Varus foot deformity in children
The baby’s first steps are a joyous event. But along with them in the life of parents comes a period of doubt and anxiety, since it is with the first steps that pathologies of development of the feet are usually revealed, which were previously impossible to notice. What to do if the child has legs “by the wheel”, what is the varus deformity of the foot, we will tell in this article.
What it is
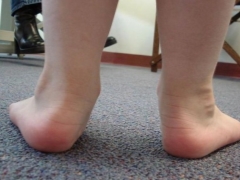
Varus foot deformity is a pathology of the lower extremities in which distorted axis and dome stopWhen walking, the baby rests on the outer edge of the foot, respectively, the very “wheel” is formed between the knees.
The knees do not close when the legs are held parallel. Pathology also received the name of the O-shaped curvature.
Quite often, varus deformity is confused with clubfoot. In fact, these are two different pathologies. The clubfoot has a congenital nature, and the varus of the foot is always acquired.
For children up to 3-4 months, the “wheel” legs are a variant of the norm. But after this age, only an experienced orthopedic surgeon can assess the situation.
The child’s joints are weak, plastic, muscular tissue is not sufficiently developed, and therefore improper loads on the legs are capable of causing this type of foot anomaly. If improperly installed, the load on all types of joints and tendons increases, the knee joint, hip and ankle, are particularly affected.
If the pathology in time does not consider and begin treatment, then the child may become disabled. Excessively loaded joints wear faster, improper and insufficient depreciation leads to deformities, hernias, spinal cysts, and intervertebral space.
The best forms of the ailment are best corrected; the actual formulation can be corrected as long as the bones of the child are actively growing. A critical age is considered to be 8 years old.
If, before this time, it was not possible to correct the varus curvature, it's time to think about surgical intervention, because after 8 years the pathology will only progress.
The reasons
To the curvature of the axes and the inability to close the knees can cause a great many reasons.
The disease is most common in children belonging to the so-called risk group - it includes:
- premature;
- lightweight babies;
- babies with cerebral palsy;
- children who in the first year of life suffered rickets;
- children injured ankle, knees, hip joint.
A large share of responsibility lies with the parents. Babies that are brought to an upright position early, are put on their feet until they reach the age of 9-10 months, are placed in a variety of verticalizers (walkers and jumpers), especially if they are sufficiently well-fed and weigh more than the age norm, they are more susceptible to such O-shaped deformations of the legs.
The reason for the development of the varus foot can also be uncomfortable shoes, which poorly fix the legs of the baby, who has already begun to stomp on his own two feet, as well as poor nutrition, in which the child has a deficiency calcium and important vitamins.
Symptoms and signs
At the initial stage, it is difficult to consider varus deformity. The child does not bother. But as they grow, clinical signs of pathology begin to appear, which, by the way, is developing at a rather slow pace.
A child may have pain while walking, in the evenings he may develop puffiness in his legs, he may not run very well, and too active and active games quickly tire him.
In some types of varus deformity, systematic gastrocnemius seizures may occur.
Since the baby relies on the outer part of the foot, any pair of shoes he will wear unevenly, in case of a varus deformity, the outer part of the sole will wear out much faster than the inner part.
When the disease progresses, the child has a specific "duck" gait, he is very clumsy, rolls over while walking, throws up his arms when trying to run and tries to balance.
Diagnostics
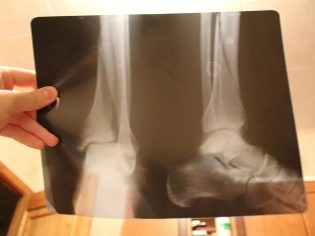
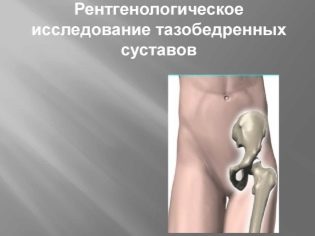
An orthopedic surgeon in case of suspected varus deformity prescribes X-ray of the feet and lower legs in three projections. If the stage is already quite advanced, then an X-ray examination of the features of the hip and knee joints may be required.
In cases of varus deformity, doctors always try to establish the true cause of the development of pathology, and therefore the child can be assigned impressive list of analyzes, including blood tests for calcium and phosphorus, consultation with a neurologist, pediatrician and traumatologist.
