally, such secretions appear without pain, they do not contain blotches and impurities, blood streaks, do not bother a woman. They usually stop after the future mother's body fully adapts to the new situation and circumstances.
In the later periods (a week or two before the expected date of delivery), a woman can pay attention to the brown streaks that have appeared. Usually they are accompanied by the release of mucus in small quantities or rather impressive mucous clot. In this case, we are talking about the discharge of the mucous membrane, which, during the gestation period, closed the cervical canal and prevented the penetration of everything foreign and dangerous into the uterus, where the baby was growing.
Cork discharge is a precursor of imminent labor. He also does not need treatment.
Small brown discharge after sex or examination by a doctor is also a variant of the norm. The reason for them lies in the extreme vulnerability of the genital tract of a pregnant woman. Under the action of progesterone, they become friable, vulnerable even to minor mechanical effects.
Such secretions usually do not last long - no more than a day, they are not accompanied by any unpleasant sensations and additional symptoms. There are no clots in them, they do not increase, their number changes in descending order. These are the three main reasons why brown secretions can be considered normal. All other situations, alas, relate exclusively to the pathological.
Risk of miscarriage
The brown discharge in the early stages is often accompanied by the threat of miscarriage. Recognizing the threatening condition is not difficult: the woman notes not only the color change of the vaginal secretions, but also a general deterioration of her state of health. There may be severe bouts of dizziness, pain in the lower abdomen and lower back is almost always present.
Pain syndrome can be severe and intense, or it can be in the form of aching, weak pain. However, the combination of “pain and brown discharge” should alert the pregnant woman and make her seek medical help as soon as possible.
The blood in the discharge appears due to the detachment of the ovum. A space filled with blood appears between the membranes of the fetus and the wall of the uterus. With a small retrochorial hematoma, the discharge will be predominantly pink-brown and not abundant, with substantial detachment - abundant, with clots, red-brown.
The threat can develop for a variety of reasons. These include abnormalities in the structure of the uterus, genetic abnormalities of the fetus, which are incompatible with its further development, inflammatory and infectious diseases of the genital tract and reproductive organs, hormonal insufficiency, as well as bad habits, severe stress, excessive exercise.
For developing a miscarriage is characterized by increased discharge over time, the appearance of cramping pain in the lower back and in the cervix, as well as nagging pains with "echo" in the anus. Brown daub turns into a more saturated color, the consistency is diluted until liquid red blood begins to flow with blood clots.
Such a metamorphosis usually indicates that a miscarriage has already taken place, and fragments of the fetal membranes and the embryo come out with the vaginal secretion. What is it really and at what stage the threat of miscarriage, can only understand the doctor. Therefore, with the appearance of the characteristic symptoms described above, it is imperative to call an ambulance. In 95% of cases, pregnancy can be maintained with timely treatment.
Hormonal insufficiency
Hormones “manage” menstrual bleeding. Progesterone gradually decreases in the second half of the cycle, the estrogen concentration rises and menstruation begins. Do not think that menstrual discharge during pregnancy is a variant of the norm. As a rule, this happens in the first months after conception due to the lack of progesterone.
Of course, there are rare situations in which menstrual bleeding during pregnancy can be considered conditionally normal. This happens if a woman has developed two eggs instead of one in the current cycle, and ovulation occurred twice with a difference of several days. In this case, the first egg cell was not fertilized, it died and sank into the uterus, and the second one fertilized and went into the uterus for implantation.
The spotting will come on the day of the expected menstruation, but such periods will differ significantly. In the first place, there will be few selections. In a few days the scanty and incomprehensible periods will cease and will not be repeated within the next 9 months. People used to say about such a phenomenon that “the fruit is washed”, but in practice this happens infrequently.
When hormonal deficiency or hormone imbalance in the body excretions resemble slight pale brown marks on linen or thin daily hygienic lining. They may increase slightly or disappear completely, after which they appear again.
A woman needs to consult a doctor in order to be tested for hormones and to start maintenance treatment with appropriate hormonal drugs, which will bring the balance of these active substances in the body to the norm necessary for safe childbearing.
