Laryngitis in infants
Airway inflammations can occur at any age, even in newborns. In children under one year, such pathologies usually proceed quite hard and with the development of complications. In order to prevent them, you should know how to recognize the disease in its earliest stages.
What it is?
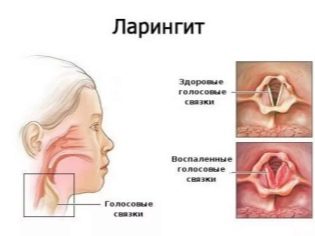
Laryngitis in infants is an inflammatory pathology of the vocal apparatus. For the development of this disease in the smallest children, various reasons lead.
The inflammatory process in laryngitis is quite acute. This leads to the fact that unfavorable signs of the disease appear in a short time.
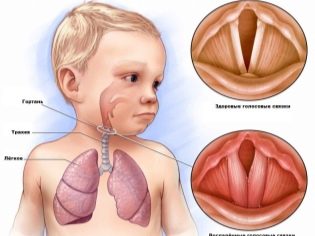
Larynx - a real breathing apparatus.. This organ carries out respiratory function in the body. Through the larynx passes the air with oxygen dissolved in it from the external environment into the body. The emergence of any pathological processes in this organ contributes to the appearance of symptoms associated with respiratory failure.
Respiratory organs, like the immune system, in an infant are not yet fully formed.. They function quite differently from adults. This feature causes a strong susceptibility of the child to any infectious and non-specific factors that can cause inflammation of the larynx and other pathologies of the respiratory tract.
The diameter of the larynx is very small. Inside this organ are the vocal cords, which provide voice formation. Inflammation contributes to the appearance of various symptoms associated with voice disorders. This is explained by vocal cords in infants are still rather short. During this disease, the inflammatory process leads to the development of severe edema, which only contribute to the fact that the child's voice is noticeably disturbed.
It is important to note that the muscles surrounding the larynx are very easily excitable in children. This contributes to the fact that any provocative factor leads to their reduction.
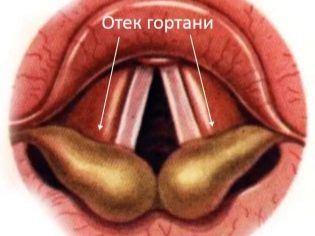
This situation provokes a strong narrowing of the lumen of the glottis. With the development of inflammation, mast cells emit a huge amount of biologically active substances that increase edema, which provokes the development of adverse symptoms.
Laryngitis in older children is less aggressive. Usually, babies of the first year of life, having become ill, can suffer the disease in a rather severe form.. There are also frequent cases of complications. In some situations, inpatient treatment is required. With timely diagnosis and the correct tactics of therapy, even in a newborn baby, the disease ends with full recovery.
The reasons
Influence of a variety of causes can cause illness in a baby. They can be isolated or act simultaneously. For a newborn baby, even mild or moderate intensity is sufficient for the development of adverse symptoms.
To the appearance of clinical signs laryngitis in infants, the following reasons are given:
- Infections caused by bacterial flora. Typically, the incubation period for these pathologies ranges from 5 to 10 days. Bacterial forms of laryngitis in very young children occur in a rather severe form. They are characterized by persistent febrile, as well as severe intoxication. To eliminate the dangerous clinical signs, antibiotics are required.
- Congenital infection. In this situation, the first signs of the disease appear in the child immediately after birth. Infection occurs during the passage of the baby through the birth canal of the mother. This form of laryngitis is relatively rare in pediatric practice.
- The consequences of viral infections. Timely vaccination against childhood infections begins with the first hours of childbirth. The development of viral forms of laryngitis in infants and babies is most often caused by the effects of influenza. The course of the disease may noticeably deteriorate when joining the bacterial flora.
- Pronounced local hypothermia. The immune system of a newborn baby is not yet able to withstand the effects of cold. If the baby is very cold, then he may quickly develop adverse symptoms of laryngitis.
- Exposure to dirty air. Dust particles dissolved in it, as well as the smallest components of industrial emissions, can provoke real microtrauma on the mucous membranes of the respiratory organs. According to statistics, for babies living in large cities and near major highways, chronic laryngitis is recorded several times more often.
