Hip dysplasia in children
Hip dysplasia in children
Diseases of the musculoskeletal system, which can lead to a persistent gait disturbance, are often found in toddlers of different ages. It is better to treat such pathologies as early as possible before serious complications arise. Hip dysplasia in children is also quite common in children.
What it is?
This disease develops due to the effects of various provoking causes that lead to the appearance of adverse effects on the joints. As a result of congenital structural disorders, the hip joints cease to perform all the basic functions that are imposed on them by nature. All this leads to the emergence and development of specific symptoms of the disease.
This pathology is more common in babies. In boys, dysplasia is recorded much less frequently. Usually every third out of hundreds of babies born to orthopedists find this disease. There are also geographical differences in the incidence of hip dysplasia in babies born in different countries.
For example, in Africa, the incidence of this disease is much less. This can easily be explained by the way of wearing the babies on the back, when the legs are widely spread apart.
The reasons
Various factors can lead to the development of the disease. Large joints, including the hip joints, begin to be laid and formed even in utero. If certain disturbances occur during pregnancy, this leads to the development of anatomical anomalies in the structure of the musculoskeletal system.
The most common causes of dysplasia include:
- Genetic predisposition. In families in which close relatives have manifestations of the disease, there is a higher probability of having a child with this disease. It is more than 30%.
- Violation of the formation of the baby's joints during pregnancy as a result of an unfavorable environmental situation or exposure to toxic substances on the body of the expectant mother.
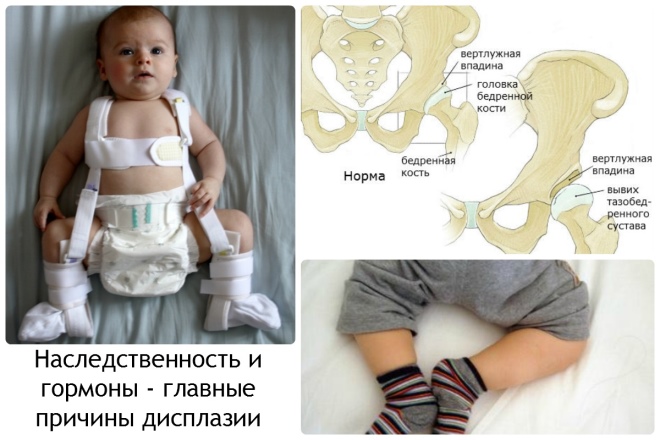
- High levels of hormones during pregnancy. Oxytocin, which is produced in the body of the future mother, causes an improvement in the mobility of the ligamentous apparatus. This property is necessary before giving birth. Oxytocin also affects the improvement of mobility of all joints, including provokes further excessive amplitude of movements. The hip joints are most susceptible to this effect.
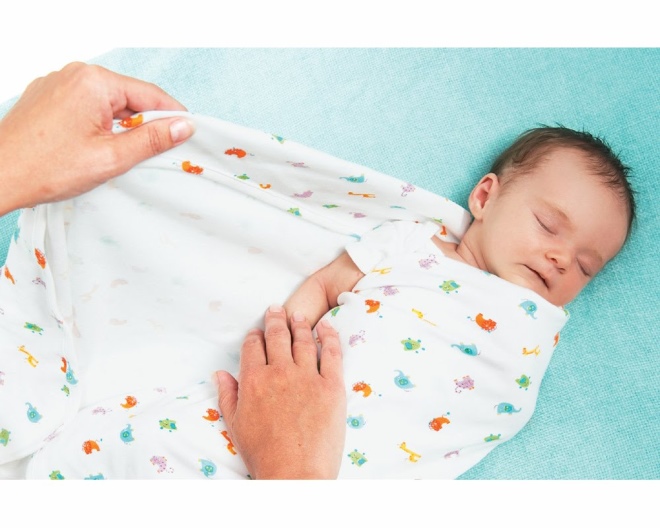
- Tight swaddling. Excessive tightening of the legs during this daily procedure leads to the formation of dysplasia. Changing the type of swaddling leads to improved functioning of the joints and prevents the development of the disease. This is also confirmed by numerous studies conducted in Japan.
