How to treat flat feet in adolescents?
Flat feet in adolescents are diagnosed more often than in children of other ages. Such a medical verdict is not given to babies at all, since up to 4-5 years the feet of all children are physiologically flat.
In preschool and primary school flatfoot, it is usually detected by chance, but in adolescents who are beginning to undergo medical examinations at school, the pathology can no longer be hidden. If this happens, the question of treatment arises. In this article we will tell you what methods you can get rid of foot deformities in adolescence.
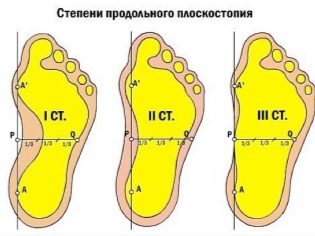
Types and degrees of the disease
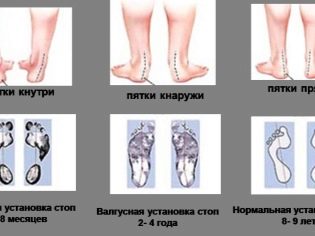
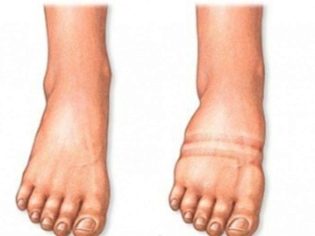
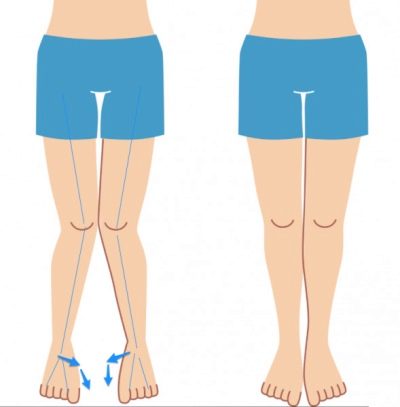
Deformation of the arches of the feet in adolescence can occur in two types - longitudinal or transverse. Sometimes there is a mixed combined flatfoot.
With a longitudinal flattening of the foot occurs along the entire length, the child's legs over the entire area in contact with the floor surface. When the transverse foot becomes wider due to the flattening of the metatarsal bones.
For the purpose of treatment plays a big role type of disease. With transverse, some therapeutic measures are effective, with a longitudinal - others. In addition, the orthopedic surgeon determines the degree of the violation:
- 1 degree transverse flatfoot is characterized by an angle of 10-12 degrees between the metatarsal bones No. 1 and 2, as well as the angle of deviation of the thumb 15-20 degrees from the normal position.
- 2 degree of transverse deformation is the angle between the metatarsal bones at 15 degrees, the thumb is inclined from the natural position by 30 degrees.
- Grade 3 transverse flatfoot is accompanied by an angle between the metatarsal bones No. 1 and 2 at 20 degrees, with the first finger sticking out at 40 degrees.
- Grade 4 transverse pathology is a value greater than that specified for the third degree.
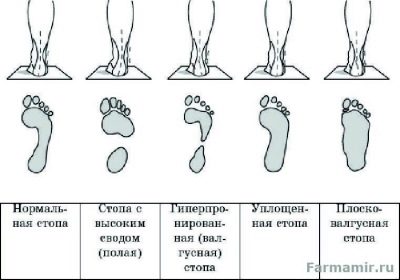
Longitudinal deformation of the foot is measured by the height of the arch:
- 1 degree - arch (the distance from the floor to the top of the arch, as far as possible from the floor) is 25-35 mm.
- 2 degree - arch from 25 to 17 mm.
- 3 degree - arch less than 17 mm.
The reasons
The reasons why a flat foot can develop in a teenager are quite extensive and varied.
Most often in children older than 10-11 years old, static flatfoot is detected, associated with external influence on the leg. This may be wearing uncomfortable and wrong shoes, excess weight, and, as a result, increased stress on the legs.
In adolescence, traumatic flatfoot is often encountered, resulting from improper accretion of bones after injuries - fractures and ruptures of the ligaments and muscles of the ankle, calcaneus and other bones of the foot.
Paralytic flat-footedness can be a sign of previous poliomyelitis, other diseases, including damage to the nervous system, which led to partial paralysis and paresis of certain muscles involved in the formation of the feet.
Congenital flatfoot is not so often detected in adolescence, because it can be seen much earlier, but if the orthopedist was not visited for some reason, then the diagnosis of congenital flatfoot can be heard for the first time only when the child enters puberty.
Adolescents who are professionally involved in sports associated with weight lifting, excessive physical exertion, often suffer from flatfoot than their peers who do not experience such loads.
Usually the prerequisites for the development of flat feet occur long before adolescence. Therefore, the early stages of leg deformities are rarely detected in adolescents, usually these are already quite serious anomalies, with treatment which should not be delayed, since time is short - conservative measures are good only when the foot is still growing rapidly.