- Excessive use of a variety of cough medicine. Usually, the first signs of this clinical form of the disease appear in a 6-month-old baby. Sprays and aerosols used for a long time, contribute to the formation of a chronic variant of the disease.
According to statistics, it is more common in babies aged from 8 months to 5 years.
- Allergies. The ingress of allergenic factors on sensitive laryngeal cells contributes to the formation of an allergic variant of the disease. It is most common in babies predisposed to the development of allergies. The presence of allergic pathologies in parents or close relatives may indicate the presence of congenital hypersensitivity to certain allergens in the child.
- Congenital pathologies of internal organs. Anatomical defects often contribute to the formation of various diseases. So, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can contribute to the development of diseases of the respiratory system. Congenital immunodeficiency conditions often lead to the onset of the disease. With these pathologies, the functioning of the immune system is reduced several times.
- Special constitution. There have been cases of inflammation of the larynx in babies with lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis. This is due to some physiological features. Usually, all babies have similar signs: rounded face, very loose and pasty subcutaneous fatty tissue, pale skin. They also suffer from an excessive tendency to form edema on the body.
Symptoms
The severity of adverse clinical signs may be different. In newborn babies, the disease usually manifests itself with numerous symptoms that severely affect one’s well-being. Also in weakened babies, manifestations of the disease can be quite acute.
The disease in babies-babies is manifested by the appearance of the following symptoms:
- Coarse voice timbre. In newborn babies, this symptom is better defined while the baby is crying. The timbre of the voice in this case becomes hoarse. At an older age, the child starts wheezing. This is well manifested during the pronunciation of several simple syllables or sounds by babies.
- Cough. It can be different: dry or productive (wet). Typically, an unproductive cough is characteristic of viral laryngitis. If the bacterial flora joins, it becomes wet. The amount of sputum may be different and depends on the severity of the disease.
- Strong weakness. During the acute period of the disease, the baby becomes quite sluggish. During the daytime, drowsiness increases substantially.Active games cause fatigue in a child, so he tries to avoid them.
- Sleep disturbance. Often there is abnormal daytime sleepiness. At the same time, the duration of sleep noticeably suffers at night. A child may wake up several times in the middle of the night, cry. Some babies often ask for hands.
- Decreased appetite. Soreness in the neck leads to the fact that the baby refuses to breastfeed.
- Increase in body temperature. Quite often, it rises to febrile numbers. The use of antipyretics usually has only a temporary positive effect. It may take several days to normalize body temperature.
- The appearance of whistling. The appearance of this symptom is a very unfavorable sign. It occurs as a result of the passage of air through a highly narrowed glottis.
Whistling while breathing also indicates that the vocal cords are quite inflamed and swollen. When this symptom appears, the child should be shown to the doctor as soon as possible.
- Behavior change. Sick kids become capricious. They have increased nervousness. They may avoid bodily contact. Newborn babies begin to whimper. Severe pain can manifest itself in a child crying.
- Soreness in the neck. In infants, babies, this symptom is difficult to identify. Children still cannot complain to mom or pediatrician about where and how they hurt. Suspect pain can be yourself. This is usually manifested by the refusal of the baby from breastfeeding.
- Red throat. The inflammatory process in the larynx usually quickly leads to the spread of inflammation in the tonsils, as well as on the mucous membranes of the oral cavity. This is manifested by severe swelling and redness.
- Choking attack. It occurs as a complication of the disease. Such a respiratory failure is possible due to a strong narrowing of the glottis. Choking is a very dangerous condition. To eliminate the symptoms, emergency medical care is required.