Treatment
Doctors try to treat children with varus deformity by conservative methods. With light degrees of curvature, this is quite enough to completely eliminate the anomaly and restore the normal setting of the legs.
Surgical intervention is recommended only to children who have not been helped by conservative treatment and to preschool children with severe curvature.
When starting a treatment, parents should understand and be fully aware that therapy may take not only months, but also years. Pathology is eliminated even more slowly than it develops.
Treatment will require an adult systemic approach, strict adherence to all medical recommendations, a serious attitude to home procedures, many of which will become daily and mandatory.
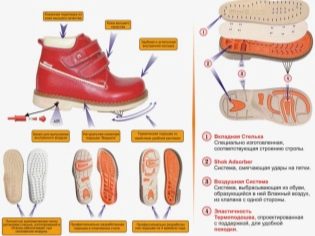
Child can be assigned wearing orthopedic shoes. It is made by special individual measurements, the order can be made in an orthopedic salon. These are not ordinary sandals and shoes. Such shoe pairs have serious insteps, orthopedic insoles, heavy and massive soles, hard backs and sides for reliable fixation of the foot and ankle in the anatomically correct position.
Universal shoes for the treatment of varus deformity does not exist. For each child, taking into account his stage, the degree of deviation of the position of the feet from the norm, the wearing of a certain shoe pair is shown. That is why you should not choose such shoes at your discretion. It is necessary to use recommendations of the orthopedist.
The entire course of treatment will be followed. therapeutic massage sessions. Two weeks of massage are usually alternated with a three-week rest, after which the massage effect is repeated. Massage is not difficult, but because every mother or grandmother can master his technique and techniques.
Massage includes classical techniques with rubbing, kneading and vibration effects. First, the feet are massaged, then the ankle. When correcting the varus deformity, it is important to pay attention to the heel and arch of the foot, as well as to the lower leg. They knead quite intensively, diverting to this massage zone up to half the time of the entire session.
Be sure to massage the hips, lumbar and lower back. The movements of the masseur should be intense, but not painful at the same time for the child.
Parents should teach the child to perform special exercises. Exercises aimed at improving the state of muscle tissue, connective tissue and tendons, can be shown by an exercise therapy instructor from any children's clinic. To him the orthopedist must send, prescribing treatment.
Not only depends on the parents whether the child will do the exercises properly, but also how effective such a gymnastics will be.If the baby is interested in this process, if mom and dad managed to arrange treatment as a game, and not as a forced event, then the effect comes much faster.
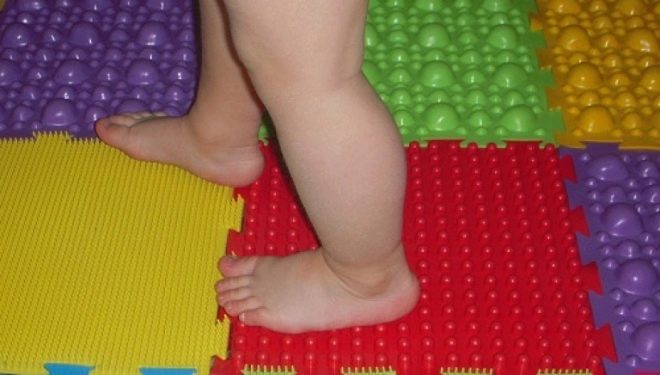
As with flatfoot, and valgus foot, with varus it can be used at home massage mats - foot applicators. The harder the material and the greater the pattern of the coating, the better in terms of usefulness.
Quite often, the child will have to attend a physiotherapy room. Magnetic therapy, electrophoresis, as well as paraffin therapy and mud applications, together with stimulation of the muscles of the legs with electrical impulses, have a very good effect on the final result.
The magic pill for varus deformity does not exist, and therefore no drug treatment is prescribed.
Children with severe pain syndrome, which usually accompanies quite severe forms of foot deformity, can be treated symptomatically — painkillers that the doctor advises.
Operations to eliminate the varus of the foot can be carried out by various methods. Quite often, children carry out surgical correction of the meniscus, ankle joint, and sometimes the knee joint. The recovery period is quite long; a child can spend several months in the Elizarov apparatus.
After the operation, when the child stands on his feet, he is shown the full range of conservative treatment, which was described above, including massage, gymnastics, exercise therapy and physiotherapy.
On how to avoid the varus deformity of the foot in a child, you can find out in the next video.