Ointment "Hydrocortisone" for children: instructions for use
Glucocorticoid hormones in the form of an ointment are very in demand for diseases of the skin and eyes. One of the popular tools in this group is Hydrocortisone. Not everyone knows whether such a drug is used in childhood, when its use is justified and what side effects this drug may cause in a child.
Release form
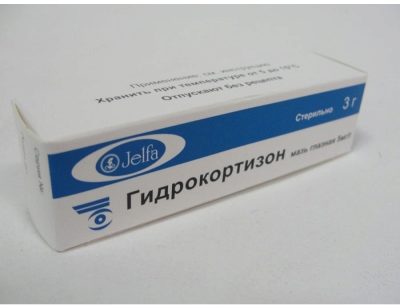
Ointment "Hydrocortisone" is of two types.
1% ointment for external use
It is sold in tubes containing 10 g of light yellow or white-yellowish mass.
0.5% eye ointment
One tube of such a medicine contains 3 g or 5 g of a white substance, which may have a grayish, yellowish or greenish tint.
"Hydrocortisone" is also available in ampoules, inside of which is a suspension. It is used for injection into the muscle or tissue of the joints. This form of the drug is used for inhalation when coughing, and with adenoids and a long runny nose, the suspension can be incorporated into complex drops (add «Dioxidine», Farmazolin, «Nazivin " and other drugs prescribed by the doctor). In candles, tablets, nasal drops, powder, and other forms, such a drug is not produced.
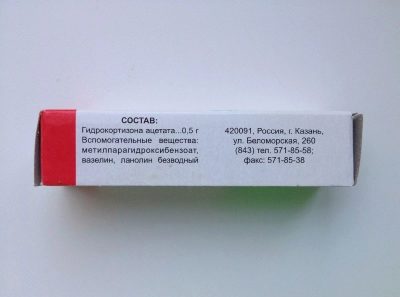
Composition
The main ingredient of the drug is hydrocortisone in the form of acetate. In 1 gram of ophthalmic ointment, such a substance is contained in a dose of 5 mg, and the amount of this compound per 1 g of ointment for external use is 10 mg. Additionally, eye ointment includes anhydrous lanolin, petrolatum and nipagin. Auxiliary components of the preparation for the skin are propyl parahydroxybenzoate, lanolin, water, methyl parahydroxybenzoate, stearic acid and petrolatum.
Operating principle
Hydrocortisone has a pronounced anti-inflammatory effect. This substance is referred to as synthetic glucocorticoid. It activates steroid receptors, affects the formation of prostaglandins, stabilizes cell membranes, participates in the metabolism of arachidonic acid and inhibits the release of compounds responsible for the inflammatory response. Under the influence of "Hydrocortisone" inhibits the release of interferons and interleukins, which support inflammation.
The drug also has an antipruritic and anti-edema effect. With local processing, the drug reduces the inflammatory process, interfering with the migration of lymphocytes and macrophages into the affected tissues, with the result that cellular infiltrates dissolve faster. If the dosage of ointment is not exceeded, the drug only accumulates in the epidermis or mucous membrane and almost does not penetrate into the blood, so there are no systemic side effects.
Indications
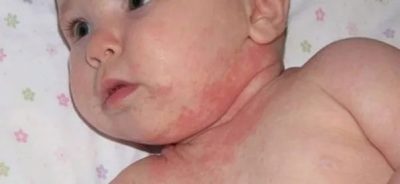
Ointment for external treatment is prescribed for various allergic and inflammatory skin pathologies:
- With eczema.
- With psoriasis.
- With contact dermatitis.
- With atopic dermatitis.
- With neurodermatitis.
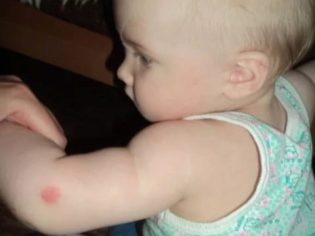
- When insect bites.
Eye ointment is used:
- In allergic lesions - for example, from conjunctivitis or blepharitis.
- When inflammation of the conjunctiva, eyelids or corneas of a non-bacterial nature (if the corneal epithelium is not damaged).
- In case of chemical or thermal eye burns, when corneal defects are completely epithelized.
At what age is it allowed to take?
Skin treatment with 1% of the drug is prescribed from the age of two, however, in the annotation to this medicine, it is noted that use in children under 12 years old should be under the supervision of a specialist. The reason for such precautions is a more rapid inhibition of the adrenal cortex in children than in adults. The drug can affect the production of growth hormone.