Diagnostics
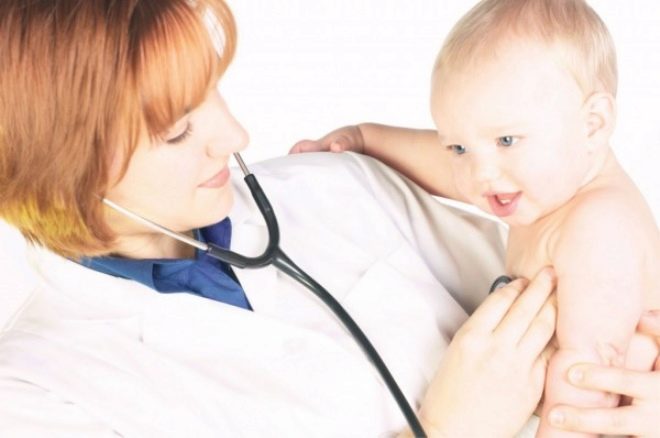
A complete clinical examination is sufficient to establish the diagnosis. When the first symptoms of the disease appear, be sure to show the child to the pediatrician. The doctor will examine the neck and also conduct auscultation (listening) of the chest organs. This will help the specialist to establish the correct diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
In some cases, additional consultation with a pediatric otolaryngologist may be required. It is needed to determine the presence of concomitant diseases of the upper respiratory tract, which could be the root cause of the development of laryngitis or contribute to the deterioration of the disease.
If the baby has congenital diseases of the upper respiratory tract, consultation with an otolaryngologist is also a prerequisite for drawing up the correct treatment tactics.
To establish the severity of the disease and determine the degree of functional respiratory disorders arising, the appointment of additional diagnostic tests is required. They help doctors establish a complete clinical diagnosis, as well as contribute to full control over the course of the disease:
- To establish the cause of the disease, a general blood test is performed. This simple and informative test helps to establish signs of a viral or bacterial infection. Laryngitis is accompanied by an increase in the total number of leukocytes - leukocytosis. Accelerated ESR is evidence of the presence of an inflammatory process in a child’s body.
- To identify the complications of the disease is carried out ultrasound. Using an ultrasound scanner, pathological changes in the lung tissue can be determined. For older children, x-rays are used for these purposes.
In newborn babies, no X-ray examination is performed.Such a high radiation load is contraindicated for them.
- To identify the causative agent of the disease is carried out bacposa sputum. This study helps to identify bacteria or viruses that contributed to the occurrence of adverse symptoms of the disease in the child. This test also establishes sensitivity to antibiotics and phages. This is necessary to create a complete scheme of treatment of laryngitis.
Treatment
Therapy of the disease in babies of the first months of life is usually carried out in the hospital. In the event of a pronounced stenosis (contraction) of the larynx or during an attack of suffocation, the baby is hospitalized in the intensive care unit. To eliminate the dangerous symptoms, it may be necessary to supply oxygen and administer medications through droppers.
Treatment of non-complicated forms of laryngitis is possible at home. The decision on the need for hospitalization in this case is made by the attending physician after conducting a full-fledged clinical examination of the baby.
Chronic laryngitis, which is also mild, does not require the hospitalization of the baby in the hospital.
In the treatment of disease, various drugs are used. Dosage, frequency and duration of use is selected individually. It depends on the initial state of the child, his age, the characteristics of his physiological state, as well as the presence of concomitant chronic and congenital pathologies.
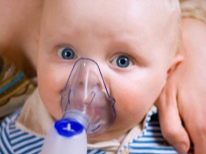
To eliminate the adverse symptoms in infants, various anti-inflammatory drugs are used. They are most often prescribed by inhalation. In severe cases, hormone preparations based on glucocorticosteroids are used. They effectively contribute to improving the well-being of the child and the elimination of dangerous symptoms.
If the disease was caused by bacterial flora, then various antibiotics are used to treat the disease. These are mainly drugs with a wide spectrum of action. During treatment with antibiotics, performance monitoring is required.
The effect of the therapy is assessed by improvements in the overall blood count, as well as improvement in breathing parameters during auscultation.
Treatment of laryngitis at home without prior consultation with a doctor is quite dangerous. This can only lead to worsening of the course of the disease and contribute to the appearance of dangerous complications of the disease. Proper treatment and timely diagnosis will help your child recover and not acquire the chronic form of laryngitis in the future.
About what is laryngitis in children and how to treat it, will respond Dr. Komarovsky in the next video.