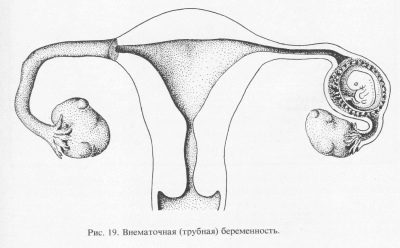
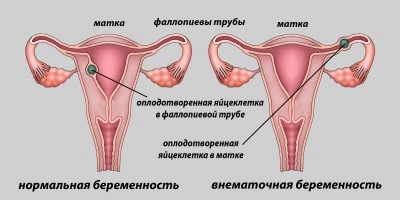
Ectopic pregnancy
If for some reasons the fertilized egg cannot get into the uterine cavity and be implanted where it should be, it can be fixed in the fallopian tube or lowered below and fixed in the cervix of the uterus. This is possible if the woman has difficulty in passing the egg through the tubes due to the narrowed lumen of the tube. The cause can be inflammatory diseases of the tubes, appendages, ovaries, as well as endometriosis, the presence of tumor mass in the uterus, in the fallopian tubes.
If the transfer of the zygote, and subsequently the blastocyst, is disturbed, then the development of the embryo outside the uterus is possible. An ectopic pregnancy until a certain time may not be felt. The delay will be, the tests will show the second strip (slightly paler than in uterine pregnancy, but this is an optional sign). And only when the embryo becomes quite large, the pathology can manifest.
Rejection of the ovum if it is attached in a place for which nature has not intended, is inevitable. This process, at best, will begin before the organ to which the fertilized egg has attached has been seriously injured.
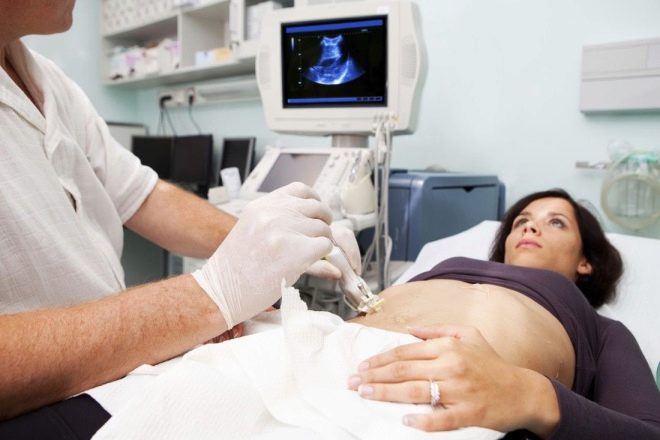
Rejection is accompanied by a strong cutting pain in the abdomen, rather abundant brown secretions that quickly become brighter red. In the worst case, a rupture of the fallopian tube can occur with massive bleeding into the abdominal cavity, which can be fatal for a woman. The exact place of attachment of the ovum is determined quite well on an ultrasound at 5-6 weeks of gestation.
Women with a history of ectopic pregnancies, as well as miscarriages, gynecological inflammatory diseases, operations on the reproductive organs, after which scars and adhesions could remain, with a positive pregnancy test, you should visit a doctor as soon as possible and do an ultrasound scan to exclude the wrong fetal attachment. When ectopic pregnancy is another option, as the removal of the ovum, no.
With more rare and more dangerous types of such pregnancy - cervical and isthmus pregnancy, it is usually not possible to preserve the uterus.In tubal ectopic pregnancy, if there is no rupture, it is most often possible to preserve the tubes, and the woman can later become pregnant and give birth to a child.
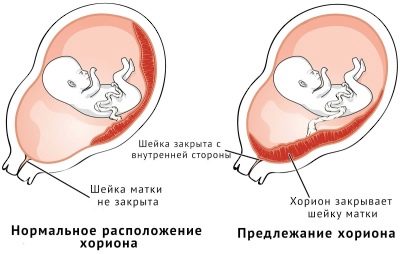
Placenta previa or abruption
If the placenta (or the chorion is its predecessor) is low in a woman, then brown daub or highlighting of all shades of brown can be a sign of placental abruption. The most dangerous are brown intensive discharge, which occurs with complete and incomplete placenta previa.
