Valgus deformity in children
Watching how funny kids stomp, all adults love. However, upon closer observation, it becomes clear that all the crumbs stomp in different ways. Looking at the first steps of their child, parents sometimes wonder if everything is in order with his gait, whether he steps on his feet correctly.
The fears are quite understandable, because the crown legs under the influence of new loads for themselves can undergo pathological changes. About one of them - valgus deformities - we will tell in more detail.
What it is
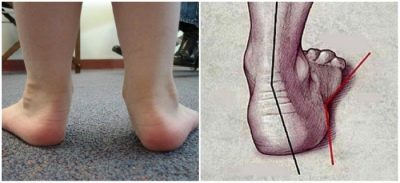
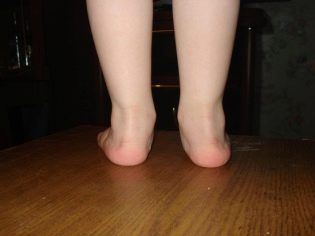
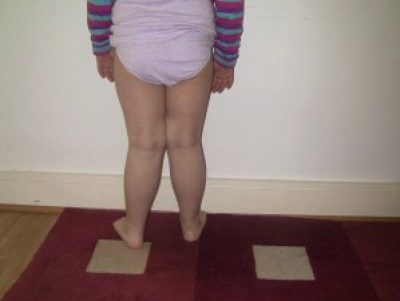
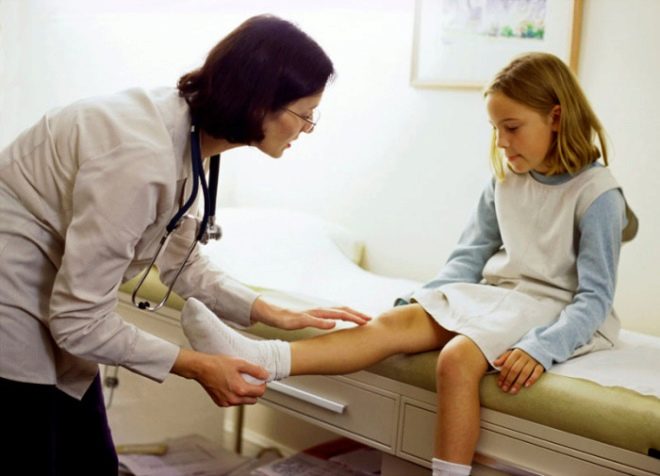
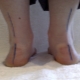
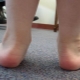
The valgus deformity of children's feet is very difficult to confuse with something else. Too characteristic it looks. Valgus is called such a deformation of the legs, in which the fingers and heels are shifted to the outside, and the inside of the foot "collapses."
If you straighten your legs at the knees and press tightly against each other, then the distance from one ankle to the other will be more than 4 centimeters. It clearly looks like the letter X, therefore, valgus deformity is often called X-shaped.
Symptoms
In childhood, such orthopedic pathology is common. Moreover, in most cases, valgus curvature is accompanied by a decrease in the height of the arches of the feet, that is, flat-footedness. Such a combined pathology is called "flat-valgus foot".
When the X-shaped curvature of the feet flattened metatarsal joints This leads to deformation of the forefoot, toes. The tendons and ligaments begin to work with a greater amplitude than they are supposed to, which can not but affect the baby’s well-being and his walk. Normally, the child’s feet should be parallel to each other, the same parallelism should be traced in the first steps.
During valgus deformity, the load falls on the inside of the foot, and not the area under the toes and the heel, as provided by nature. The little fingers, thus, almost "hang" in the air, the depreciation of the foot is broken.
Causes
The baby’s feet may become deformed during fetal development. The likelihood of such a pathology is influenced by the metabolism of the mother, especially the period of gestation.
In fact congenital abnormality is quite rare. More often, orthopedists are forced to state the acquired valgus curvature. To understand why such a deformation develops, it should be understood that the ligaments and tendons of babies are very weak, because in the first year of life there is no load on the lower limbs.
Closer to the year when the baby begins to stand on its feet, the deformation becomes apparent. Children are most often affected by it. with weakened muscles, overweight babies. Strong loading on weak legs can lead to X-shaped deformation.
Often after a year, the pathology is found in children who were born prematurely, with low weight, in babies weakened by frequent diseases of infectious and non-infectious origin, as well as in children with congenital connective tissue weakness.
A disease like can affect the development of acquired valgus rickets. When it is broken mineral metabolism in the bone tissue, which creates prerequisites for the development of various disorders of the musculoskeletal system.Quite often, valgus-type deformity develops in children suffering from cerebral palsy and other ailments with neuromuscular symptoms.