- The birth of a child over the age of 35 years.
- Baby weight at birth more than 4 pounds.
- Prematurity
- Buttock previa.
- Close location of the fruit. This is usually found in a narrow or small uterus. If the fetus is large, it can fit snugly enough to the walls of the uterus and hardly move.
Development options
Doctors distinguish several different variants of this disease. Various classifications allow you to establish the diagnosis most accurately. It indicates the variant of the disease and severity.
Options for dysplasia in violation of the anatomical structure:
- Acetabular. The defect is in the area of the cartilage of the limbus or on the periphery. Excess intraarticular pressure leads to impaired mobility.
- Epiphyseal (Mayer's disease). In this form, there is a strong compaction and point ossification of cartilage. This leads to severe stiffness, progression of pain, and can also cause deformities.
- Rotary. There is a violation of the anatomical location of the elements forming the joint in several planes relative to each other. Some doctors refer this form to the borderline state, and do not consider it an independent pathology.
By severity:
- Easy Also called predislocation. Small deviations are formed, under which there is a violation of architecture in the structure of the largest joints of the child’s body. Violations of active movements occur slightly.
- Medium degree. Or sublimation. In this variant, the acetabulum is somewhat flattened. Movement is significantly impaired, there are characteristic symptoms of shortening and gait disturbance.
- Heavy current. Also called dislocation. This form of the disease leads to numerous deviations in the performance of movements.
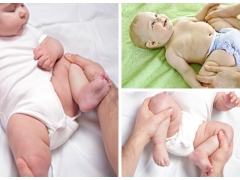
Symptoms
In the early stages of the disease is difficult to determine. Usually it becomes possible to identify the main clinical signs of the disease after a year from the moment of birth of the baby. In infants, the symptoms of dysplasia are easily determined only with a sufficiently pronounced course of the disease or consultation with an experienced orthopedist.
The most important manifestations of the disease include:
- Sound "click" when breeding hip joints while bending the knee joints of the baby. In this case, a small crunch appears when the femoral head enters the joint. When you move back - you hear a click.
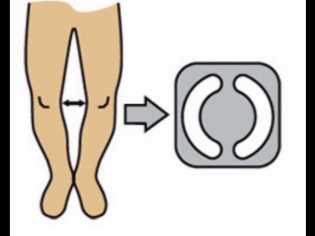
- Lead disturbances. In this case, an incomplete dilution occurs in the hip joints. In moderately severe or dislocated, severe movement disturbance is possible. Even if the dilution angle is less than 65% - this may also indicate the presence of resistant pathology.
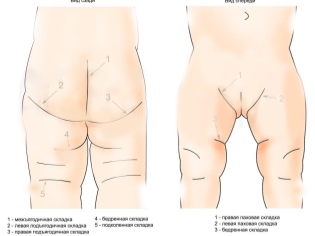
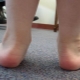
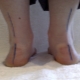
- Asymmetric position of skin folds. By this feature, often even newborns you can suspect the presence of the disease. When examining skin folds, one should also pay attention to their depth and level, where and how they are located.
- Shortening of the lower extremities from one or two sides.
- Excessive foot reversal on the injured side outside. So, if the left hip joint is damaged, the foot on the left side turns strongly.
- Gait disturbance. The child, sparing the injured leg, begins to tiptoe or to limp. Most often this sign is registered in babies at 2 years. If a child has a complete dislocation, then his movements become more artsy.
- Pain syndrome. Usually develops in children with a rather severe course of the disease. The long course of the disease leads to the progression of pain. To eliminate the pain usually requires the use of drugs.
- Muscle atrophy on the affected leg. This symptom can occur with severe disease, as well as with the long-term development of the disease. Usually, the muscles on the other leg are more strongly developed. This is due to a compensatory response. Usually there is increased pressure on a healthy foot.
Diagnostics
In order to establish the diagnosis of dysplasia in the early stages, additional examination is often required. Already in the first six months after the birth of a child, he is necessarily advised by a pediatric orthopedist. The doctor will be able to identify the first symptoms of the disease, which are often non-specific.