Symptoms and signs
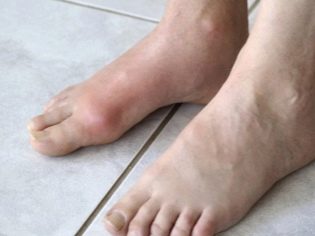
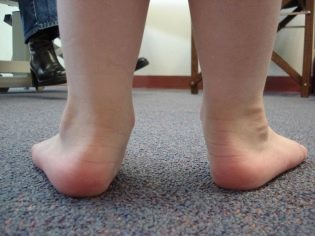
A teenager with flat feet gets tired faster when walking, his legs often hurt, especially in the evening. Swelling of the ankles may occur, with sufficiently pronounced flat-footedness, the gait is disturbed, awkwardness appears.
Shoes such a child tatty always on the inside. Frequent attacks of headaches, complaints that “reduces” the legs, pain in the knees are not excluded.
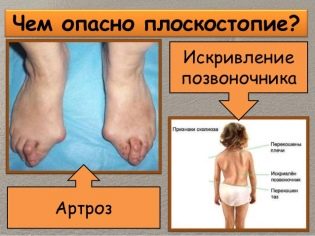
With severe anomalies of the development of the feet (from 3 degrees and above), the deformities become visible and visually distinguishable. It is becoming more and more difficult to find comfortable shoes, and longer walking becomes more and more painful. Arthrosis may begin to develop.
Teenage girls with flat feet painfully given wearing shoes with heels, because the legs get tired very quickly, and there is shooting pain.
Treatment
Features of treatment of flatfoot in adolescence lie in the fact that there is not much time left for correction - the feet will soon stop growing, and conservative treatment may not bring the desired result.
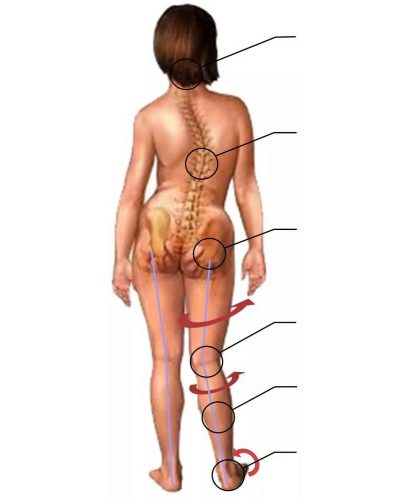
Therapy is associated not only with correction of the feet, but also with a decrease in the load on the spine. In case of insufficient depreciation, adolescents walk with a slight forward inclination of the body, as a result the spine suffers moreOh, than younger children.
Due to the fact that the weight of adolescents is higher than the weight of children of primary school age, with flat feet, boys and girls have a stronger load on their knees and hip joints, respectively, the probability of their deformation and injury is higher.
All these age factors must be taken into account by the doctor before prescribing a particular treatment method.
In most cases, adolescents up to the age of 13–14 are prescribed conservative treatment, or rather a set of measures, which, when interacting with each other, provide a sufficiently effective result.
Conservative treatment
Young men and women with a slight stage of deformity of the feet are prescribed physical therapy and massage.
Considered very effective visit a chiropractor. Manual therapy sessions can reduce the load on the spine, and massage the ankle and foot muscles helps to strengthen them.
Parents can quite massage independently. This is a classic therapeutic massage, which is best to start with the feet, paying particular attention to little fingers and arch lifting feet.
Stroking should be followed by kneading, then intensive deep kneading and vibrating touch technique. Following the foot, the shin is massaged in a similar manner, especially deeply - its inner side, thighs and buttocks, as well as the lower back. Massage should be carried out courses for 14 days with intervals of 10 days.
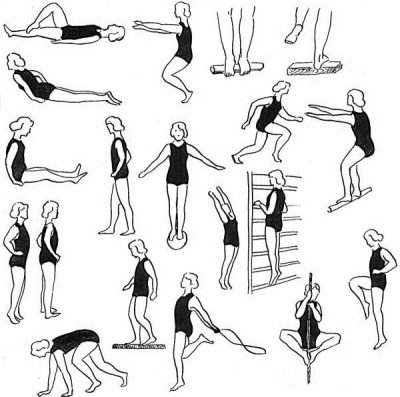
Physical therapy offers more than 25 different types of exercises to strengthen the muscles of the feet in particular and all the muscles of the lower limbs in general. The most common tricks are available for classes at home.
You can fix minor deformations. systematic gymnastics, including walking on tiptoe and heels, rolling from socks to heels, walking with the support on the outer part of the foot, on its inner part. For charging, you can use a special foot massage mat.
Orthopedic salons offer a large selection of such rugs - applicators. Before buying, be sure to consult with the orthopedist, who observes the patient. He will give all the recommendations on the size, degree of rigidity of the product, its relief.
Needle applicators are suitable for some adolescents, others are textured ("stones", "pebbles", "thorns"). A young man or girl will have to study on the rug every day; the first positive results will not be noticeable from the first days. Comprehensive treatment - using a rug, gymnastics and massage gives a more beneficial effect.