Much less often, pathology may occur as a consequence of injury due to tendon rupture, muscle, foot fractures, and shin, in which the child was forced to spend a long period of time in a cast.
Doctors regret to state that often the cause of the disease lies in parental errors. Sometimes mom and dad want to see their child as an adult so much that they put him on their feet too soon. Walkers and jumpers, in which the child is placed up to the age of 9-10 months, other verticalizing devices, unfortunately, only contribute to the incorrect position of the feet and the exorbitant load on the spine.
After the baby has started to walk, the risk of the development of valgus deformity is preserved, if the baby makes its first steps in wrong picked up uncomfortable shoes. An example of such shoes - booties. They do not fix the foot, they are too soft, and the foot of the baby at first needs additional fixation and support.
Whatever the reason, the processes are approximately the same - the ankle mixes inwards, “pushing” the outer part of the foot, the fingers and the heel, forcing them to take a turn position to the outer side.
Congenital valgus deformity of the feet can be seen with the naked eye in the first months of a child’s life. The foot is unnaturally bent inward.
Before the fact of acquired X-shaped foot, parents usually end up when the child is one or one and a half years old. By this age, babies are beginning to walk, and some signs can be seen even without being an orthopedic surgeon:
- the child is slow and difficult to master walking;
- when making steps, the baby relies on the inner edge of the feet;
- the baby gets tired quickly, cannot stay upright for a long time.
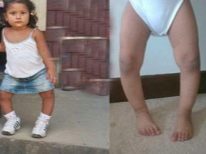
Over time, the feet take on a characteristic look, resembling the letter X, the child’s gait is awkward, uncertain, shuffling. The kid gets tired quickly, cannot play for a long time, it is difficult for him to move active and active games. There are aching pains in the legs and spine, in the evenings parents may notice a slight swelling of the lower extremities.
A child with X-shaped curvature of the feet can not run like his peers. It is the running that is most difficult for him, parents can pay attention to the fact that when trying to run, the kid is waving his arms strongly, trying to keep the balance.
Shoes wear out in those places that bear the main load when walking, usually the inside of shoes and sandals is erased.
Types and degrees
Valgus deformity of the feet in different children may have significant differences. So, there are several main types of this pathology:
- Static deformation. It begins in children with curvature of posture, is a compensatory consequence of problems with the spine.
- Structural deformation. Such X-shaped curvature is congenital. When it is the talus is located anatomically wrong.
- Spastic deformity. This is the curvature of the foot position associated with neuromuscular diseases, cerebral palsy.
- Rachitic deformation. The curvature that occurred after suffering rickets.
- Traumatic deformity. Pathology following injuries, fractures, tendon and muscle tissue ruptures.
Much of the correction and predictions depends on the degree of pathology. To visualize the criteria for assessing degrees, the child should be placed exactly, straighten the legs at the knees.
Normally, from the thigh to the heel along the back of the legs, two parallel straight lines can be drawn. When valgus deformity lines will be refracted in the area of the ankle joint. The angle of refraction will determine the severity of the pathology:
- 1 degree.The angle of deviation of the line from the straight parallel is 10-15 degrees. This stage is perfectly amenable to correction.
- 2 degree. The angle of deviation is 15-20 degrees. Deformation will require a longer course of treatment.
- 3 degree. The angle of deviation is 20-30 degrees. The treatment will be time consuming and long.
- 4 degree. The angle of deflection is above 30 degrees. It is advisable surgery.
Diagnostics
If the parents noticed that the crumbs of the feet "mow" inwards, you should definitely visit an orthopedic doctor who can confirm or deny the fears of the mother and father. But even if nothing in the baby’s parents ’walk is alarming, the pathology can be detected orthopedic surgeon on a routine medical examination or on passage of the commission at registration of the child in a day nursery.
Only one visual inspection by a specialist to establish such a diagnosis is not enough. Special examination required. It includes:
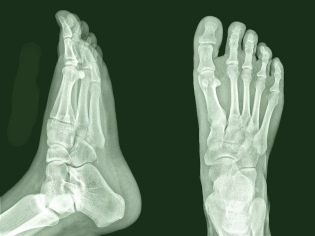
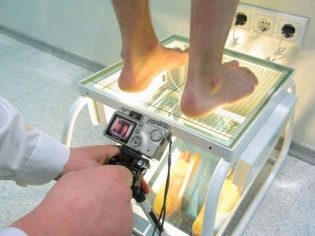
- radiographic images of the feet in three projections;
- computer plantography;
- podometryu;
- ultrasound of the joints;
- visit to the neurologist.