The most common method of examination is ultrasound. This diagnostic method allows you to accurately establish all the anatomical defects that occur with dysplasia.This study is highly accurate and informative enough. It can be used even in very young children.
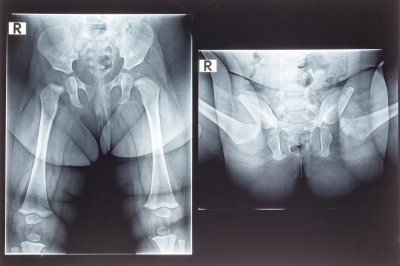
Also, to establish dysplasia quite successfully used radiodiagnosis. However, the use of X-rays in early childhood is not shown. Such a study in infants is dangerous and can cause adverse effects.
The use of X-ray diagnostics can be quite informative in babies who can lie quietly for some time without strong movement. It is necessary for the correct setup of the device and accurate conduct of the study.
At establishment of the diagnosis and carrying out all previous inspections in some cases additional carrying out a computer or magnetic resonance tomography is required. Often these studies are resorted to before performing surgical operations. Such methods allow you to accurately describe all the structural and anatomical anomalies of the joints that a child has. Such surveys are very accurate, but very costly. Instrumental examinations of the joints are not widespread.
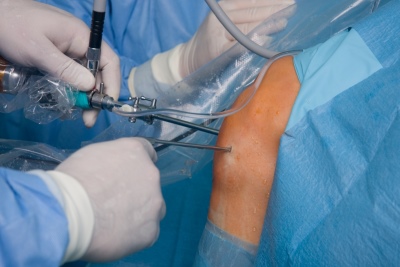
Arthroscopy - This is a survey of the joint cavity with the help of special devices. It has not received wide application in our country. This study is quite traumatic. In case of violation of the tactics of arthroscopy, a secondary infection can enter the joint cavity, and severe inflammation can begin. The presence of such a risk led to the fact that such studies are practically not used in pediatric practice for the diagnosis of dysplasia.
With the timely determination of specific symptoms of the disease and the conduct of an accurate diagnosis, treatment can be started in due time. However, in case of severe disease or late diagnosis, the development of dysplasia can lead to the appearance of various adverse conditions.
Effects
Quite often unpleasant outcome of the long development of the disease and poorly performed treatment is a gait disturbance. Usually babies start to limp. The degree of lameness depends on the initial level of hip joint damage.
With complete dislocation and untimely provision of medical care, the child subsequently limps badly and practically does not step on the damaged leg. Walking causes increased pain in the baby.
In children aged 3-4 years, pronounced shortening of the lower limbs may be observed. In a two-way process, this symptom can manifest itself only in a slight lag in growth.
If only one joint is affected, then shortening can also lead to gait disturbance and lameness. Kids start not only to limp, but also to jump a little. This way they try to compensate for the inability to walk properly.
This pathology of the musculoskeletal system can cause the establishment of a disability group. The decision to issue such a conclusion is made by a whole commission of doctors. Doctors assess the severity of violations, take into account the nature of the damage and only then make a conclusion on the establishment of the group. Usually with dysplasia of moderate severity and the presence of persistent complications of the disease, a third group is established. With more severe disease - the second.
Treatment
All medical procedures that can help prevent the progression of the disease are given to the baby as early as possible. Usually, already at the first visit to the orthopedist, the doctor may suspect the presence of dysplasia. Prescribing medications is not required for all variants of the disease.
All therapeutic measures can be divided into several groups. Currently, there are more than 50 different methods that are officially used in medicine for the treatment of dysplasia in children at different ages. The choice of a particular scheme remains with the orthopedist.Only after a thorough examination of the child can an accurate treatment plan be prepared for the baby.
All methods of treatment of dysplasia can be divided into several groups:
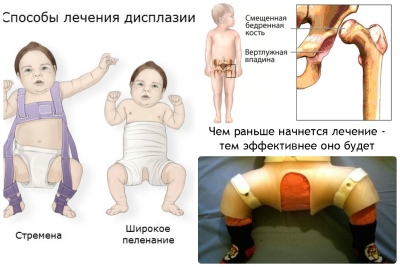
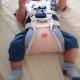
- Looser swaddling. Usually this option is called wide. With this swaddling, the baby's legs are in a somewhat diluted state. A broad way to eliminate the first adverse symptoms of the disease and prevent its progression. Becker pants are one of the variants of such swaddling.