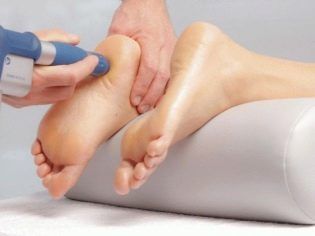
Useful extra and physiotherapy - electrophoresis, including the use of drugs (method SMT), magnetic therapy, UHF.
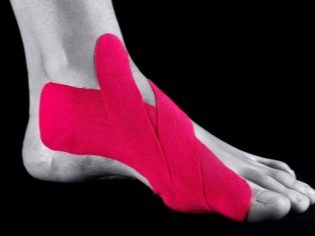
Recently, a new method of treatment is gaining momentum - taping At the same time, special retention tapes are glued onto the foot, which redistribute the load in different muscles. With these ribbons, a teenager goes to school, does gymnastics and exercises, leads the most ordinary life. Tapes are changed every few days.
One of the most important points of conservative therapy is wearing orthopedic shoes. The need for it may occur with 2-3 degrees of pathology.
Shoes with a rigid supporting back and special instep supports are purchased in an orthopedic salon as prescribed by a doctor. A shoe pair will be made for the child, taking into account the individual characteristics of the foot, the turning angle, the deviation angle from the norm, the height of the arch, and so on.
Orthopedic shoes are heavy enough to wear and expensive. Adolescents with an easy stage can do without the purchase of orthopedic insoles, which are invested in ordinary shoes.
Medicines
Drug treatment of flatfoot is recommended for grade 2-3 pathology. It is essentially symptomatic, aimed at eliminating unpleasant sensations. It is not independent and is used only in combination with the conservative methods described above.
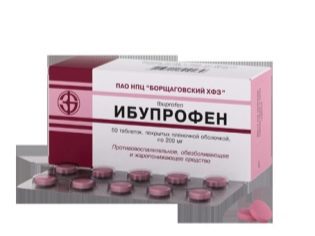
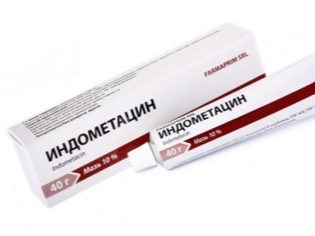
For pain relief use “Ibuprofen” in pills, “Indometacin ointment”, “Nurofen” and “Ortofen”. To reduce swelling of the fingers and ankles, use ointment.Troxevasin". With paralytic lesions of the muscles and a tendency to convulsions, muscle relaxants are recommended.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is recommended to the adolescent when conservative treatment has not brought the desired result, as well as at the 3-4 degree pathology, bypassing conservative therapy. Experienced surgeons and existing techniques can cure flat feet.
Transverse flatfoot, in which a protruding “painful bone” is often formed, is operated on, removing the overgrown bone, and sometimes 2-3 metatarsal bones. In the future, a teenager for several months wears special orthopedic sandals that allow the foot to properly merge.
Methods of surgical intervention for longitudinal flatfoot developed more. This plastic tendons, and plastic muscles. The most popular operation is Evansin which the calcaneus lengthens due to the implantation of a part of its own bone tissue into it, which reduces the risk of rejection.
Often, surgeons implant a titanium implant in the subtalane sinus of the foot. The implant rigidly fixes the arch. After some time, usually until the age of 18, the implant is removed, and the arch continues to maintain the correct position.
After surgery, a teenager is shown physiotherapy, and after a few months - massage, gymnastics, sports, and sometimes wearing orthopedic shoes.
Implications and predictions
Flatfoot is curable. The predictions are quite favorable if parents take the treatment seriously:
- In more than 75% of cases, correcting problems is obtained with the help of conservative treatment.
- 97% of surgeries end without complications and with the desired results, because surgeons use low-impact methods, make small incisions.
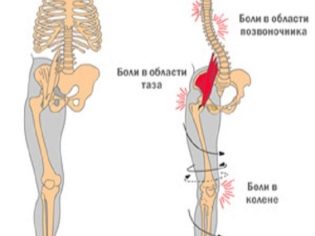
Teenage flat-footedness in the absence of the necessary treatment quite often leads to disability.The disease is dangerous primarily because its complications are pathological changes in the spine, in the pelvic region, in the knees.
The consequences of such changes are arthrosis, and severe fractures, and violation of posture and gait, and vertebral hernia, displacement of the vertebral discs, infringement of spinal nerves, paralysis, dysfunction of the nervous system.
The third degree of pathology is considered the most unfavorable from the point of view of the possibility of developing a disability. In this case, the depreciation properties of the foot are lost almost completely, and the joints, which take on an unbearable load, are rapidly destroyed.
In itself flat feet in adolescents fails, it is not considered physiological, like in young children, and therefore the lack of treatment makes the doctors' forecasts unfavorable - the deformity will progress, and other parts of the musculoskeletal system will also be involved.
For more information about flatfoot and its treatment, see the following video.