Only on the basis of the photographs taken and the study of the morphological properties of the foot and the distribution of the load when walking, the orthopedic surgeon will be able to make a final conclusion about the presence of valgus curvature, its type and extent, after which appropriate treatment will be prescribed.
Treatment
The treatment is aimed at ensuring that the muscles and ligaments are stronger, able to take on a vertical load. Only this will allow the foot to return to its normal position.
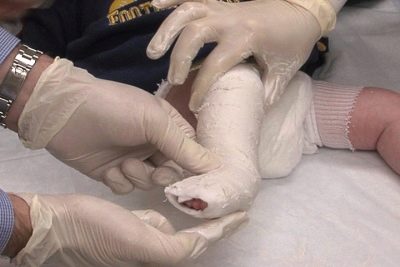
If a baby has a congenital valgus deformity, then they can impose plaster on both legs, fixing the foot in the correct position. This is done by an orthopedic surgeon who, when applying a bandage, will take into account all the features of the pathology of a particular child.
Further treatment will be one-to-one repeat therapy, which is prescribed in cases of acquired valgus curvature. The treatment of acquired deformity may vary depending on the degree of the affliction. Light pathologies do not require surgery, quite conservative measures are enough.
True, parents should prepare for the daily systematic work on the correction of the position of the child's legs.
Foot baths
It is recommended to do them daily before bedtime. Legs of the child hold in warm water with broths chamomile pharmacy, as well as burdock root. You can add a little ordinary soda to the water. The purpose of such procedures is to relax the lower limbs, improve blood circulation.
Baths do after the massage, but in this case, the procedure should be contrasted. First, the child takes a warm bath, and then cold water is gradually added to it.
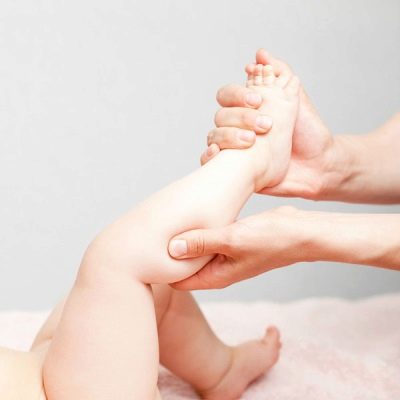
Massage
Massage with valgus curvature is very similar to massage with flat-footedness - it uses the same techniques - rubbing, kneading, vibration. The massage begins with the feet, carefully kneading the fingers, the area of the metatarsal stones, the lateral parts of the foot, transfer to the ankle and the knee joint, and then rise higher.
In case of valgus deformity, it is important to massage not only the legs, but also the lumbosacral area. Massage is prescribed in courses of 10-14 days with a break of 10 days. You can do it with a professional masseur, and you can do it yourself at home, as there is nothing difficult in such manipulation.
Useful daily massage classes mat-applicator. The orthopedic surgeon will help to choose it. For therapeutic purposes, preference is usually given to rugs made from dense and rigid materials, with high relief patterns or needle applicators, while preventive mats can be softer and more pleasant.
You should do at least 20 minutes a day, performing a set of exercises from a standing position.It includes the usual barefoot walking on the applicator, walking on the toes and heels, on the outside and inside of the foot, jumping, rolling from heel to sock.
Paraffin therapy
In the treatment of valgus deformity, a procedure such as paraffin boots has especially proven itself. For the feet use a special type of paraffin, which is free from impurities. It retains heat for a long time and effectively warms the lower limbs, improving blood circulation in the feet and all muscle groups.
Such procedures can be done in the clinic, and you can master the technique of creating shoes yourself, especially since the paraffin used in medical practice is commercially available in pharmacies.
Heated elastic material is applied to the feet, covered with polyethylene and left for 15-20 minutes.
Mud applications
For this treatment uses a special mud that has healing properties. In fact, it is oily sludge that accumulates at the bottom of salt lakes, estuaries. Such procedures are performed under the supervision of a physician.
Usually, the mud imposes on the legs of the child every other day during the course of therapy, which usually ranges from 10 to 20 days.
Physiotherapy
Of the physiotherapeutic methods for the correction of valgus curvature, electrophoresis, magnetic therapy and electrical stimulation of the muscles of the lower extremities are most common. All these procedures can be performed in the direction of the orthopedic surgeon in the clinic at the place of residence.
During the course of treatment, which can last for years, physiotherapeutic procedures will be prescribed several times.