With full previa, the “baby seat” is located at the bottom of the uterus and completely blocks the entrance to the cervical canal. If incomplete, the entrance to the cervical canal is closed by about two thirds or less. Any negative impact and even the most common stress can cause severe bleeding in a woman with such a pathology of pregnancy.
In any form of the presentation of the chorion (placenta), abrupt movements, emotional shocks, sex, physical exertion, jumping, shaking in traffic, and bending forward are prohibited. In some women, occasional bloody discharge is repeated until delivery.
If a diagnosis such as low placentation has already been made and confirmed by ultrasound data, the woman should be very careful. If there is no such diagnosis and the placenta is located normally, the woman still risks testing her detachment. This becomes possible with a fall, especially with a stomach injury, a sharp jump in hormone levels, severe emotional distress, weight lifting, or taking some medications that are prohibited during pregnancy.
Vaginal discharge in detachment is usually quite abundant, although the pain may not be. The limitation of the problem can be judged by the hue of the discharge. Fresh blood that has just separated and come out is always bright, red. If, after the detachment, the blood did not come out for some time and was in the space between the “children's place” and the wall of the uterus, then it will have brown shades of varying intensity.
Other gynecological problems
Inflammatory diseases of the reproductive and urinary system during pregnancy - this is not at all uncommon. Immunity of the future mother is significantly reduced (and this is also the merit of progesterone!), Which is why any fluctuations in the balance of microflora can cause local inflammation.
If a woman before the onset of the “interesting situation” had chronic diseases of the genital or urinary system, then in the period of maximum decrease in immunity, by the middle of pregnancy they may well have an effect. Many inflammatory processes of non-infectious origin occur with the release of a vaginal secretion of yellow, light brownish tint.
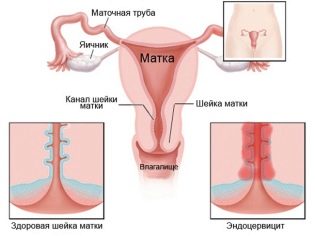
Discharges are always accompanied by additional symptoms, such as with adnexitis - pains in the right or left side, pulling and cutting pains in the appendages, with cervicitis - discomfort in the depths of the vagina, as well as the appearance of mucous impurities in the brownish vaginal secretions.
Diseases of infectious origin are not excluded. These can be sexually transmitted infections as well as venereal diseases. Many of them have a rather long incubation period; therefore, at the time of registration, the examination may not reveal any pathology, and the real symptoms will appear later.
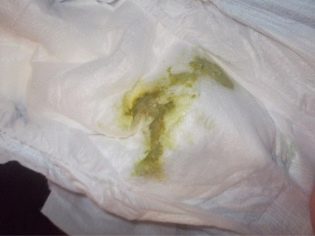
The most dangerous are brown and brown discharge, which have greenish purulent impurities, as well as an unpleasant and pungent odor. They indicate the bacterial origin of the problem, which, in case of late treatment, can result in intrauterine infection of the fetus and even its death. Brown secretions of the spotting nature can cause problems with the cervix, inflammation of the cervical canal.
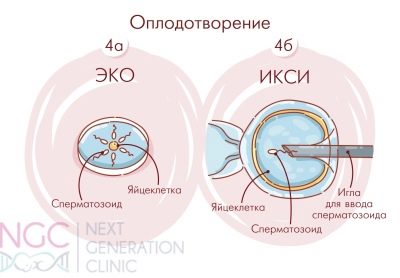
After IVF
If the couple had to resort to assisted reproductive techniques, such as IVF, you should be prepared for the fact that the discharge will be significantly different from the discharge, normal for pregnancy, occurred naturally. So, after embryo transfer for almost two weeks, brownish secretions are considered a variant of the norm. This is the reaction of the female body to hormone therapy, which she underwent before embryo grafting and passes after it.
And also brown smearing discharge from the vagina can speak about successful implantation. If they are a sign of implantation, then usually brown streaks or scanty smear appears on the 5-6th day after hatching. By one third of women, a change in the color of the vaginal secretion is manifested only 8–10 days after transplantation.