As for the eye ointment, in the contraindications to this medication you can see the age of 18 years. However, in practice, the drug can be administered to children, but only by a physician, who will correlate the possible risk and necessity of such treatment, and also prescribe the appropriate dosage.
Contraindications
Hydrocortisone in the form of an ointment is prohibited to use in case of intolerance of its active substance or other components.
Treatment of the skin with 1% medicine is not carried out with:
- Ulcerative lesions.
- Open wounds.
- Bacterial infections
- Syphilitic or tuberculous lesion.
- Viral skin infections.
- Fungus on the skin.
- Skin tumors.
- Perioral dermatitis.
- Vulgar acne.
- Rosacea.
The use of 0.5% medication in the eyes is contraindicated in:
- Purulent eye infections.
- Damage of the organ of vision with viruses, tuberculosis or fungus.
- Glaucoma.
- Vaccination.
- Trachome
- Corneal damage.
The use of 0.5% medication in the eyes is contraindicated in:
- Purulent eye infections.
- Damage of the organ of vision with viruses, tuberculosis or fungus.
- Glaucoma.
- Vaccination.
- Trachome
- Corneal damage.
Side effects
At the site of application of 1% of the drug on the skin may cause itching, swelling or redness. If you use the ointment for too long, atrophic changes may develop in the skin. The risk of secondary bacterial infection and hypercorticism increases.
In treating eye ointment, a burning sensation may appear. In addition, this medication can provoke allergies, a temporary decrease in the clarity of vision and redness of the sclera. Excessive prolonged use increases the likelihood of increased intraocular pressure and damage to the optic nerve. A long course of treatment with this drug can cause a fungal or bacterial infection (secondary).
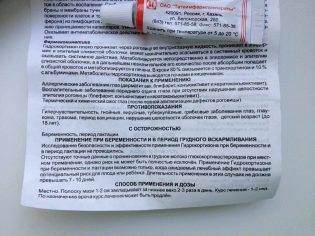
Instructions for use and dosage
- Skin treatment with 1% ointment is carried out twice or thrice a day. A thin layer of the drug lubricates only the affected areas. The duration of use is determined by the physician (based on the effectiveness of the treatment and the nature of the disease). Usually the treatment is carried out within 6-14 days.
- Eye ointment in the form of a strip with a length of 1-2 cm is placed over the lower eyelid. Such treatment is prescribed 2-3 times a day for 7-14 days.
Overdose
The use of an overdose may enhance the local reaction to the ointment, but if you cancel, such symptoms quickly pass.
Interaction with other drugs
About the incompatibility of "Hydrocortisone" with other drugs say only with very long treatment, if the hormone enters the bloodstream. In such a situation, it affects treatment with insulin, anticoagulants, salicylates, antihistamines, silver medications, diuretics, and many other medicines noted in the annotation. If a child has a disease in which he constantly takes medication (for example, from childhood epilepsy), the compatibility of such drugs must be clarified with a doctor.
Terms of sale
Both eye ointment and external preparation are non-prescription drugs. The price of such drugs depends on the manufacturer and the amount of the drug in the tube. Usually 1% ointment costs 25-30 rubles.
Storage conditions and shelf life
Storage of "Hydrocortisone" requires a place inaccessible to small children. The optimal temperature for storing medications is the range from +5 to +20 degrees. The shelf life of the ointment for external use is 3 years, and the eye ointment is 2 years.
Reviews
On the treatment of children "Hydrocortisone" in the form of ointment found a lot of good reviews.They moms say that the tool is very effective for skin manifestations of allergies and insect bites. Parents say that such a drug acts fairly quickly, and the price of ointment is low (compared to similar drugs). The disadvantages of the drug include its hormonal nature, high risk of side effects and a fairly large list of contraindications.
Analogs
- Replacing 1% hydrocortisone ointment can be drugs that contain the same active compound:
- Ointment or cream Lokoid. Such a drug is allowed from the age of six months, so it is often chosen as a substitute for "Hydrocortisone" for children up to a year. It is also available in lotion and lipocrem.
- Lotion, cream or ointment "Latikort". This drug can also be used under the supervision of a physician for children from 6 months.
In addition, instead of "Hydrocortisone," the doctor may prescribe remedies with a similar effect — for example, «Advantan», «Elokom», «Sudokrem», Afloderm, Beloderm, Protopic, «Akriderm» or «Elidel». However, all these drugs differ in their composition, therefore, it is worth choosing an analogue only with a specialist.
Eye treatment in children with the use of ointments adds problems to the parents. To get the most out of your treatment, watch the following video.