Sport
Children with a valgus foot are not recommended to run, jump, play football. Hockey and figure skating are contraindicated. Any sport in which the load on the legs is large, is banned, in any case, until the moment of cure. But this does not mean that a child with such an orthopedic pathology can not engage in sports.
With valgus curvature useful swimming, synchronized swimming, cycling. If the child’s age allows, after the installation of such a diagnosis, it should be recorded in the pool.
And it's not about Olympic hopes, just swimming will contribute to a faster correction of pathology, since this will involve all muscle groups of the legs without gravitational load, in water.
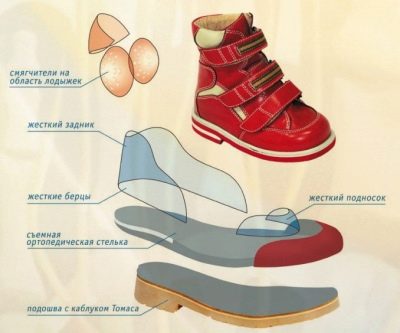
Orthopedic shoes
The question of wearing special orthopedic shoes is decided by the attending physician. Usually, heavy and expensive shoe pairs from an orthopedic salon have, according to individual measures, sew the parents of children with 2-3 degrees of valgus curvature.
This shoe is different from the usual in the first place that it has already been created taking into account the angle of deviation of the position of the baby’s feet from the norm Recommendations to manufacturers wrote attending orthopedic surgeon.
When walking in these shoes, the child's foot is in the correct position. Gradually, the load begins to be distributed correctly, the pathology disappears completely or significantly decreases.
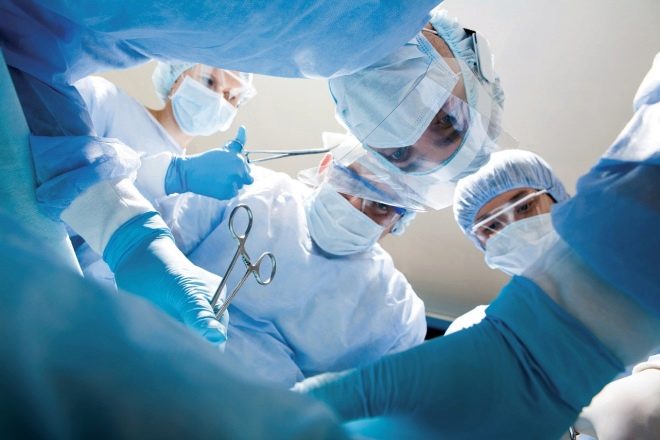
Surgical intervention
The operation a few decades ago with the X-shaped feet of the child was considered the only way to solve the problem. Now medicine looks at the operative treatment of pathology differently - only 6-7% of children with an established and confirmed diagnosis of valgus deformity of grade 3–4 show such treatment.
The doctor may also suggest surgery if all the above described methods of conservative therapy have not yielded the desired result.
Most often, surgeons use tendon transplant method from the calf muscle to the inside of the foot, thereby strengthening and strengthening them. In parallel with this, surgeons extend the Achilles tendon. Surgeons may place special tires on the feet, fixation devices. After the operation and the end of the recovery period, a course of physiotherapy, therapeutic gymnastics, and massage is shown.
Forecasts
The small-sized valgus deformity detected at an early age is perfectly amenable to correction, and it is possible to restore the functions of the feet completely.
With respect to congenital forms of foot distortion, the forecasts are not so bright, even after a surgical operation, it is not always possible to give the feet a completely normal position.
In the absence of timely treatment, severe degrees of deformity can make a child disabled for several years, because all joints, especially the knee and hip joints, are gradually involved in the destructive process, the spine suffers.
Prevention
Parents can prevent the development of acquired pathology, observing the principles of rationality when setting up a child on legs. Up to 8-9 months, this is not recommended in principle. It is desirable that the child before walking has mastered the sitting and crawling, then his spine and muscular system will be better prepared to adopt an upright position.
At an early age should be engaged rickets prevention, preventing the child's body to begin to experience a deficiency of vitamin D. The child should have a sufficient number of walks in the fresh air, a balanced diet.
When the pussy starts walking, you need to choose the right shoes for him, make sure that she was a baby in size, did not sting and did not dangle on her leg, had a small heel, was not too soft.
Up to 3 years, children are advised to buy a pair of shoes with a rigid back and good ankle fixation. Be sure to encourage walking barefoot around the house, on the grass, sand, earth, if there is such an opportunity.
You can buy a child preventive massage mat for the feet.
See the following video about the danger of valgus deformity of the child's foot.