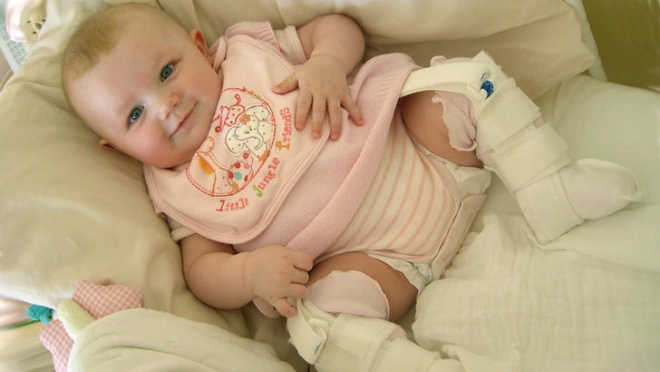
- The use of various technical means. These include a variety of tires, cushions, stirrups, and many others. Such products allow you to securely fix baby's legs divorced.
- The use of breeding tires when walking. They allow you to maintain the correct angle of breeding in the hip joints and are used only as directed by the attending physician. Usually used Volkov or Vilensky tires.
- Surgery. It is used quite rarely. Usually in difficult cases of the disease, when other methods have been ineffective. Such orthopedic operations are performed in children older than one year, as well as with frequent recurrences of the disease and the absence of the effect of previous treatment.
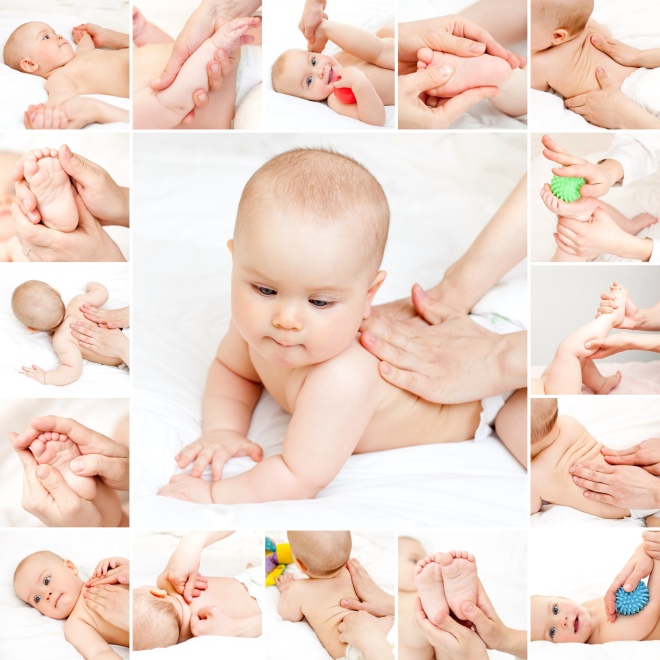
- Massage. Usually this treatment is enjoyed by almost all babies. Even newborns perceive massage not as a therapy, but as a real pleasure. It is conducted by his specialist, who has not only a specialized education in child massage, but also has sufficient clinical experience in working with children who have a diagnosis of dysplasia. During the massage, the area of the hip joints, as well as the neck and back is actively worked through.