If the discharge of an unusual color lasts more than 14 days, this is regarded by the doctors as an alarm signal - not everything is all right with the pregnancy.
But you do not need to despair, because after analyzing the concentration of the hormone hCG in the blood, a treatment will be prescribed that will help keep the pregnancy and make a healthy baby, maybe a few babies. In the worst case, brown discharge after two weeks from the moment of replanting may indicate that the embryos stopped developing and their rejection began. After treatment, an IVF attempt can be repeated.
What to do?
With the appearance of brown discharge, a pregnant woman should in no case be engaged in self-diagnosis. All of the above is nothing more than a material for self-education for reference purposes, and not a guide for making any diagnoses for oneself.
There are not so many options for the physiological norm with this kind of vaginal secretion, but there are more than enough options for pathologies. For this reason, a woman should immediately see a doctor. An ultrasound scan, a vaginal smear, and blood and urine tests will help find the exact answer to the question of why blood has appeared in the secret of the genital tract.
If the discharge is scarce and not accompanied by pain, you should consult a doctor in the antenatal clinic at the place of residence. If the brown discharge is abundant, with clots, pain, then you should go to bed, eliminate standing or walking and wait for the ambulance brigade called right away.
Arriving physicians should be informed of the gestational age (from the first day of the last menstrual period), describe in detail all the symptoms, including even the most, in your opinion, minor, as well as tell about all previous pregnancies and their outcomes. All this information will help doctors promptly guess the cause of the bleeding and take you to the gynecological hospital or emergency department of the maternity hospital with the most accurate formulation of the problem. Every minute can be decisive, you need to help doctors understand you correctly.
If the brown discharge is repeated sporadically, the obstetrician-gynecologist should inform the obstetrician so that he can give the most complete and accurate recommendations regarding the future mother’s lifestyle, day regimen, work and rest, sex the reasons.
When a low placentation is threatened with miscarriage, antispasmodic drugs are prescribed that relax the uterus muscles, prevent its tone, as well as vitamins, drugs for improving uteroplacental blood flow and light vegetable sedatives. In case of placental abruption after inpatient treatment, a woman can be prescribed hemostatic drugs. When hormonal problems, progesterone deficiency recommend certain dosages of hormonal drugs that completely fill the deficit in the body.
Useful tips
Any problem that occurs during gestation of the baby, including the appearance of atypical discharge, will be solved faster and more correctly, If you follow simple safety rules, such as:
- it is necessary to control the nature of the discharge daily throughout pregnancy;
- only hygienic pads should be used; tampons should not be used during pregnancy;
- Responsibly it is necessary to treat intimate hygiene issues in order to prevent inflammatory processes due to its violation;
- should not be changed during pregnancy, sexual partner;
It is necessary to comply with all the recommendations of the doctor regarding medication and lifestyle.
- you need to take care of your reproductive health, not to allow too harsh and rough sex, trauma to the genital tract and cervix;
- it is necessary to regularly attend the antenatal clinic and undergo all the necessary examinations and analyzes;
- should stop smoking, do not take alcohol and drugs during pregnancy;
- It is necessary to avoid stress, conflict, do not lift weights and limit physical activity, which can provoke the threat of abortion.
Reviews
According to reviews of pregnant women, left by them on thematic forums, with such a phenomenon as the allocation of brown, women usually face in early pregnancy. In the later - it happens much less frequently.
In most cases, the history of pregnant women have a happy ending - they managed to keep the pregnancy, even with an impressive placental abruption. In some, the discharge was of the type of abundant and sudden bleeding, but even in these cases, the children were rescued and they came to light in due time perfectly healthy.
Experienced mothers emphasize that it is impossible to wait, it is necessary to get to a medical facility as soon as possible in order to be examined and begin treatment. However, with such a symptom as brown daub at 5-6 weeks of gestation, it is better not to get to some doctors at all. They do not prescribe any treatment.
Among obstetricians, there is a whole army of adherents to the theory that pregnancy will continue if it is destined to continue. Such doctors send the upset woman home, lie with their legs raised and not think about the bad. Their behavior is a topic for another conversation. If you wish, you can always visit another doctor.
See if there is a cause for concern with brown secretions in the next video.