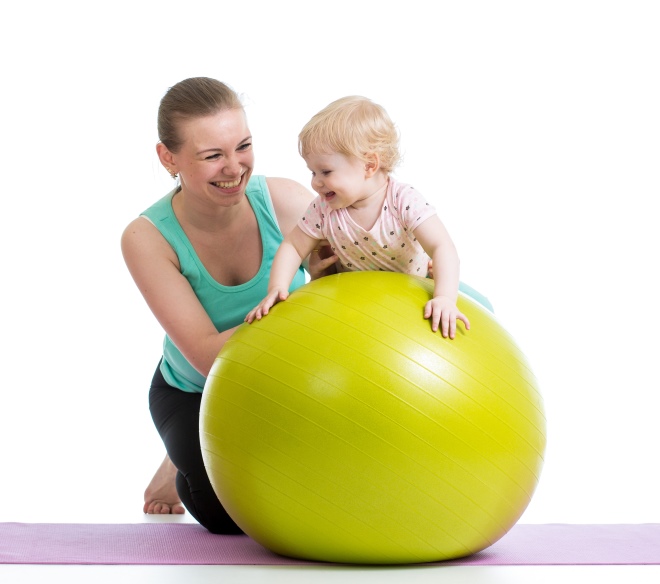
- Exercises physical therapy. They have a pronounced effect in the initial stages of the disease. Doctors carry out such exercises 2-3 times a week, and in some forms of the disease - daily. Usually the duration of classes is 15-20 minutes. Exercises can be carried out by mom or nurse in the clinic. They can not be carried out immediately after a meal or before bedtime.
- Electrophoresis on the area of the hip joints. Allows you to reduce the severity of pain, improves blood flow to the cartilage that forms the joint. Electrophoresis is prescribed by the course. Usually apply 2-3 courses during the year. The effect of the treatment is assessed by the orthopedic surgeon.
- Gymnastics with newborns. Typically, this method is used to detect small deviations in the work of the hip joints. It helps prevent the development of dysplasia and can be used not only for medicinal purposes, but also as a preventive measure.
- Conducting physiotherapy treatment. To improve the blood supply and improve the innervation of articular cartilage, you can apply various types of thermo - and induction therapy. Such methods are appointed by a physiotherapist and have a number of contraindications. They are usually used for mild and moderately severe variant of the disease. Also quite successful after surgical treatment to eliminate the adverse symptoms that occurred during the operation.
- Mud therapy This method is widely used not only in sanatoria and health centers, but also can be performed in the physiotherapy room of the children's clinic. Biologically active components of the mud, which are included in its composition, have a healing and warming effect on the joints, which leads to a decrease in the manifestation of adverse symptoms of the disease.
Prevention
In order to reduce the likelihood of developing dysplasia in babies, parents should pay attention to the following tips:
- Do not try to tightly and tightly swaddle the child.
Choose a wide swaddle. This method is mandatory if the baby has the first signs of dysplasia.
- Keep your baby right. During the wrong position of the child in the hands of adults, often the baby’s legs are strongly pressed against the body.Such a situation can cause dysplasia or other pathologies of the hip and knee joints. Pay attention to the comfort of the child during breastfeeding.
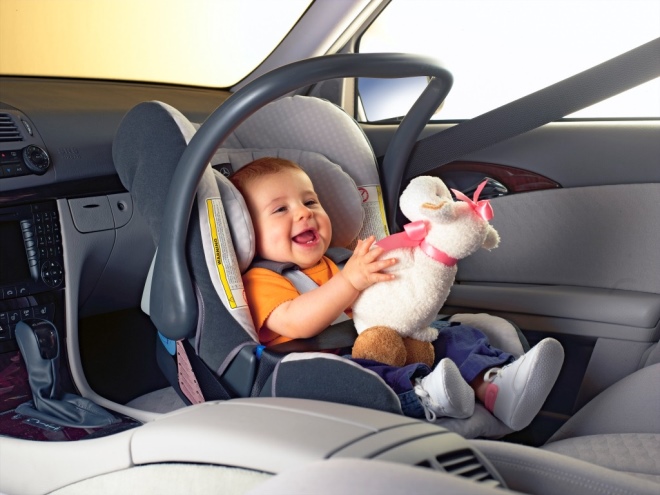
- Choose special child seats for transporting the baby in the car. Modern devices allow you to maintain the functional and correct position of the legs of children while in the car during the entire trip.
- Do not forget to visit the orthopedic surgeon. An orthopedic consultation is included in the mandatory list of necessary research in babies of the first year of life.
- Meet with hip dysplasia each mom can. The treatment of this disease is quite laborious and will require a huge concentration of forces and attention of parents. To prevent the development of serious complications is possible only with the daily implementation of all recommendations.
- With timely diagnosis and treatment prescription Kids have almost no negative consequences, and they lead a fairly active lifestyle.
You can find out more about dysplasia in children in the following video: